Histology of Oral Cavity and Esophagus Presentation
advertisement

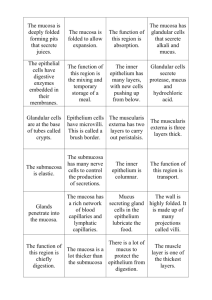
HISTOLOGY OF ORAL CAVITY AND ESOPHAGUS Structures in oral cavity ❑ ❑ ❑ ❑ ❑ Lip Tongue Palate salivary glands Tooth Esophagus ORAL CAVITY 1. Vestibule or buccal cavity: bounded by lips and cheeks on the outside and the teeth and gums inside 2. Oral cavity proper: extends from behind the teeth and gums to the throat three types of mucosa a-lining mucosa: stratified squamous epithelium.submucosa present only in certain regions b-masticatory mucosa of gingiva and hard palate c- specialized mucosa : dorsal surface of the tongue LIP The lips consist of three regions 1. Cutaneous region, covered by thin skin-keratinized str. Squam.epith.with hair follicles , sebaceous and sweat glands 2. The red region, str.squam.epith. Supported by tall papilla containing blood vessels-red color 3. The oral mucosa region is continous with the mucosa of the cheeks and gums, cutaneous The three regions of lip Keratinized str squam epith. Hhair follicle cutaneous region lip oral mucosa Red region tall papilla Tonsils Consists of lymphatic nodules that are clustered around the posterior opening of the oral and nasal cavities Tonsillar (Waldeyer’s ) ring Palatine Tubal tonsils posterior to the opening of the auditory tube Pharyngeal tonsils (adenoid) roof of nasopharynx Lingual tonsils base of the tongue The dorsal surface is divided into an anterior two thirds and a posterior one third by a V shaped depression-sulcus terminalis Apex of V is the location foramen cecum Filiform papilla Fungiform papilla Circumvallate papilla Foliate papilla P.Circumvallate bitter taste P.Fungiform (Anterior tip) Sweet taste P.Fungiform (behind tip and lateral) Salty taste P.Filiformis SALIVARY GLANDS Parotis pure serous Submandıbular gland Sublingual gland mıxed mıxed Connective tissue septa divides the glands into lobules Acini form the secretory units Myoepithelial cells surround the acinar cells SECRETORY PORTIONS OF SALIVARY GLANDS SEROUS CELL Protein and polysaccharide secretion Single, round, basally located nucleus Well-developed GER and Golgi complex basal mitochondria Abundant secretory granules rich in ptyalin basal infoldings interdigitating with those of neighbouring cells MUCOUS CELL Pyramidal in shape Flattened nucleus Fewer mitochondria Less extensive GER and greater Golgi complex Submandibular gland . Sublingual gland Duct system Intercalated ducts (low columnar or cuboidal) Striated ducts Tall columnar epithelium) Interlobular ducts (pseudostratified epith.) Main duct of the gland (Ciliated epithelium) Excretory Ducts Small ducts: simple cuboidal epithelium Larger diameter: stratified cuboidal or pseudostratified columnar epithelium As the duct approaches the oral epithelium, stratified squamous epithelium may be found PALATE palate Esophagus trachea and esophagus This is a normal esophagus with the usual white to tan smooth mucosa seen at the left. The gastroesophageal junction (not an anatomic sphincter) is at the center, and the stomach is at the right. The upper GI endoscopic view of the transition from tan squamous mucosa to pink columnar mucosa is seen below. esophagus In the esophageal mucosa - Esophageal epithelium is non-keratinized stratified squamous. Esophageal lamina propria is less cellular (fewer lymphocytes) than that in the stomach and intestine, presumably because the protective stratified squamous epithelium is more effective at keeping out foreign antigens. ◼Muscularis externa of the esophagus consists of the standard inner circular and outer longitudinal layers of smooth muscle, with Auerbach's plexus in between. Esophageal muscularis mucosae is noticably thicker than that in the stomach and intestine, and includes only longitudinal muscle fibers. Connective tissue of the submucosa is typically more fibrous and less cellular than that the lamina propria of the mucosa. Esophageal submucosa includes scattered esophageal and a venous plexus). 1 - tunica mucosa 2 - tunica submucosa 3 - tunica muscularis propria 5 - epithelium of the mucosa 6 - lamina propria of the mucosa 9 - glands in the submucosa Tooth Gingiva and mature tooth fetal rat (early) (developing tooth) (H&E) BUD STAGE EARLY BELL STAGE CAP STAGE LATE BELL STAGE Enamel is the hardest component of the human body, consisting of %96 calcium hydroxyapatite and 2-3 % organic material including very few proteins and no collagen Dentin is a calcified tissue harder than bone consisting %70 hydroxyapatite. Organic matrix contains type I collagen and proteoglycans secreted from the apical ends of odontoblasts. The periodontal ligament, commonly abbreviated as the PDL, is a group of specialized connective tissue fibers that essentially attach a tooth to the alveolar bone within which it sits. It inserts into root cementum one side and onto alveolar bone on the other. Periodontal ligament mature tooth, Sharpey's fibers