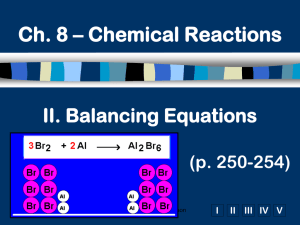
III. Colligative Properties (p. 436 - 446) Ch. 13 & 14 - Solutions C. Johannesson A. Definition • Colligative Property – property that depends on the concentration of solute particles, not their identity C. Johannesson B. Types • Freezing Point Depression (tf) – f.p. of a solution is lower than f.p. of the pure solvent • Boiling Point Elevation (tb) – b.p. of a solution is higher than b.p. of the pure solvent C. Johannesson B. Types Freezing Point Depression View Flash animation. C. Johannesson B. Types Boiling Point Elevation Solute particles weaken IMF in the solvent. C. Johannesson B. Types • Applications – salting icy roads – making ice cream – antifreeze • cars (-64°C to 136°C) • fish & insects C. Johannesson B. Types • Vapor Pressure: pressure of the vapor resulting from evaporation of a liquid above a sample of the liquid in a closed container. – Depends on • Type of sample: greater intermolecular force results in lower vapor pressure • Temperature: higher temp, greater vapor pressure • Dissolved particles C. Johannesson B. Types • Vapor Pressure Reduction – When a solute is added to a solvent, the vapor pressure of the solvent is lower than the pure solvent. C. Johannesson B. Types Vapor pressure of sucrose solution C. Johannesson B. Types Pure Water 1.0M NaCl Solution -more water molecules above surface -fewer water molecules above surface C. Johannesson • Osmosis: water flow through a semipermeable membrane that blocks the transport of salts or other solutes through it – from the volume of low solute concentration, to the volume of high solute concentration C. Johannesson B. Types Osmotic Pressure -the pressure required to stop osmosis -The osmotic pressure does not depend on the solute type, or its molecular size, but only on its molar concentration If there is only water in the device, the level will be the same at both arms. When solute molecules are added to one arm, water will start to flow into it, so that its level will go up at this arm, and down at the other arm. C. Johannesson