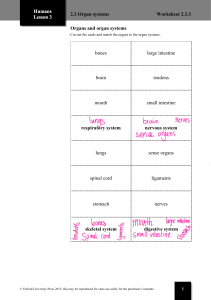
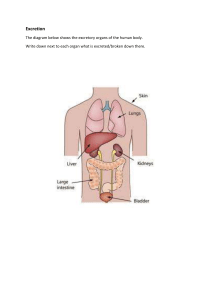
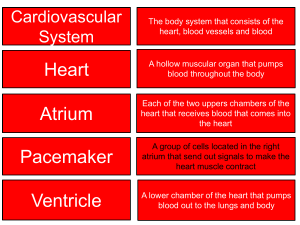
The Human Body 101 Anatomy and physiology Levels of Organization in the Human Body 5. Organ Systems 6.Organism 1.Chemicals 4. Organs 2. Cells 3. Tissues Chemicals in the Human Body • Water • Makes up 60 – 70 % of human body • Protein • Protein is the main component of muscles, bones, connective tissue, organs, skin, nails, hormones, enzymes • Lipids (fats) • Stored under skin and around organs • Carbohydrates • Glucose and glycogen • DNA • Makes up your genes • Gases Cells. What are they? • A cell is the simplest unit of life. • It is the smallest part of an organism that can exist on its own. • All organisms are made up of cells How many cells are in the human body? • As much as 40 trillion (40,000,000,000,000) cells 5 Types of Cells in the Human Body • Epithelial cell • Nerve cell • Muscle cell • Connective tissue cell Epithelial Cells • They cover over the interior of hollow organs, like blood vessels or digestive organs, or else form the surface of things, like the skin • They protect the more delicate tissue beneath Nerve Cells • Also called NEURONES. • Carry electrical impulses through the nervous system and allows us to sense and respond to our environment Muscle Cells • Contract and relax to allow movement • They also form the thick outer walls of hollow organs, like blood vessels and digestive Connective Tissue Cells • Provide structural strength to the body • Bone, cartilage, fat • Defend against foreign invaders like bacteria. • White blood cells Tissues • A tissue is a group of similar cells that perform the same function. E.g muscle tissue, nerve tissue What is an Organ? An organ is made up of different types of tissues that work together E.g. heart, brain stomach What are the five most important organs in the human body? • The brain • The heart • The lungs • The liver • The kidneys 13 What is an Organ System? An organ system is made up of several organs that work together to perform a particular function. E.g. the digestive system LEARNING ABOUT ORGAN SYSTEMS How many body systems are in the human body? 11 16 Test Yourself: List the organ systems • Integumentary • Lymphatic • Skeletal • Respiratory • Muscular • Digestive • Nervous • Urinary • Endocrine • Reproductive • Cardiovascular The Digestive System • Breaks down / digests food • Organs include the stomach, pancreas, intestines, liver, gall bladder • Substances present include: • Partially digested food, digestive juices, enzymes, hydrochloric acid, feces, gases Salivary glands Oesophagus Stomach Liver Gall bladder Pancreas Small intestine Rectum Large intestine (colon) Anus What happens in digestive tract after death? • The location and state of partially digested food in the digestive tract gives an indication of the time of their last meal • Enzymes and bacteria present begin to breakdown cells and tissues (autolysis) • Bacteria expel gases like methane and ammonia that create the bloating frequently seen in the abdomen after death. • Any partially digested food in stomach and intestines and feces is removed The Cardiovascular /Circulatory System • Transports substances around the body The Heart • The pump of the system • Made of CARDIAC muscle • Is made up of FOUR chambers The Blood • Blood is a constantly flowing transport medium (fluid) • Contains dissolved substances that provide the body with nutrition, oxygen, hormones, water • Helps with waste removal and control of body temperature What is the approximate volume of blood in an adult human? • 1.2 – 1.5 gallons / 5 litres Livor mortis • Livor mortis is the gravitational settling of blood which is no longer being pumped through the body after death • Damaged blood cells begin to spill out of broken vessels and, aided by gravity, settle in the capillaries and small veins, • Causes a bluish-purple discoloration of the skin • Sets in 20- 30 minutes after death Blood Vessels ARTERIES • Takes blood from • heart to body • • Have thick, muscular walls • • Have a narrow lumen • VEINS Brings blood from body back to heart Have thinner walls than arteries Have a wide lumen Have valves CAPILLARIES • Brings blood with nutrients, oxygen, water directly to body cells and tissues • Walls are very thin. Only 1 cell thin. Test Yourself VEIN CAPILLARY ARTERY Major Arteries and Veins Body part/organ Brain Heart lungs Liver Arms stomach intestines kidneys legs Artery Carotid artery Coronary artery Pulmonary artery Hepatic artery Subclavian artery Celiac artery Mesenteric artery Renal artery Iliac artery Vein Jugular vein Coronary vein Pulmonary vein Hepatic vein, Subclavian vein Hepatic portal vein Hepatic portal vein Renal vein Iliac vein The Cardiovascular system and the Embalming Process • The act of pumping arterial embalming fluid into arteries forces the person's blood out through the venous system • Embalming fluid pumped through carotid artery or iliac artery • Embalming machine acts like the heart to push fluid through all the blood vessels to all of the tissues The Respiratory System • Allows breathing. Brings oxygen into the body and gets rid of carbon dioxide • Includes organs like the • Lungs • Trachea • Bronchi Pharynx Epiglottis Right lung Larynx Trachea Left bronchus Left lung Diaphragm Integumentary System • The integumentary system is the largest organ of the body that forms a physical barrier between the external environment and the internal environment • Includes: • The skin • Hair • Glands • Nails • Nerves and blood vessels Functions of the skin • Physical, water proof barrier against pathogens • Temperature control • Excretion of wastes • Sensation The Skin • Has three layers • Epidermis (top layer) • Dermis: glands, hair follicles • Subcutaneous (fat) layer Skin Slippage • Skin slippage is a part of the decomposition process when the top layers of skin become disconnected from layers below The Muscular System • The muscular system is an organ system consisting of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. • Permits movement of the body, • Maintains posture, • Circulates blood throughout the body. • Controlled by the nervous system although some muscles can be completely autonomous. Rigor mortis • Stiffening of the joints and muscles of a body a few hours after death, • Usually lasts from one to four days. • Body relaxes again once muscle tissue breaks down Rigor mortis • In life, muscle cells contract and relax due to the actions of two proteins (actin and myosin), which slide along each other. • After death, the cells are depleted of their energy source and the protein filaments become locked in place. • This causes the muscles to become rigid and locks the joints. The Skeletal System • Allows movement and support of the body • Protects organs • Makes red blood cells • Includes organs like the • Bones • Cartilage • Tendons • Ligaments • Joints The Reproductive System • Produces offspring • Includes organs like the • Penis • Testes • Ovaries • Uterus The Urinary System • Filters the blood and removes metabolic wastes • Produces urine • Includes organs like the • kidneys • bladder The Nervous System • Controls the activities of the body • Includes organs like the • Brain • Spinal cord • Nerves The Endocrine System • Made up of hormone producing glands • Hormones control • metabolism, • growth • sexual development. The Lymphatic System The lymphatic system has three main parts: • The lymphatic vessels: the tubes along which the lymph flows. Resembles veins • The lymph: the fluid • The lymph nodes: to clean the lymph Functions of the Lymphatic System • Drains tissue fluid from cells and tissues as lymph • Returns clean fluid back to the blood • The lymph vessels return the fluid to the bloodstream through the subclavian vein in the upper arm and neck THE END