Learning Theories: Constructivism, Behaviorism, Cognitivism
advertisement

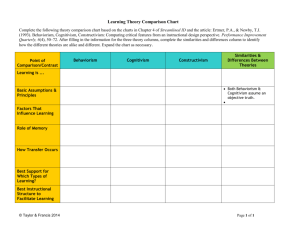
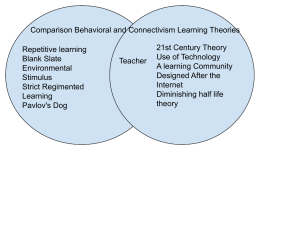
Constructivism learning theory is based on the idea that students actually create their own learning based on their previous experiences. is a student-centered learning theory that is based on cumulatively building understandings from students' prior experiences and knowledge Behaviorism defines learning as observable behavioral change that occurs in response to environmental stimuli. First on our education theories list is behaviorism. Behaviorism in education definition is a pedagogical theory that defines learning as a process of knowledge acquisition that takes place through observation (i.e., based on objectively quantifiable events rather than introspective psychology). Cognitivism Cognitivism, as suggested by the name, is one of the educational theories and the learning theory that focus on cognitive processes of the mind such as thinking, memory, recall, and problem-solving. Similar to behaviorism, cognitivism is about learning via association; however, the emphasis is placed on internal processing rather than the external environment. Humanism Humanism approaches learning and education with a growth mindset. Similar to constructivism, humanism is a school of educational thought that is inherently studentcentered. Humanistic education derives many of its values from the intellectual movement of the seventeenth century, where philosophes such as Voltaire (1642-1778) believed that humans were born with innate potential. Humanistic education, therefore, focuses on fostering individual potential and personal growth. Humanism tends to be even more individual-focused than constructivism, with an emphasis placed on choice and autonomy. Educators adopting a humanist approach aim to foster self-directed learning among students, in the belief intrinsic motivation to learn comes from this. In order to support self-directed learning, teaching students how to learn becomes a key priority. Along the same lines, humanist educators believe that learners should be given opportunities to evaluate their own learning, whether that be through formalized self-assessment or descriptive, reflective journaling. Connectivism Connectivism is inherently a future-focused learning theory and education of theory. It is a relatively recent pedagogical view that takes into account the changing nature of knowledge acquisition in our digital age. In contrast to constructivism, which revolves around what a learner already knows, connectivism pinpoints what a learner needs to know, and targets the learning at a relevant time of need. While connectivists generally believe that expanding knowledge is ultimately more important than taking into account prior knowledge, connectivism allows learners to situate new knowledge within existing schemas of understanding. Similar to humanism, connectivism empowers students to make their own learning decisions. Students are aided in this learning process by technology, which assists in threading together different strands of knowledge. Experientialism also shapes theories of organizational learning, including workplace design and professional training. Such programming