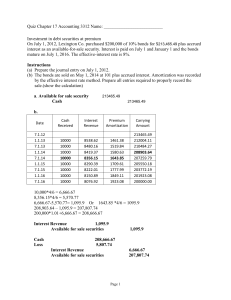
Lecture 2 Presented by Amir Khan Case Study: McDonald’s Dim Sum Bonds: “Lovin’ It” Case Study: McDonald’s Dim Sum Bonds: “Lovin’ It” Case Study: McDonald’s Dim Sum Bonds: “Lovin’ It” Case Study: McDonald’s Dim Sum Bonds: “Lovin’ It” Case Study: McDonald’s Dim Sum Bonds: “Lovin’ It” Case Study: McDonald’s Dim Sum Bonds: “Lovin’ It” Case Study: McDonald’s Dim Sum Bonds: “Lovin’ It” Case Study: McDonald’s Dim Sum Bonds: “Lovin’ It” Case Study: McDonald’s Dim Sum Bonds: “Lovin’ It” Case Study: McDonald’s Dim Sum Bonds: “Lovin’ It” Global Fixed-Income Market Global fixed-income markets represent the largest subset of financial markets in terms of number of issuances and market capitalization Global fixed-income markets can be classified by: Type of Issuer Bond Maturity, Credit Quality, Geography, Currency Denomination and Type of Coupon Bond Issue and Trading Location Sovereign Bonds Sovereign bonds are the bonds issued by national governments. Bond names vary depending on the country of issue and the bond’s maturity. Sovereign bonds are usually unsecured obligations of the sovereign issuer. That is, they are not backed by collateral but by the taxing authority of the national government. The majority of the trading in secondary markets is of sovereign securities that were most recently issued. These securities are called “on the run.” Sovereign Bonds Classification Local currency sovereign bonds have low(er) credit risk because of the taxing and money-issuing power of the government. Foreign currency sovereign bonds’ credit risk depends on the strength of the national economy and government finances. Ways of Investing in Fixed-Income Market Primary market: Placement of competitive / non-competitive bids in SBP’s auction Secondary market: Purchasing fixed income securities through brokers or directly from primary dealers Local Fixed-Income Market The main players in the local fixed income market are: Issuers Primary Dealers Investors Issuers In most emerging markets, the government is the largest issuer Government use funds for: Deficit financing Project financing Corporates also issue debt to raise capital Tax advantage Ownership is not diluted Borrow long-term Functions of Primary Dealers Participate in auction and “when issued” trading (both buying and short selling) Place bids on behalf of non-PD financial institutions and investors Settle purchase and sale transactions through RTGS / DVP / Other payment modes Maintain investor portfolio securities (IPS) accounts for investors Primary Dealers of Government Securities Bank Alfalah Limited Habib Bank Limited National Bank of Pakistan United Bank Limited Pak Oman Investment Company Limited JS Bank Limited MCB Bank Limited Bank of Punjab Citibank NA (Pakistan Operations) Standard Chartered Bank (Pakistan) Limited Investors Corporate clients Institutional investors such as Asset Management Companies Insurance companies and pension funds High net-worth individuals Functions of Secondary Market To facilitate liquidity and marketability of outstanding debt instruments To contribute to economic growth through allocation of funds to the most efficient channel through the process of disinvestments to reinvestment To provide instant valuation of securities affected by changes in the internal environment To facilitate valuation of the cost of capital and the rate of return of economic entities at the micro level by take into account local as well as international factors To protect investors’ interests through readily available market information To stimulate companies to improve performance since the market price at the stock exchanges reflects the performance of the company To update investors about the market price of their investment Classification of Fixed-Income Portfolio Held to Maturity (HTM): Intention and ability to hold security till maturity Held for Trading (HFT): Intention to trade security to take advantage of short-term interest rate movements Available for Sale (AFS): Intention to hold security long term Accounting of Fixed-Income Securities Accounting Category Description Balance Sheet Income Statement Unrealized Gains/Losses Other Trading Securities acquired mainly for short-term or trading gains (usually less than three months) Fair Value Recognize in net income Recognize realized gains/losses and interest income in net income Available-forSale Securities neither held for trading nor held-to-maturity Fair Value Not recognized in net income, but recognized in comprehensive income Recognize realized gains/losses and interest income in net income Held-toMaturity Securities acquired with both the intent and ability to hold to maturity Amortized Cost Not recognized in either net income or comprehensive income Recognize realized gains/losses and interest income in net income Fixed Income Securities Types of Fixed Income Securities Pricing a Fixed Income Security The price of the bond is the PV of its cash flows Discount Rate (yield) is the return required by the investors Price of a zero coupon bond: Coupon Bonds Coupon bonds can be interpreted as portfolio of zeros. Time Path of the Bond Price