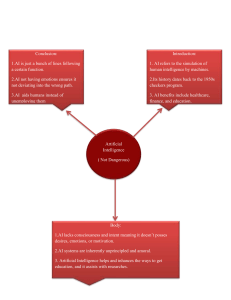
AI, or Artificial Intelligence, refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and learn like humans. It encompasses a wide range of technologies and techniques aimed at enabling computers to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include problem-solving, decision-making, language understanding, visual perception, and more. AI systems can be categorized into two main types: narrow AI and general AI. Narrow AI, also known as Weak AI, is designed and trained for a specific task, such as playing chess or recognizing speech. In contrast, General AI, also known as Strong AI or AGI (Artificial General Intelligence), would have the ability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a wide range of tasks – similar to human intelligence. AI technologies include machine learning, which involves training algorithms to recognize patterns in data and make predictions or decisions based on that data, and deep learning, a subset of machine learning that uses neural networks with many layers to analyze complex data. Reinforcement learning is another AI technique where an agent learns to make decisions by trial and error, receiving feedback from its environment. Overall, AI holds the potential to revolutionize various industries and aspects of our lives, from healthcare and transportation to finance and entertainment, by automating tasks, improving efficiency, and unlocking new capabilities. However, it also raises important ethical, societal, and economic considerations that need to be carefully addressed as AI continues to advance. ㅁ