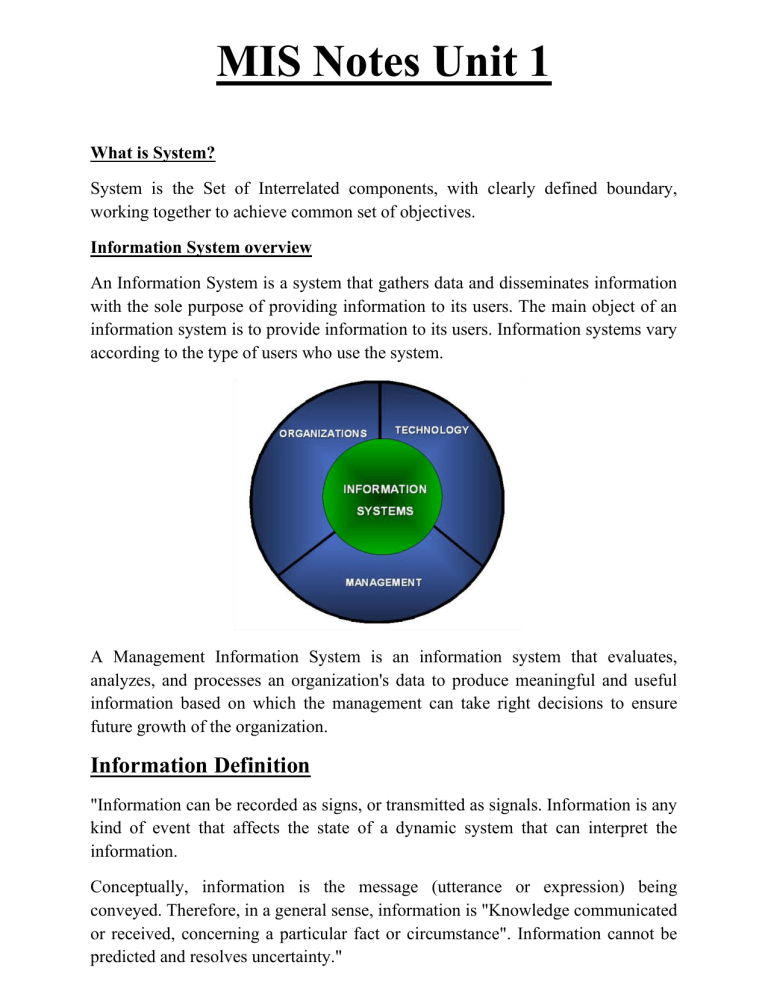
MIS Notes Unit 1 What is System? System is the Set of Interrelated components, with clearly defined boundary, working together to achieve common set of objectives. Information System overview An Information System is a system that gathers data and disseminates information with the sole purpose of providing information to its users. The main object of an information system is to provide information to its users. Information systems vary according to the type of users who use the system. A Management Information System is an information system that evaluates, analyzes, and processes an organization's data to produce meaningful and useful information based on which the management can take right decisions to ensure future growth of the organization. Information Definition "Information can be recorded as signs, or transmitted as signals. Information is any kind of event that affects the state of a dynamic system that can interpret the information. Conceptually, information is the message (utterance or expression) being conveyed. Therefore, in a general sense, information is "Knowledge communicated or received, concerning a particular fact or circumstance". Information cannot be predicted and resolves uncertainty." Information vs Data Data can be described as unprocessed facts and figures. Plain collected data as raw facts cannot help in decision-making. However, data is the raw material that is organized, structured, and interpreted to create useful information systems. Data is defined as 'groups of non-random symbols in the form of text, images, voice representing quantities, action and objects'. Information is interpreted data; created from organized, structured, and processed data in a particular context. According to Davis and Olson: "Information is a data that has been processed into a form that is meaningful to recipient and is of real or perceived value in the current or the prospective action or decision of recipient." Role of MIS in Business Organization The MIS is defined as a system based on the database of the evolved for the purpose of providing information to the people in the organization. Management information systems are distinct from regular information systems in that they are used to analyze other information systems applied in operational activities in the organization. MIS involve three primary resources: technology, information, and people. MIS provides information for the managerial activities in an organization. MIS provides accurate and timely information necessary to facilitate the decision making process and enable the organizations planning, control and operational functions to be carried out effectively. MIS provides Right information, to the right person, at the right place, at the right time, in the right form and at the right cost. The role of MIS in an organization can be compared to the role of heart in the body. The information is the blood and MIS is the heart. In the body the heart plays the role of supplying pure blood to all the elements of the body including the brain. The MIS plays exactly the same role in the organization. The system ensures that an appropriate data is collected from the various sources, processed, and sent further to all the needy destinations. The system is expected to fulfill the information needs of an individual, a group of individuals, the management functionaries: the managers and the top management. The MIS satisfies the diverse needs through a variety of systems such as Query Systems, Analysis Systems, Modeling Systems and Decision Support Systems. The MIS helps in Strategic Planning, Management Control, Operational Control and Transaction Processing. Purpose and Objectives of MIS in Business Organization • To provide information for planning, organizing and controlling purposes. • To store and manage data efficiently from all the functional areas of the business. • To process the collected data and derive information out of them. • To provide information quickly as and when required. • To reduce the risk and uncertainties in the managerial decision-making. • To collect and store the data for the purpose of internal research. • To assist in identifying the managerial problems and their solution. • To provide information regarding work force planning. • To provide the information regarding the financial health of the business organization. • To provide information regarding production and inventory. • To provide information regarding sales and other marketing aspects i.e. product, price, promotion, market, physical distribution, payment collection, market segmentation etc. • To speed up the execution of the results with the reliable data available. • To smooth up the flow of data through various levels of the organization. • To provide information regarding work force planning. • To provide the information regarding the financial health of the business organization. • To speed up the execution of the results with the reliable data available. • To smooth up the flow of data through various level of the organization. Importance of MIS • It helps in minimizing risk in decision making. • It processes the data and derives information out of them. • It provides information about the various aspects of business. • It helps the executives to avail the information regarding the functional areas quickly. • The database helps in inducting research. The data stored are used as secondary data. • It provides sound information regarding the financial health of business organization. • It helps in preparing corporate report. • It helps the HRD manager in finding out the requirement of the human resource, their wages and salary, performance appraisal, training, promotion, absenteeism and employee’s turnover, which is useful in drafting sound HRD polices. • The data regarding production helps the production manager in deciding about capacity utilization, number of rejections per batch, frequency of break down, status of shipment of processed order and product, region wise. • It provides information regarding inventory position, and ensures that the chances of inventory out of stock may be minimized. • It provides information regarding product, price, promotion, segmentation, demand, sale etc. to marketing manager instantly and ensures smooth functioning of that department. Characteristics of MIS Management-oriented: The basic objective of MIS is to provide information support to the management in the organization for decision making. Management directed: When MIS is management-oriented, it should be directed by the management because it is the management who tells their needs and requirements more effectively than anybody else. Integrated: It means a comprehensive or complete view of all the subsystems in the organization of a company. Common data flows: The integration of different subsystems will lead to a common data flow which will further help in avoiding duplicacy and redundancy in data collection, storage and processing. Heavy planning-element: The preparation of MIS is not a one or two day exercise. It usually takes 3 to 5 years and sometimes a much longer period. Subsystem concept: When a problem is seen in 2 sub parts, then the better solution to the problem is possible. Common database: This is the basic feature of MIS to achieve the objective of using MIS in business organizations. Computerized: MIS can be used without a computer. But the use of computers increases the effectiveness and the efficiency of the system. User friendly/Flexibility: An MIS should be flexible. Information as a resource: Information is the major ingredient of any MIS. Features of MIS Timeliness Accuracy Completeness Relevance Consistency Component of MIS Marketing Research System (MRS) Marketing research can be seen as the systematic and objective search for analysis of data and information relevant to the identification and solution of any problem in the field of marketing. Marketing Intelligence System (MIS) The process of acquiring and analyzing information in order to understand the market (both existing and potential customers) to determine the current and future needs and preferences, attitudes and behavior of the market; and to assess changes in the business environment that may affect the size and nature of the market in the future. Internal Record System (IRS) Marketing managers rely on internal reports on orders, sales, prices, costs, inventory levels, receivables, payables, and so on. By analyzing this information, they can spot important opportunities and problems. Decision Support System(DSS) A decision support system (DSS) is a computer-based information system that supports business or organizational decision-making activities. DSS serve the management, operations, and planning levels of an organization and help to make decisions, which may be rapidly changing and not easily specified in advance. Types of MIS Transaction processing systems: These systems process a large volume of routine, recurring transactions. Operations information systems: These systems gather comprehensive data, organize it and summarize it in a form that is useful for managers. Decision support systems: These systems help mangers with the necessary information to make intelligent decisions. Expert systems: They are meant to mimic humans in making decisions in a specific field. Elements of MIS Executives: Executives are the people who utilize MIS. These people are computer professionals who operate MIS for data processing to achieve organizational goals like planning and decision-making. Hardware: The hardware components of MIS include various input and output devices that helps in feeding data as well as displaying the information when required. The input devices include the keyboard, scanners and mouse. The output devices may be the monitor, printer, network devices, and so on. Software: Computer programs which are designed to do a specific task for example, MS Office, Banking Software’s, Railway’s applications etc, different kinds of software available to process the data/information in an organization such as ERP (enterprise resource planning) and CRM (customer relationship management). Organizational Procedures: Procedures are sets of rules or guidelines that an organization establishes for the use of a computer-based information system. The procedures may vary from one organization to another. It may also vary from one department to another as per the requirement. For example, the working of production department is different from the working of sales department. The production department requires information regarding the raw material or quantity of goods to be produced. So, the production department sets its procedures in such a way that the MIS system helps in retrieving the information required by the department. In the similar way, the sales department requires information regarding the quantity of goods sold and the other expenses that occurred during the sales of the product. Therefore, the sales department sets the procedures in such a way that they get only that information which is required from the MIS. Output Of MIS Scheduled reports: which are produced periodically, or on a Schedule (daily, weekly, monthly). Key-indicator report: which summarizes the previous day’s critical activities and also it is typically available at the beginning of each day. Demand report : Which gives certain information at a manager’s request. Exception report : Which is automatically produced when a situation is unusual or requires management action. Benefits of MIS It improves personal efficiency. It expedites problem solving(speed up the progress of problems solving in an organization). It facilitates interpersonal communication. It promotes learning or training. It increases organizational control. It generates new evidence in support of a decision. It creates a competitive advantage over competition. It encourages exploration and discovery on the part of the decision maker. It reveals new approaches to thinking about the problem space. It helps automate the Managerial processes. Functions of MIS To collect useful data: MIS executes the data through computer system using the sources of an organization. The organizational data is stores in computer system or as a paper record by its end users. Data Processing: Processing data includes converting the storage data into the required information to take beneficial actions. Data processing includes mathematical and logical operations like, calculations, sorting, classifying and summarizing the data. The data processing signifies processing activities as: • • • • • Organize data Analysis on data Apply statistical, mathematical, operations To create predictive modeling Research and forecasting Information storage and retrieval: MIS stores data as an organizational record and processed for future use. The data organizes as a fields, records, files and databases for future use. Information retrieval comprises to access the stored data as per the requirements of the management users. Disseminating management information: Information of finished product is categorizes and dispersed to the users in an organization as per the needs. This information could be periodic, through reports or online through computer terminals. Figure shows various functions performed by MIS. Pre-requisites of an effective MIS Qualified system and Management Staff Control and Maintenance of MIS Common Data Base Evolution of MIS Support of Top Management Qualified system and Management Staff System and Computer Experts: Who in addition to their expertise in their subject area, they should also be capable of understanding management concepts to facilitate the understanding of problems asked by concern. They should also be clear about the process of decision making and information requirements for planning. Management experts: Who should also understand quite clearly the concepts and operations of Computer. This basic knowledge of computer will be useful will place them in a comfortable position, while working with systems, technicians in designing or otherwise, of the information system. Control and Maintenance of MIS Control of the MIS means the operations of the system as it was designed to operate. Sometimes, users develop their own procedure or short cut methods to use the system which reduces its effectiveness. To check such habits of users, the management at each level in the organization should device checks for information system control. Maintenance is closely related to control. There are times when the need for improvement to the system will be discovered. Formal methods for changing and documenting changes must be provided. Common Data Base It is an integrated collection of data and information which is utilized by several information sub systems of an organization. A common database may be defined as a super file which consolidates and integrates data records formerly stored in a separate data file. Such a database can be organized as an integrated collection of data records into a single super file or it can be organized as an integrated collection of several data file. Evolution of MIS An effective MIS should be capable of meeting the information requirements of its executives in future as well. It requires timely actions. The evolution of MIS should take into account the following points: 1. Ascertaining the views of users and the designers about the capabilities and deficiencies of the system. 2. Guiding the appropriate authority about the steps to be taken to keep the effectiveness of MIS alive. 3. Examining whether enough flexibility exists in the system, to cope up with any expected information requirement in future. Support of Top Management For a management information system to be effective, it is essential that it must receive the full support of top management. The reasons for this are as follows: 1. Subordinate managers are usually lethargic about activities which do not receive the support of their superiors (top management). 2. The resources involved in computer based information system are large and are growing larger and larger in view of importance gained by management information system. To gain the support of top management, the officers should place, before top management, all the supporting facts and state clearly the benefits which will accrue from it to the organization. This step will certainly enlighten management and will change their attitude towards MIS. Their whole hearted support and co-operation will help in making MIS an effective and successful one. MIS Applications in Business MIS application in business falls into several different categories that provide information on all forms of functioning within an organization. Executives and departments within an organization could obtain any of the following forms of data: • Business Intelligence System: In BI, all levels of management and executives can print data and graphs showing information or trends relating to growth, costs, strategic control, efficiency, risk and performance. • Executive Information System: An EI system provides the same information as a BI system, but with greater attention to detail and more confidential information, designed to help top-level executives make choices that impact the entire organization. • Marketing Information System: MI systems provide data about past marketing campaigns so that marketing executives can determine what works, what does not work and what they need to change in order to achieve the desired results. • Transaction Processing System: TPS handles sales transactions and makes it possible for customers to sort search results by size, color or price. This system can also track trends related to sales and search results. • Customer Relationship Management System: Keeping up with customers is key to overall success, and CRMS helps companies know when and how to follow up with customers in order to encourage an ongoing sales relationship with them. • Sales Force Automation System: Gone are the days when sales teams must do everything manually. SFA systems automate much of what must be done for orders and to obtain customer information. • Human Resource Management System: HRM systems track how much employees are paid, when and how they are performing. Companies can use this information to help improve performance or the bottom line. • Knowledge Management System: Customers with questions want answers right away and knowledge management systems allow them to access frequently asked questions or troubleshoot on their own timetable. • Financial Accounting System: Financial accounting systems help to track accounts receivable and accounts payable, in order to best manage the cash flow of a company. • Supply Chain Management System: SCM systems record and manage the supply of finances, goods and data from the point of origin domestically or abroad, all the way to its destination in the hands of a customer. Information in Decision Making Meaning Decision making is a process of selecting the best among the different alternatives. It is the act of making a choice. There are so many alternatives found in the organization and departments. Decision making is defined as the selection of choice of one best alternative. Before making decisions all alternatives should be evaluated from which advantages and disadvantages are known. It helps to make the best decisions. Importance Implementation of managerial function: Without decision making different managerial function such as planning, organizing, directing, controlling, staffing can’t be conducted. In other words, when an employee does, s/he does the work through decision making function. Therefore, we can say that decision is important element to implement the managerial function. Pervasiveness of decision making: The decision is made in all managerial activities and in all functions of the organization. It must be taken by all staff. Without decision making any kinds of function is not possible. So it is pervasive. Evaluation of managerial performance: Decisions can evaluate managerial performance. When decision is correct it is understood that the manager is qualified, able and efficient. When the decision is wrong, it is understood that the manager is disqualified. So decision making evaluate the managerial performance. Helpful in planning and policies: Any policy or plan is established through decision making. Without decision making, no plans and policies are performed. In the process of making plans, appropriate decisions must be made from so many alternatives. Therefore decision making is an important process which is helpful in planning. Selecting the best alternatives: Decision making is the process of selecting the best alternatives. It is necessary in every organization because there are many alternatives. So decision makers evaluate various advantages and disadvantages of every alternative and select the best alternative. Successful operation of business: Every individual, departments and organization make the decisions. In this competitive world; organization can exist when the correct and appropriate decisions are made. Therefore correct decisions help in successful operation of business. Sources of Information in Decision Making Sources located in your Business Internal Statistics IT Department Finance Department Sales Department Colleagues Researchers Business Library Market Research Sources located outside your Business Family Friends Contacts Competitors Stakeholders Events Publications Press Releases External Researchers Universities Media Internet Social Media Research Publications Industry News Consultants Types of Information Instructions Answers Command Historical Advisory Predictive. Instructions: It refers to information that guides behavior in a particular way. In other words, it supports performance to carry out a task by prompting on what to do and when to do it. A simple sign telling people to enter or not enter a door would be one example. Command: Messages give a very straightforward statement on what is or what is not permitted. 'Do not enter', 'do not smoke', 'do not eat or drink', are examples of command messages. Sometimes they are similar to instructions, but are much more focused on simple statements that refer to high priority items. Advisory: Messages are somewhat watered down versions of command messages. In some cases, these will be recommendations to avoid a situation, at other times they would be information allowing for the preparation or planning of particular activities. For example, we might be advised that our train is late by a spoken message and we might, possibly, be given an accurate time estimate for when the train will be available. Answers: Information may be provided in response to a particular enquiry that has been made. This is typical of an interactive information handling situation, where we have a particular question in mind or degree of uncertainty and we seek information from a source with regard to removing that uncertainty. It turns out that most of the information that is sought from displays is of the answer kind. If we want to know what the time of day is, we look at our watches and clocks to find the answer. Historical: Displays are used to look back at the state of a variable over a period of minutes, hours, days or even years. A graphical representation of road accidents over the last century would be a historical display of information. If we want to know what the temperature fluctuation has been in an office on a daily basis, then specialist devices can be brought in and placed in the office that will give a pen recording over a fixed period of time. It is much easier to see if there is a trend in information if it is displayed in this way. Predictive: Displays are much more specialized, but increasingly found in complex processes. In the same way that historical data support performance in making a judgment based on the current value, predictive information enables examination of the current value and indicates any likely change in the future. Predictor displays enable better control over vehicles, typically at sea or airborne, and enable smoother transitions from one state to another. They are used in slow response systems where it is difficult to see the immediate effect of an action that has been carried out. Predictive displays will enable a variable to be plotted into the future. The same graphs that are used as historical displays can also be used as predictive displays. If a steady decline in road accidents over time is seen, then the best prediction of the future would be a continued decline. Information Requirements with particular reference to Management Levels Information as required at different levels of management can be classified as: Operational Tactical Strategic Operational : Operational information relates to the day-to-day operations of the organization and thus, is useful in exercising control over the operations that are repetitive in nature. Since such activities are controlled at lower levels of management, operational information is needed by the lower management. For example, the information regarding the cash position on day to day basis is monitored and controlled at the lower levels of management. The operational information pertains to activities that are easily measurable by specific standards. The operational information mainly relates to current and historical performance, and is based primarily on internal sources of data. Tactical: Tactical information helps middle level managers allocating resources and establishing controls to implement the top level plans of the organization. For example, Information regarding the alternative sources of funds and their uses in the short run, opportunities for deployment of surplus funds in short term securities, etc. may be required at the middle levels of management. The tactical information is generally predictive, focusing on short term trends. It may be partly current and partly historical, and may come from internal as well as external sources. Strategic: While the operational information is needed to find out how the given activity can be performed better, strategic information is needed for making choices among the business options. The strategic information helps in identifying and evaluating these options so that a manager makes informed choices which are different from the competitors and the limitations of what the rivals are doing or planning to do. Such choices are made by leaders only. Strategic information is used by managers to define goals and priorities, initiate new programs and develop policies for acquisition and use of corporate resources. For example, information regarding the long-term needs of funds for ongoing and future projects of the company may be used by top level managers in taking decision regarding going public or approaching financial institutions for term loan. Strategic information is predictive in nature, relies heavily on external sources of data, has a long term perspective, and is mostly in summary form. It may be remembered that each type of information has its role to play in managerial effectiveness. Each type of information is needed with varying degree by the managers at all levels. Thus, a part of operational information may be used even by the chief executive officer of a company. Relevance of Information in Decision Making Managerial decision making is a process of making choices. If a choice is to be made among alternatives, there must be differences among the alternatives. Relevant information should be used by the decision maker in evaluating the alternatives and in making decisions. Relevant information has two characteristics: 1. Impact on the Future: Relevant information has bearing on the future. Relevant information focuses on the future because every decision deals with selecting courses of action for the future. Nothing can be done to alter the past. The consequences of decisions are born in the future, not the past. Information to be relevant (i.e. relevant costs and benefits) to a decision should imply a future event. Since relevant information involves future events, the managerial accountant must predict the amounts of the relevant costs and benefits. In making these predictions, the accountant often will use estimates of cost behavior based on historical data. There is an important and subtle issue here. Relevant information must involve costs and benefits to be realized in the future. However, the accountant’s predictions of those costs and benefits often are based on data from the past. 2. Different under Different Alternatives: Relevant information includes costs and benefits that differ among the alternatives. Expected future revenues and costs that do not differ or remain the same across alternatives have no impact on the decision and therefore irrelevant and should be eliminated from the relevant information analysis. Further, in relevant information, due weight-age must be given to qualitative factors and quantitative non financial factors. According to Hilton, information to be useful for decision making should possess three characteristics: 1. Relevance 2. Accuracy 3. Timeliness




