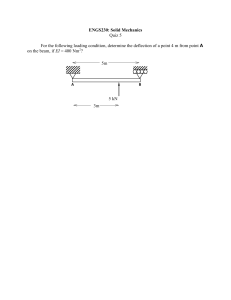
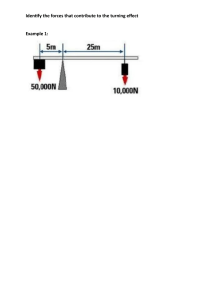
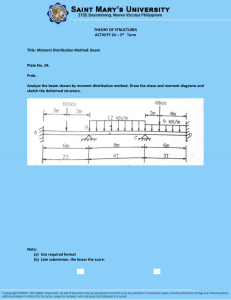
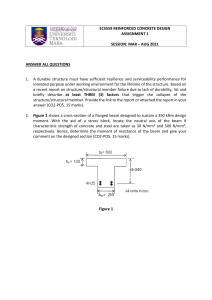
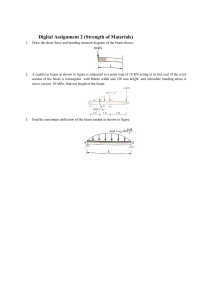
University of Engineering & Technology Taxila Department of Industrial Engineering Lab Session # 01 Course Title: Mechanics of Materials Lab Instructor: Mr.Waqar Ahmed Semester: 4th Session: 2K22 Total Marks: Obtained Marks: Name of Student: Roll No: Evaluation Sheet Knowledge components Domain Student has conducted the experiment by practicing the hands on skills and following standard procedures. Student has achieved required accuracy in performance and Calculations. Student is aware of safety rules Student used the safety equipment during experiment. Student has followed all the timelines provided during the lab session Student is aware of the basic concepts Student has analyzed and compared the results. Taxonomy level Contribution Affective Obtained marks 10 Manipulate (P2) Psychomotor Max. marks 70% Precision (P3) 5 Receiving (A1) 3 Respond (A2) 20% 3 2 Valuing (A3) Knowledge (C1) Cognitive 10% 2 Total 25 Normalize marks out of (5) 5 Evaluate (C4) Lab Instructor’s Signatures: _________________________________ Safety Instructions for the Experiment Work deliberately and handle the weights carefully. Do not wear open toed shoes. Remove the weights after taking readings. Objective Determination and comparison of deflection of a simply supported beam under the action of concentrated loads applied at the center of the beam. Apparatus 1. Beam Deflection Apparatus 5. Weight Pan 2. Beam 6. Slotted Weights 3. Vernier Calipers 7. Level Gauge 4. Dial Gauge 8. Geometry Box Theory A beam is a structural element that primarily resists loads applied laterally to the beam's axis. Its mode of deflection is primarily by bending. The loads applied to the beam result in reaction forces at the beam's support points. The total effect of all the forces acting on the beam is to produce shear forces and bending moments within the beam, that in turn induce internal stresses, strains and deflections of the beam. Beams are characterized by their manner of support, profile (shape of cross-section), length, and their material. Construction Beam deflection apparatus consists of a measuring scale and supports mounted on L shaped brackets. On the supports, beam is placed and a dial gauge is mounted on the upper bar of the apparatus shown Procedure 1. Take the rectangular cross section of the beam using Vernier calipers 2. Measure the length of the beam 3. Place the beam on the knife edge supports in such a way that midpoint of beam is in the middle of the supports 4. Attach a weight pan at the midpoint of the beam and fix the dial gauge over the weight pan 5. Set the reading of the dial gauge to zero and note down the least count of the dial gauge 6. Apply the weight on the beam and note the deflection of the beam by taking reading of the dial gauge 7. Take four readings and calculate theoretical deflections by using formula of deflection of the beam 8. Compare experimental and theoretical values of the deflection and draw graph. Precautions 1. Do not take readings unless the weights are in rest position. 2. Avoid dropping the weights while performing the experiment. 3. Do not apply the loads for longer period of time. 4. Level the apparatus before the start of experiment. 5. Note the zero error of the dial gauge. Results Observations Length of the beam Width of the beam Height of the beam Young’s Modulus Sr. No. Weight (N) 1 2 3 4 Sample Calculations Deflection Moment of Inertia Deflection Percentage (exp.) (mm) of the beam (mm4) (th.) (mm) Error Graphical Results Conclusion Comments State the mass moment of inertia and define the area moment of inertia of the beam Differentiate among different types of beams based on the supports and explain the reactions provided by each type of support. State the safety measures you have taken while performing the experiment? Write down the time taken for each task Activity Time Taken Understanding Performance Analysis