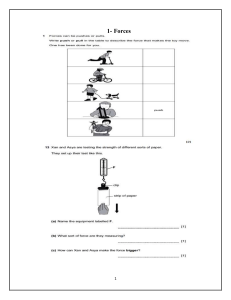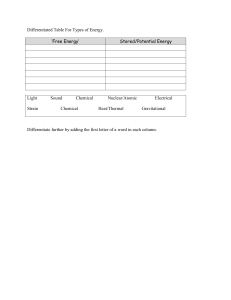
Basic Electrical Engineering Prof. Ramya Selvaraj Dept. of Electrical Engineering Introduction Course objectives • To impart the basic knowledge of the Electric and Magnetic circuits. • To understand the basic concepts of single phase and three phase AC circuits. • To impart basic knowledge of various electrical machines and measuring instruments. Why electricity? Why is it popular? • Progress of a nation depends on the per capita consumption of electrical energy • India – 300; UK-12-15 times more; USA- 30 times more • Main reasons for its popularity • • • • • Cleaner environment Higher efficiency Better controllability Long distance transportation Easier to convert electrical energy into other versions like thermal, illumination, sound, mechanical etc Sources for Generation of electricity • Conventional methods • • • Thermal Hydro-electric (Hydel) Nuclear • Non-conventional methods • • • • Wind Solar Biomass Waste to energy The break up of renewable energy sources (RES) is: •Solar power (36,910.53 MW) •Wind power (38,433.55 MW) •Biomass (10,145.92 MW) •Small hydro (4,740.47 MW) •Waste-to-energy (168.64 MW) Comparison of sources of electricity generation • Initial cost • Running costs • Limitations • Perpetuity-efficiency-reliability-cleanliness-simplicity Transmission and Distribution of Power Why do we need insulators? What is the typical no of phases and frequency used for generation of electric power? Contd.. • Why are we transmitting the power at a higher voltage as compared to the generating voltage? Typical voltage levels in a power system Lesson 1: Overview Generation, Transmission and Distribution of Electric Power Goals • Different methods of generating electrical power. • Issues involved in transporting this power to different types of consumers located generally at far off places from the generating stations • Necessity of substations to cater power to consumers at various voltage levels. A.C. Generator 3Φ 50 Hz supply Thermal Basic components of a thermal power plant Merits • Fuel (=coal) is cheap • Less initial cost is required • Less space • Therefore the cost of generation for 1 unit of electrical energy is cheaper Disadvantages • Atmospheric pollution is quite high • Transportation cost might become high in the future Hydro-electric Basic components of a Hydel power plant Merits • Renewable • Emission free • Reliable • Adjustable • Create lakes • Faster developed lands Disadvantages • Impact on fish • Limited Plant locations • Higher initial costs • Susceptible to droughts • Flood risks Nuclear Basic components of a nuclear power plant Merits • Quantity of fuel required for one unit of electricity gen. is less • Cheaper running costs • More reliable • Efficient when running at the rated capacity Disadvantages • Fuel is expensive and not available in abundance • High capital costs • Maintenance is high • Nuclear waste disposal is a problem