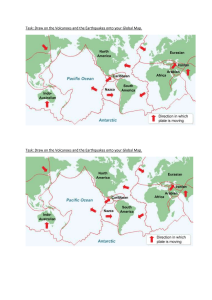
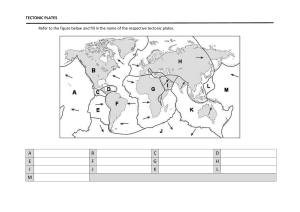
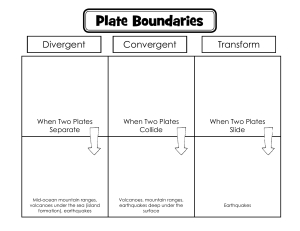
Earthquakes, Mountains, and Volcanoes: Forces of Nature Earth's surface is constantly changing due to the dynamic forces of nature. Three significant natural phenomena that shape our planet are earthquakes, mountains, and volcanoes. Earthquakes are caused by the movement of tectonic plates beneath the Earth's surface. These plates, which are like giant puzzle pieces, are always shifting and colliding. When the stress along the edges of these plates becomes too great, it releases in the form of seismic waves, causing the ground to shake. The magnitude of an earthquake is measured on the Richter scale, with higher numbers indicating stronger quakes. While earthquakes can be devastating, they also play a crucial role in shaping the Earth's surface over time. Mountains are formed through a process called tectonic uplift. This occurs when tectonic plates push against each other, forcing the Earth's crust to rise and form mountain ranges. Over millions of years, erosion from wind, water, and glaciers shapes these peaks into the majestic landscapes we see today. Mountains provide habitats for diverse plant and animal species and are a vital source of resources such as water and minerals. Volcanoes, like earthquakes, are closely linked to tectonic activity. They form at the boundaries of tectonic plates, where magma from deep within the Earth's mantle rises to the surface. When this molten rock erupts, it can create spectacular displays of lava, ash, and gas. While volcanic eruptions can be destructive, they also contribute to the creation of new land and enrich the soil with nutrients, making it fertile for agriculture. Questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What are earthquakes, and what causes them? How are mountains formed, and what processes shape them over time? Explain the relationship between volcanoes and tectonic activity. What role do earthquakes play in shaping the Earth's surface? Why are mountains important for ecosystems and human activities?