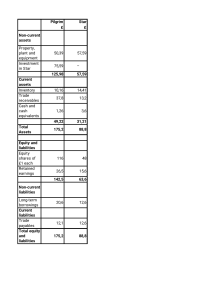
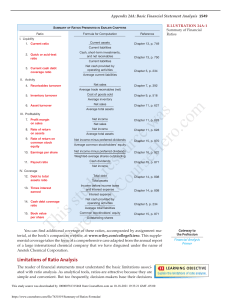
Chapter 3 Financial Statement Analysis Chapter Overview • • • • • • • • • The Statement of Financial Position The Income Statement Taxes Net Working Capital Cash Flow Financial Statement Analysis Ratio Analysis The DuPont Identity Using Financial Statement Information Overview Three Important Accounting Statements The Statement of Financial Position The Income Statement The Cash Flow Statement The Statement of Financial Position What are the firm’s assets and how are they funded? The Statement of Financial Position The Accounting Equation Liabilities Shareholders’ Equity Assets The Statement of Financial Position Centrica plc 2018 Non-Current Assets £m Non-Current Liabilities £m Property, Plant and Equipment 4,059 Bank Loans and other Borrowings 4,359 Intangible Assets 2,009 Other Long-Term Liabilities 4,234 Interests in Joint Ventures 1,727 8,593 Goodwill 2,678 Current Liabilities Other Non-Current Assets 1,779 Trade Payables 12,252 Other Current Liabilities Current Assets Trade Receivables Inventories Bank Overdrafts and Loans 4,524 347 Total Liabilities Other Current Assets 1,597 Total Shareholders’ Equity Cash and Cash Equivalents 1,538 4,995 1,749 898 7,642 16,235 4,023 8,006 Total Assets 20,258 Total Assets 20,258 The Statement of Financial Position Important Characteristics of Statements of Financial Position Current and NonCurrent Assets Current and NonCurrent Liabilities Equity Net Working Capital The Income Statement How has the firm performed over the previous period? The Income Statement The Income Equation Revenues Expenses Income The Income Statement Centrica plc 2018 Revenue Expenses Profit Before Interest and Taxes Finance Costs Profit Before Tax Tax Profit After Tax Number of Shares EPS £m 15,321 14,617 704 289 415 177 238 5667 0.042 The Income Statement Important Characteristics of Income Statements Non-Cash Items Variable and Fixed Costs Tax Operating Profit and Net Income Taxes How to calculate tax Taxes Average vs. Marginal Tax Rates Average Tax Rate Marginal Tax Rate •Tax paid/profit before taxes •Tax (%) you pay if you earn one more unit of currency Taxes Average vs. Marginal Tax Rates The first €200,000 earned by Dutch firms pay 16 per cent tax; extra earnings pay 22.25 per cent tax. Suppose Dutch corporation has taxable income of €400,000. Tax Paid • 16% × €200 + 22.25% × €200 = €76.5 Tax Rates • Average: 76.5/400 = 19.125% • Marginal: 22.25% Net Working Capital How to calculate net working capital Net Working Capital How to Calculate Net Working Capital Current Assets Current Liabilities Net Working Capital Net Working Capital Centrica plc 2018 The Cash Flow Statement Where has the cash come from and what has the firm spent? The Cash Flow Statement Centrica plc 2018 Financial Statement Analysis How to assess firm performance, risk and liquidity Financial Statement Analysis Important to Compare Like for Like Financial Ratios Common Size Statements Ratio Analysis The important financial ratios Ratio Analysis What do Ratios Measure? Short-Term Solvency or Liquidity Long-Term Solvency or Leverage Asset Management or Turnover Profitability Market Value Ratio Analysis Short-Term Solvency Ratios Current assets Current ratio = Current liabilities Quick ratio = Cash ratio = Current assets - Inventory Current liabilities Cash and cash equivalents Current liabilities Ratio Analysis Long-Term Solvency Ratios Total assets - Total equity Total debt ratio = Total assets Debt-equity ratio = Total debt/Total equity Equity multiplier = Total assets/Total equity Times interest earned ratio = Profit Before Interest and Taxes Interest Cash coverage ratio = EBIT + Depreciation Interest Ratio Analysis Asset Management Ratios Inventory turnover = Inventory turnover = Cost of goods sold Inventory Operating Expenses Inventory Days’ sales in inventory = Receivables turnover = Days’ sales in receivables = 365 days Inventory turnover Revenues Trade receivables 365 days Receivables turnover Total asset turnover = Revenues Total assets Ratio Analysis Profitability Ratios Net income Profit margin = Revenues Net income Return on assets = Total assets Net income Return on equity = Total equity Ratio Analysis Market Value Ratios Net income EPS = Shares outstanding PE ratio = Price per share Earnings per share Market-to-book ratio = Market value per share Book value per share The DuPont Identity Disassembling return on equity The Du Pont Identity What Drives Performance? Net income Net income Assets Return on equity = = x Total equity Total equity Assets Net income Assets = x Assets Total equity Using Financial Statement Information Practical aspects of financial statement analysis Using Financial Statement Information Choosing a Benchmark Time Trend Analysis Peer Group Analysis Concept Quiz How Much do You Understand? Quiz Identify two circumstances where negative operating cash flow might not necessarily be a sign of deteriorating financial health. When can negative operating cash flow become problematic for a company? Both ROA and ROE measure profitability. Which one is more useful for comparing two companies? Why? A financial ratio by itself tells us little about a company because financial ratios vary a great deal across industries. There are two basic methods for analysing financial ratios for a company: time trend analysis and peer group analysis. Why might each of these analysis methods be useful? What does each tell you about the company’s financial health?