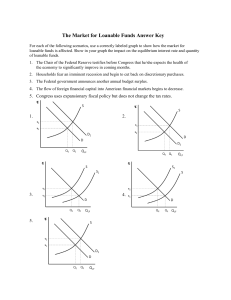
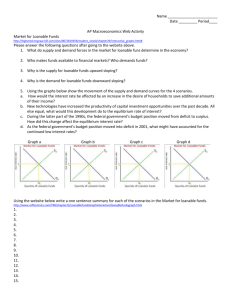
ECONOMICS 1022b-002/004 Department of Economics Western University Jeannie Shearer Marks: 50 Time: 2 hours MIDTERM 1, Version 111 February 9, 2019 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. The examination begins at 4:00 p.m. and ends at 6:00 p.m. You will not be given additional time after 6 p.m. to complete the scantron. 2. Check that your examination paper contains 13 pages including the cover page. Check that your scantron version matches the exam version, which is 111. 3. Please complete the following on your Scantron: Print your NAME and complete your SIGNATURE. Use the name that matches your Western University registration. Enter your STUDENT NUMBER. Complete your SECTION NUMBER. Section 002 meets at 9:30 a.m. Section 004 meets at 1:30 a.m. 4. For every question, fill in your chosen answer on your Scantron. 5. Please hand in your scrap paper AND your Scantron. Please take your exam paper when you leave the exam room. You may use a non-programmable calculator. Your cell phone may not be used as a calculator. Your cell phone must be switched off and left in your bag at the front of the exam room. 6. On your desk you may have pens, pencils, rulers, erasers, and a drink. Place your student card on the right corner of your desk. All other items must be left at the front of the exam room. M U L T IPLE C H O I C E. C hoose the one alternati ve that best completes the statement or answers the q uestion. Use the information below to answer the following questions. Fact 1 T he components and robots for Toyota auto assembly lines in Canada are built in Japan. Toyota assembles cars for the Canadian market in O ntario. 1) Refer to Fact 1. C hoose the statement that is incorrect. A) If any parts for the cars come from Japan, they are recorded as a negative entry in calculating Japan's G DP. B) Expenditure on the cars is part of consum ption expenditure in calculating Canada's G DP. C) If any parts for the cars come from Japan, they are Canadian imports. D) Expenditure made by Toyota on building the assembly plant in O ntario is recorded as investment. E) T he assembly line components and robots appear as exports in Japan's G DP. Use the information below to answer the following questions. Fact 2 Classify each of the follow ing items as a final good or an intermediate good, and identify w hich is a component of consumption expenditure, investment, or government expenditure on goods and services: Item 1. A D V D bought by a household Item 2. A new airplane bought by W estJet 2) Refer to Fact 2. Item 1 is ________ and item 2 is ________. A) a final good that is consum ption expenditure; a final good that is consu mption expenditure B) a final good that is consu mption expenditure; a final good that is investment C) an intermediate good; a final good that is investment D) an intermediate good; a final good that is consumption expenditure E) an intermediate good; an intermediate good 3) W hich of the follow ing are equal to one another? I. aggregate production II. aggregate expenditure III. aggregate income A) II equals III, but II does not equal I. B) III equals II, but III does not equal I C) I equals II, but I does not equal III. D) I equals II equals III. E) I equals III, but I does not equal II. 4) Stock and bond sales are not included in G DP because they A) are not goods an d services. B) are not sold in the country in w hich they are produced. C) represent corporate production. D) can be sold online. E) have volatile prices. 2 5) W hich of the follow ing is not correct? A) G ross investment is the amount by w hich the value of capital increases. B) D epreciation decreases the value of a firm's capital. C) Investment is the purchase of new plant, equipment, and buildings and the additions to inventories. D) N et investment equals gross investment minus depreciation. E) G ross investment is the total amount spent buying new capital an d replacing depreciated capital. Use the table below to answer the following questions. T ab le 1 Data From Eastland Item W ages, salaries, and supplementary labour income Other factor incomes Government expenditures on goods and services D epreciation Investment Personal income taxes net of transfer pay ments Indirect taxes N et exports Consumption expenditure 6) Refer to Table 1. Gross domestic product equals A) $1,350. B) $2,910. C) $1,290. D ollars 800 250 250 240 400 140 120 100 600 D) $1,150. E) $1,360. Use the table below to answer the following questions. T ab le 2 Item Other factor incomes Indirect taxes D epreciation W ages, salaries and sup plementary labour income Consumption expenditure Government expenditure on goods and services G overnment transfer payments N et exports Subsidies Statistical D iscrepancy D ollars $570 230 250 1,200 1,100 500 50 40 0 0 7) Refer to Table 2. N et domestic income at market prices is equal to A) $2,400. B) $2,000. C) $2,250. D) $1,940. E) $2,150. 8) Refer to Table 2. N et investment is equal to A) $250. B) $210. D) $860. E) $360. C) $510. 3 Use the table below to answer the following question. T ab le 3 In 2017 Item Bananas Coconuts Q uantity (bunches) 900 400 Price $3 a bunch $8 a bunch In 2018 Item Bananas Coconuts Q uantity (bunches) 600 500 Price $2 a bunch $10 a bunch 9) Refer to Table 3. The base year is 2017 and the table gives the quantities produced and the prices in 2017 and 2018. Real G D P in 2018 using the base - year method is A) $6,000. B) $6,200. C) $5,900. D) $5,800. E) $6,100. 10) W hich of the follow ing is not a reason for G DP incorrectly measuring the value of total output? A) en vironmental quality B) household prod uction C) underground economic activity D) leisure time E) depreciation 11) In comparing the U nited States and C hina we find that A) real G DP per person is approximately the same in the two countries. B) the standard of living is higher in C hina than in the U nited States. C) China's real G DP per person is less than real G DP per person in the U nited States. D) U.S. real G DP per person is much larger than C hina's real G DP per person w hen purchasing power parity prices are used but is less than C hina's real G DP per person w hen C hina's prices are converted using the market exchange rate. E) U.S. real G DP per person is less than C hina's real G DP per person once we adjust for currency differences. 12) W hy is the H uman D evelop ment Index thought to be a better measure of economic w ell - being than real G DP per person? A) The H DI ignores health, w hich is hard to measure. B) T he H D I includes only health and education measures, ignoring real G DP per person. C) The H D I includes a measure of resource depletion. D) T he H DI includes health and education measures, as w ell as real G DP per person. E) T he H DI includes leisure time and household production. 13) A ll of the follow ing statements are true except A) real G D P per person was $54,000 per year lower in 2016 than it would have been w ith no growth slow dow n. B) the Lucas wedge equals real G DP minus potential G DP. C) the Lucas wedge arises from the slow dow n of productivity growth that began d uring the 1970s. D) the Lucas wedge is the dollar value of the accumulated gap between w hat real G DP per person would have been if the 1960s grow th rate had persisted and w hat real G DP per person turned out to be. E) the Lucas wedge accu mulated to $790,000 per person by 2016. 4 Use the table below to answer the following question. T ab le 4 I n 2017 I tem Q uantity 2 9 4 Price $1 each $1 each $1 each I tem Q uantity 8 4 9 Price $7 each $6 each $5 each Pencils Pens Pizza I n 2018 Pencils Pens Pizza 14) Refer to Table 4. A n economy produces only pencils, pens, and pizza. T he table gives the quantities produced and prices in 2017 and 2018. The base year is 2017. The chained - dollar real G D P in 2018 is A) $13. B) $88. C) $21. D) $19. E) $125. 15) If the people who take early retirement are not counted in the working - age pop ulation, then A) the labour force participation rate would be higher. B) the labour force participation rate w ould be less. C) the unemployment rate would be higher. D) the unemployment rate would be lower. E) the number of discouraged searchers would decrease. 16) W hich of the follow ing statements is incorrect? A) T he unemployment rate is the number of persons w ho are unemployed divided by the labour force, all multiplied by 100. B) T he involu ntary part - time rate is the number of involuntary part - time workers divided by the number employed, all multiplied by 100. C) T he employment rate is the number of people employed divided by the working - age population, all multiplied by 100. D) T he labour force is equal to the number of people employed plus the number of people unemployed. E) T he labour - force participation rate is the labour force divided by the w orking - age population, all multiplied by 100. 17) R2 is A) long - term unemployment. B) the official unemployment rate. C) com parable to the official U.S. rate. D) short - term unemployment. E) the unemployment rate that adds discouraged searchers to the official rate. 5 18) If the number of discouraged searchers increases, everything else remaining the same, then the A) unemployment rate increases. B) employment rate increases. C) employment rate decreases. D) labour force participation rate decreases. E) labour force participation rate increases. 19) In a country w ith a w orking - age population of 30 m illion, 18 million are employed, 2 million are unem ployed, an d 2 million of the em ployed are w orking part - time, half of w hom w ish to work full - time. If 1 million of the unemployed are cyclically unem ployed, w hat is the natural unem ploy ment rate? A) 11.1 percent B) 1 percent C) 5.6 percent D) 6.7 percent E) 5 percent 20) W hich one of the follow ing people is frictionally unemployed? A steel worker w ho A) decides to leave the labour force and become a full - time student. B) becomes discouraged and stops looking for a job. C) loses her job because of technological change. D) is laid off but expects to be called back soon. E) gives up her job because she retires. 21) The natural unemploy ment rate is A) equal to 0 percent. B) the rate at w hich cyclical unemployment is equal to 0 percent. C) the rate at w hich all unem ployment is structural. D) the rate at w hich cyclical unemployment is equal to 6 percent. E) the same as the cyclical unemployment rate. 22) If the unemployment rate is 4.5 percent and the natural unemployment rate is 5.5 percent, then A) potential G DP equals real G DP. B) potential G DP is greater than real G DP. C) w e have mismeasured the natural unemployment rate. D) real G DP is greater than nominal G DP. E) potential G DP is less than real G DP. 23) Some unem ploy ment is una voidable because A) often people become discouraged searchers. B) people are making transitions through the stages of life and businesses are making transitions. C) there is al w ays some cyclical unemployment. D) many part - time workers w ould like to have full - time work. E) many peop le in the working - age population attend school an d are unemployed. 24) T he consumer price index is a measure of A) the consumer prices paid by average households for a fixed basket of goods and serv ices. B) the average of the prices paid by urban consumers for a fixed basket of consumer goods and serv ices. C) the average of the prices paid by all consumers for a fixed basket of consumer goods an d services. D) the lowest prices paid by urban consumers for a fixed basket of consumer goods and services. E) the lowest prices paid by all consumers for a fixed basket of consumer goods and services. 6 Use the table below to answer the following questions. T ab le 5 Suppose a simple economy produces three goods only. The price and output data for two years are show n below. Pop Crackers C ucumbers Price (dollars) 2002 0.75 1.25 2.00 Price (dollars) 2017 1.10 2.10 3.00 Q uantity (number) 2002 100 300 200 25) Refer to Table 5. The reference base period is 2017. The CPI in 2002 is A) 157. B) 152. C) 100. D) 63. Q uantity (number) 2017 120 280 190 E) 129. 26) Suppose a union and a firm agree to increase the wage rate by the same percentage as the increase in the Consumer Price Index. If the CPI increases by 5 percent, then the real income of w orkers w ill A) decrease by 5 percent, accounting for bias in the calculation of the CPI. B) increase by more than 5 percent, accounting for bias in the calculation of the CPI. C) increase by less than 5 percent, accounting for bias in the calculation of the CPI. D) increase by 5 percent. E) remain unchanged, accounting for bias in the calculation of the CPI. 27) Bet ween 1984 and 2017, C anada's inflation rate as measured by the C PI A) consistently fell every year. B) w as al ways positive. C) rose in some years and fell in some years. D) w as al ways bet ween 1 and 3 percent a year. E) consistently rose every year. 28) Suppose that the price level in C hina was 100 in 2007, 110 in 2008, 120 in 2009, and 130 in 2011. O ver this time period, A) zero inflation occurred. B) the inflation rate increased. C) the inflation rate was positive. D) the inflation rate decreased. E) Both C and D are correct. 29) O ne of the U nited K ingdom's borders is causing difficulty in the Brexit discussions. W hat is that border? A) England - Scotland B) Ireland - N orthern Ireland C) Scotland - N orthern Ireland D) England - W ales E) England - Scotland 7 30) The most recent interest rate announcement from the Bank of Canada was on January 9th. W hat was the decision? The interest rate A) fell to 1.5%. B) rose to 2.0%. C) rose to 2.5%. D) remained at 1.75%. E) fell to 1.25%. 31) H ow long was the most recent U.S. government shutdow n? A) 21 days B) 28 days C) 35 days D) 42 days E) 49 days 32) C hoose the statement that is incorrect . A) Real G DP per person grows only if real G D P grows faster than the population grows. B) Real G DP increases w hen the economy returns to full employment in an expansion phase of the business cycle. C) T he growth rate of real G DP per person can be calculated approximately by subtracting the population growth rate from the real G DP growth rate. D) The standard of living depends on real G DP per person. E) T he return to full employment in an expansion p hase of the business cycle is economic growth. 33) D uring the last 10 years, w hich of the follow ing had the lowest level of real G DP per person? A) Russia B) M exico C) C hina D) Japan 34) Bet ween 1926 and 2016 real G D P per person in C anada grew at an average rate of A) 3.6 percent a year. B) 2.8 percent a year. C) 2.0 percent a year. D) 4.3 percent a year. E) 1.7 percent a year. 35) A n increase in labour hours w ill lead to A) neither a movement along nor a shift of the aggregate production function. B) a dow n ward shift of the aggregate production function. C) a movement along the aggregate production function. D) an up w ard shift of the aggregate production function. E) both a movement along and an up ward shift of the aggregate production function. 36) If the money wage rate is $15.00 an hour and the price level is 120, the real w age rate is A) $10.75 an hour. B) $8.50 an hour. C) $18 an hour. D) $15.00 an hour. E) $12.50 an hour. 8 E) N igeria Use the table below to answer the following questions. T ab le 6 Real w age rate (2007 dollars per hour) 15 20 25 30 35 Q uantity of labour demanded (billions of hours per year) 70 60 50 40 30 Real G DP (trillions of 2007 dollars per year) 3 9 14 18 21 Q uantity of labour supplied (billions of hours per year) 10 20 30 40 50 Q uantity of labour (billions of hours per year) 20 30 40 50 60 37) Refer to Table 6. The top table describes an economy's labour market. The second table describes its production function. A n increase in population changes the quantity of labour supplied by 20 billion hours at each real w age rate. Potential G DP A) does not change. B) changes to $20 trillion. C) changes to $18 trillion. D) changes to $50 trillion. E) changes to $3 trillion. 38) W hen labour productivity increases, the demand for labour curve ________ and the supply of labour curve ________. A) shifts rightward; does not shift B) shifts rightward; shifts rightward C) shifts leftward; does not shift D) shifts rightward; shifts leftward E) shifts leftward; shifts rightward 39) W hen labour productivity d ecreases, there is ________ the aggregate production function an d ________ in potential G DP. A) a movement dow n along; no change B) a dow n ward shift of; a decrease C) a dow nward shift of; no change D) a movement dow n along; a decrease E) neither a movement along nor a shift of; no change 9 40) W hich of the follow ing does not contribute to achieving faster gro wth? A) increased research and development B) improvement in the quality of education C) increased saving D) provision of international aid to developing nations that is not diverted to consumption E) slow ing dow n international trade so that more countries become self - sufficient 41) W hen the inflation rate is zero, the A) demand for loanable funds increases. B) nominal interest rate is zero. C) real interest rate equals the nominal interest rate. D) sup ply of loanable funds decreases. E) real interest rate is negative. 42) Southton has investment of $100, private saving of $90, net taxes of $25, government expenditure of $30, exports of $25 and imports of $10. W hat is national saving? A) $100 B) $95 C) $105 D) $85 E) $90 43) Suppose that you took out a $1,000 loan in January and were required to pay $75 in annual interest. D uring the year, inflation was 6 percent. W hich of the follow ing statements is correct? A) T he real interest rate is 7.5 percent and the nominal interest rate is 1.5 percent. B) The nominal interest rate is 7.5 percent and the real interest rate is 13.5 percent. C) The real interest rate is 6 percent and the nominal interest rate is - 1.5 percent. D) T he nominal interest rate is 7.5 percent an d the real interest rate is 1.5 percent. E) T he real interest rate is 6 percent and the nominal interest rate is 7.5 percent. 10 Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions. F igure 1 44) In Figure 1, the initial sup ply of loanable funds curve is SLF 0 and the initial demand for loanable funds curve is DLF 0 . A n increase in the expected profit A) shifts the demand for loanable funds curve rightw ard to curve DLF 1 and does not shift the supply of loanable funds curve. B) increases the inflation rate. C) shifts the supply of loanable funds curve rightw ard to curve SLF 1 , and shifts the demand for loanable funds curve rightw ard to curve DLF 1 . D) shifts the supply of loanable funds curve rightw ard to curve SLF 1 and does not shift the demand for loanable funds curve. E) has no effect on either the demand for loanable funds curve or the supply of loanable funds curve. 11 Refer to the figure below to answer the following questions. Figure 2 45) Figure 2 sho ws the situation w here the government has a budget ________. Private saving is ________. A) deficit; $20 billion B) surplus; $15 billion C) surplus; $25 billion D) surplus; $20 billion E) deficit; $15 billion Use the table below to answer the following questions. T ab le 7 The table shows an economy's demand for loanable funds schedule and supply of loanable funds sched ule w hen the government's budget is balanced. Real interest rate (percent per year) 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Loanable funds demanded (trillions of 2007 dollars) 8.0 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 Loanable funds supplied (trillions of 2007 dollars) 8.0 8.5 9.0 9.5 10.0 10.5 11.0 46) Consider Table 7. If the govern ment's budget becomes a deficit of $1.0 trillion, w hat is the quantity of investment? A) $7.0 trillion B) $6.5 trillion C) $8.0 trillion D) $8.5 trillion E) $7.5 trillion 12 47) Consider Table 7. If the government's budget becomes a deficit of $1.0 trillion, w hat is the quantity of private saving? A) $7.0 trillion B) $7.5 trillion C) $8.5 trillion D) $8.0 trillion E) $6.5 trillion Use the table below to answer the following questions. T ab le 8 The table shows an economy's demand for loanable funds schedule and supply of loanable funds sched ule w hen the government's budget is balanced. Real interest rate (percent per year) 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Loanable funds demanded (trillions of 2007 dollars) 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 Loanable funds supplied (trillions of 2007 dollars) 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 5.5 6.0 6.5 48) Consider Table 8. If the Ricardo - Barro effect occurs, and if the government's budget becomes a deficit of $2.0 trillion, w hat is the quantity of investment? A) $10 trillion B) $6.5 trillion C) $6.0 trillion D) $5.0 trillion E) $5.5 trillion 49) A government bu dget surplus occurs, w hich ________ loanable funds. The real interest rate ________, household saving ________, and investment ________. A) increases the supply of; falls; decreases; increases B) increases the demand for; rises; increases; decreases C) decreases the demand for; falls; decreases; increases D) decreases the supply of; decreases; decreases; increases E) increases the supply of; falls; increases; decreases 50) The crow ding - out effect refers to A) government spending crow ding out private spending. B) private saving crow ding out government saving. C) private investment crow ding out government saving. D) private saving crow ding out net taxes. E) a government deficit crow ding out investment. 13 Answer Key Testname: SHEARER MIDTERM 1 FINAL 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 11) 12) 13) 14) 15) 16) 17) 18) 19) 20) 21) 22) 23) 24) 25) 26) 27) 28) 29) 30) 31) 32) 33) 34) 35) 36) 37) 38) 39) 40) 41) 42) 43) 44) 45) 46) 47) 48) 49) 50) A B D A A A B E D E C D B C A B D D E D B E B B D B C E B D C E E C C E C A B E C D D A B E C D A E 14