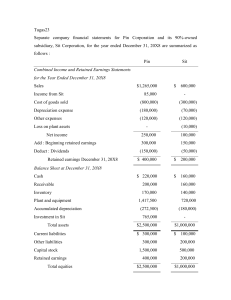
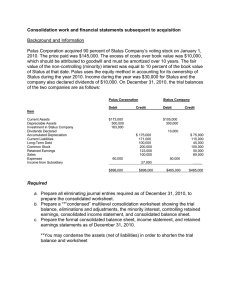
Basic Consolidation Exercises – Flashback 1. (SOFP) Basic Steps to Consolidate Payne bought all of the shares in Singer many years ago for $22,000. At the date of acquisition, Singer had retained earnings of $7,000 and no revaluation reserve. The statements of financial position of the two companies at 30 June 20X8 were as follows: Payne $ 123,000 50,000 Singer Current assets 32,400 205,400 16,550 50,550 Share capital Retained earnings Revaluation reserve 60,000 106,000 14,500 15,000 21,400 6,000 Liabilities 24,900 205,400 8,150 50,550 Non-current assets Investments 34,000 - Prepare the consolidated statement of financial position at 30 June 20X8. 2. (SOFP) Non-Controlling Interest Poodle bought 75% of the shares in Springer on 1 January 20X8 for $150,000. At the date of acquisition, Singer had retained earnings of $130,000. The statements of financial position of the two companies at 31 December 20X8 were as follows: Poodle $ 342,900 150,000 Springer $ 201,400 - Current assets 75,600 568,500 41,600 243,000 Share capital Retained earnings 120,000 379,500 70,000 145,000 Liabilities 69,000 568,500 28,000 243,000 Non-current assets Investments Prepare the consolidated statement of financial position at 31 December 20X8, assuming that the NCI is measured using the proportion of net assets method. 3. (SOFP) Goodwill Piano bought 60% of the ordinary shares in Swing on 1 August 20X8 for $170,000. At that date the fair value of the net assets of Swing was $185,000, and the fair value of a non-controlling interest of 40% was $105,000. What goodwill arises assuming that the non-controlling interest is measured using: 1. Proportion of net assets method 2. Fair value method 4. (SOFP) Reserves/ Non-Controlling Interest/ Goodwill Postal acquired 60% of Steeple on 1 October 20X4. On this date the retained earnings of Steeple were $34,000. At 30 September 20X8, the statements of financial position of Postal and Steeple were as follows: Non-current assets Investments Postal $ 420,520 105,000 Steeple $ 99,330 10,000 Current assets Total assets 78,900 604,420 26,190 135,520 Share capital $1 Share premium Retained earnings 80,000 120,000 240,620 30,000 72,440 Non-current liabilities 100,000 10,000 Current liabilities Equity and liabilities 63,800 604,420 23,080 135,320 1. As well as the investment in Steeple, Postal holds a small number of shares in various other companies. These cost $61,000 2. Steeple has not issued any shares since acquisition 3. The Postal Group measures the non-controlling interest using the full goodwill method. 4. Goodwill has not been impaired 5. The market value of one steeple share on 30 September 20X4 was $2.20 Prepare the consolidated statement of financial position for the Postal Group at 30 September 20X8. 5. (SOFP) Intra-Group Balances The following are extracts from the statements of financial position of Painter and Steamer, its subsidiary company: Receivables Cash Payables Painter $000 13,000 190 6,330 Steamer $000 11,700 213 10,870 Included in Painter’s receivables balance is $1.7 million due from Steamer. Included in Steamer’s payables balance is $1.5 million due to Painter. Steamer had sent $200,000 to Painter just before the year end, but because of a postal strike, it was not received by P until after the reporting date. What are the consolidated receivables, cash and payables balances? 6. (SOFP) Un-Realised Profits (URP) on Sale of Stock (a) During the year Sam, an 80% subsidiary, sold goods to Pam, its parent, for $1.8million. Sam adds a 20% mark up on cost to all its sales. Goods with a transfer price of $450,000 were included in Pam’s inventory at its year end of 31 March 20X8. (b) In the post-acquisition period, Play sold goods to Station, its subsidiary at a price of $6million. These goods had cost Play $4million. Half of these goods were still in the inventory of Station at its year end of 31 March 20X8. Calculate the unrealised profit and what consolidation adjustments are required to adjust the sale of goods between Parent and Subsidiary? 7. (SOFP) Un-Realised Profits (URP) on Disposal of Asset Parent buys a non-current asset for $100,000 on 1 January 20X5. It depreciates the asset over 10 years on the straight line basis. On 1 January 20X7, Parent sells the asset to Subsidiary for $98,000. Subsidiary depreciates the asset over the remaining 8 years of its useful life. What consolidation adjustments are required to adjust the sale of non-current asset from Parent to Subsidiary. 8. (SOFP) Fair Value Adjustments/Impairment of Goodwill A parent, Cushe, buys 80% of a subsidiary for $950m at the year start, when the share capital is $70m and retained earnings are $300m. A fair value adjustment upwards of $100m is required on machines with a life of five years. The fair value of the non-controlling interest is $222m. During the year the subsidiary made retained profits of $100m. Goodwill has an indefinite life and a yearend review reveals a value in use (VIU) of $440m and a fair value less costs to sell (FVLCTS) or net realisable value (NRV) of $666m. It is the group’s policy to measure the non-controlling interest at fair value. Calculate Goodwill and Non-Controlling Interest. 9. (SOFP) Mid-Year Acquisition Plaistow acquired 100% of Slough for $300,000 on 31 October 20X8. The net assets of the two companies at 31 December 20X8 are represented by: Share capital Retained earnings Plaistow $ 50,000 460,000 Slough $ 20,000 193,000 At 1 January 20X8, Slough had retained earnings of $175,000. Calculate goodwill and group retained earnings at 31 December 20X8. 10. (SOPL) Basic Steps to Consolidate/Non-Controlling Interest Pringle acquired 80% of the share capital of Sutherland a number of years ago. In the year ended 31 December 20X8, the individual income statements of the two companies were as follows: Revenue Cost of sales Gross profit Investment income Distribution costs Administrative expenses Operating profit Finance costs Profit before tax Taxation Profit for the year Pringle $000 678 (211) 467 79 (62) (215) 269 (16) 253 (70) 183 Sutherland $000 322 (165) 157 (31) (74) 52 (4) 48 (12) 36 During the year, Sutherland paid a dividend of $64,000. Prepare the consolidated income statement for the Pringle Group for the year ended 31 December 20X8. 11. (SOPL) Mid-Year Acquisition Pannal acquired 60% of the share capital of Sunbury on 1 February 20X8. This is Pannal’s only investment. In the year ended 31 October 20X8, the individual income statements of the two companies were as follows: Revenue Cost of sales Gross profit Investment income Expenses Operating profit Finance costs Profit before tax Taxation Profit for the year Pannal $000 1,214 (632) 582 12 (308) 286 (23) 263 (50) 213 Sunbury $000 421 (211) 210 (96) 128 (5) 123 (24) 99 Prepare the consolidated income statement for the Pannal Group for the year ended 31 October 20X8. 12. (SOPL) Intra-Group Balances & Un-Realised Profit (URP) on Sale of Goods: Abbreviated income statements of Primula and its 90% subsidiary Sunflower for the year ended 31 May 20X9 are as follows: Primula $ 197,000 (94,500) 102,500 (34,000) (12,000) 56,500 Revenue Cost of sales Gross profit Expenses Tax Profit after tax Sunflower $ 154,230 (81,200) 73,030 (17,600) (6,800) 48,630 During the year, Sunflower sold goods to Primula for $56,000 based on a Gross profit margin of 45%. A quarter of these remain in stock at the year end. Prepare a consolidated income statement for the Primula Group. 13. (SOPL) Un-Realised Profit (URP) on Disposal of Asset: On 1 October 20X7, Pluto transferred a machine to its 75% subsidiary Saturn for $35,000. The asset originally cost $55,000 on 1 October 20X4 and was being depreciated over 10 years on a straight line basis. Cost of sales in Pluto’s individual accounts for the year ended 30 September 20X8 is $287,650 and in Saturn’s $176,500. What is consolidated cost of sales for the year? 14. (SOPL) Fair Value Adjustments Pick acquired 75% of Stick half way through the current year. A fair value exercise was carried out for Stick at acquisition with the following results: Land Plant Book value $000 20,000 25,000 Fair value $000 23,000 30,000 The fair values have not been reflected in Stick’s financial statements. Plant is depreciated at 20% per annum on a straight line basis. Cost of sales in Pick’s income statement is $4.4 million, and in Stick’s income statement $3.6million. What is the consolidated cost of sales?