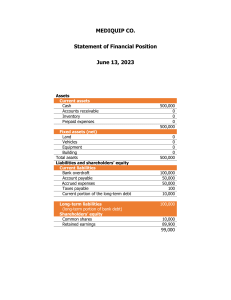
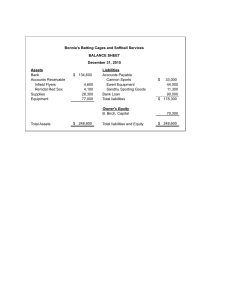
1. What is a long-term liability in accounting? a. Debt payable within a year b. Debt payable over several years c. Short-term investments d. Equity capital 2. Which financial statement typically includes long-term liabilities? a. Income Statement b. Balance Sheet c. Cash Flow Statement d. Statement of Retained Earnings 3. Which of the following is an example of a long-term liability? a. Accounts Payable b. Short-term Loan c. Mortgage Payable d. Salaries Payable 4. How are long-term liabilities different from short-term liabilities? a. Short-term liabilities have lower interest rates. b. Long-term liabilities are due within one year. c. Long-term liabilities are payable over an extended period. d. Short-term liabilities have higher principal amounts. 5. What is the purpose of issuing bonds as a form of long-term liability? a. To increase short-term liquidity b. To acquire long-term assets c. To decrease shareholder equity d. To finance operating expenses 6. How are long-term liabilities classified on a balance sheet? a. Current Liabilities b. Non-current Liabilities c. Contingent Liabilities d. Accrued Liabilities 7. What is the difference between a secured and unsecured long-term liability? a. Secured liabilities have no collateral. b. Unsecured liabilities require collateral. c. Secured liabilities are backed by specific assets. d. Unsecured liabilities are riskier for creditors. 8. What does the term "debt covenant" refer to in the context of long-term liabilities? a. An agreement between shareholders and creditors b. A promise to repay debt within one year c. Restrictions imposed on the borrower by the lender d. A legal document outlining debt terms and conditions 9. How do companies typically account for the interest expense on long-term liabilities? a. Record it as a reduction in equity b. Capitalize it as an asset c. Amortize it over the loan term d. Expense it on the income statement 10. What financial ratio is commonly used to assess a company's ability to cover its long-term liabilities with its operating income? a. Current Ratio b. Debt-to-Equity Ratio c. Return on Assets d. Gross Profit Margin