File
advertisement

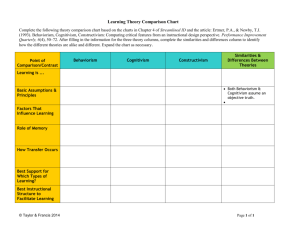
Theory Project: Reflection Theories of learning are vital to the understanding of what method of teaching can be the most effective for your students. Incorporating multiple aspects of different theories can help create a diverse classroom and immerse the teacher and his/her students into a higher level of learning. This project consisted of a solid overview of three different learning theories: constructivism, behaviorism, and humanism. Each theory has its own relationship into how we learn and a different perspective on this complex subject. Constructivism is based on experiential learning through real life experiences to construct knowledge (Liepolt, 2004). It states that people construct their own understanding and knowledge of the world through experiencing things and reflecting on those experiences. When we encounter something new, we have to reconcile it with our previous ideas and experience. This can cause us to possibly change what we believe or discard the new information as irrelevant. In any case, this theory states that we are active creators of our own knowledge. In the classroom, the constructivist view of learning can point towards a number of different teaching practices. In most cases, it usually means encouraging students to use active techniques, such as experimentation and real-world problem solving, to create more knowledge and then reflect on and discuss what they are doing and how their understanding is changing. The teacher makes sure he/she understands the students' prior knowledge and guides the activity to address this understanding and build onto it. Behaviorism is a worldview that assumes a learner is essentially passive, responding to environmental stimuli. The learner begins as a clean slate and behavior is shaped through positive or negative reinforcement. Both types of reinforcement will increase the probability that the given behavior will occur again. In contrast, punishment (both negative and positive) decreases the likelihood that the behavior will occur again (Graham, 2000). The differences between positive and negative refer to how the stimulus is applied. Positive occurs when the stimulus is applied while negative is when the stimulus is withheld from the subject. Learning is therefor defined as a change in behavior in the learner. Despite varying views on behaviorism's effectiveness in learning, it continues to be used to teach and motivate in the classroom. Learning is more meaningful and effective when the students are active. To be able to motivate students, reinforcing effort is needed. Much of their successes are dependent upon their efforts. Students should be taught the importance of effort and how to monitor their own efforts. A good example of this is the use of technology to compare student efforts and outcomes on class assignments and exams. In reinforcing effort, students are able to see a correlation with effort and achievement. Another example of behaviorism in the classroom today is homework and practice. Frequent practice of information is necessary for learning to occur. Homework offers students the opportunity to accomplish this practice and apply what they have learned. If applied appropriately, homework can be beneficial in reinforcing learning. Humanism emphasizes the value of human beings, individually and collectively. This approach emphasizes an individual's drive towards self-actualization and creativity. The fundamental belief of humanism is that people are innately good and that mental and social problems result from deviations from this natural tendency (Association of Humanistic Psychology, 2013). It encourages viewing ourselves as a whole person rather than the sum of our parts and encourages self-exploration rather than the study of behavior of other people. The humanistic classroom provides a holistic approach to learning by keeping the focus on the child. The student is respected as an individual and is responsible for making decision about his learning. Humanistic lessons are not set in stone by the teacher. Instead, lessons flow according to the needs and inquiries of the student. This open approach helps provide emotional support for the student. A good example of this style of learning is student-centered learning. This happens when the teacher becomes a facilitator while the students take on the role of developing the lesson. The student is then able to showcase his creativity in this type of open classroom, which increases self-esteem and a willingness to learn. I believe the cognitive scientist I relate to the most would be Abraham Maslow. Maslow was the “father of humanistic psychology” and had multiple theories in the realm of humanism, including his hierarchy of needs and self-actualization. According to Maslow, our actions are motivated in order to achieve certain needs. Maslow's hierarchy suggests that people are motivated to fulfill basic needs before moving on to other, more advanced needs. This led the way for understanding how life outside of the classroom can influence the behavior and learning of a student. His belief that every person has a strong desire to realize his or her full potential, or to reach a level of self-actualization, is an idea that I hold very dear. I have an optimistic point of view and tend to see the good in people. Also, his pursuit on the grounds of how people learn has laid a foundation for the student-centered classroom which should be implemented far more than it currently is in secondary schools. I plan to incorporate multiple ideas from each of the theories into my classroom. One way of thinking is not appropriate to take without involving other ideals from other theories. Our brains are far too complex for such a linear way of thinking. I will invoke ways for students to keep track of their learning and analyze how they are accomplishing tasks. I will also incorporate days where students will lead the class in a student-centered environment. As I will be teaching physics in high school, a student-centered environment is necessary for bringing out the inner physicist in my students. Another necessity for a physics classroom is experimentation and problem-solving, which will be used nearly every day in my classroom. My view on today's classroom has drastically changed after researching these theories of learning. The best way to provide the best for your students is to understand and take advantage of techniques such as the ones listed in these theories. With our current understanding of how the brain works, teachers should implement multiple different strategies to create the most diverse learning environment possible. These theories should also be used to invoke metacognition in the students. After the realization that their learning can be manipulated, students will begin to push forward and become better prepared for their future. Works Cited Liepolt, Werner. "Constructivism as a Paradigm for Teaching and Learning." Constructivism as a Paradigm for Teaching and Learning. Thirteen | Ed Online, 2004. Web. 12 Mar. 2014. Graham, George. "Behaviorism." Stanford University. Stanford University, 26 May 2000. Web. 13 Mar. 2014. "Association of Humanistic Psychology." Association of Humanistic Psychology. N.p., 2013. Web. 13 Mar. 2014.