Antibiotics Study Guide: Overview, Classes & Nursing Considerations
advertisement

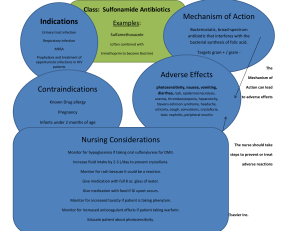
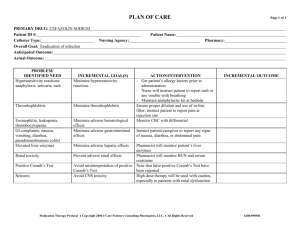
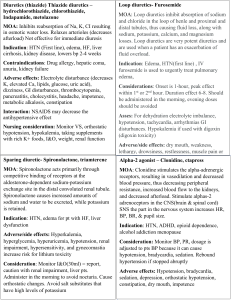
CH 9: Antibiotics Antibiotic Overview - Inhibit specific bacteria. Made in living microorganisms, synthetic, & genetic engineering Can be bacteriostatic (prevents growth of bacteria) or bactericidal (kills the bacteria directly) Culture helps choose the right antibiotic that is going to be effective in the treatment. Sensitivity testing helps to determine the organism will be most sensitive to Broad spectrum is given if the organism cannot be identifying and prevent the pt to go to aspis Bacteria classification: - - - Gram-positive: cell wall retains Gram’s statin or resists decolorization with alcohol on culture o Infections of the respiratory tract o Ex: pneumonia Gram-negative: cell wall loses a stain or is decolorized by alcohol o Associated with infection in the urinary or GI tract. o Ex: E. coli cause of cystitis Aerobic: depend on oxygen Anaerobic: do not use oxygen Aminoglycosides OVERVIEW: Powerful antibiotic to treat serious infection PROTOYPE: acin NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: - Check renal function: BUN & Creatine - Strict I & O: urine output 1200 ml/day - Monitor peak: 30 minutes & trough (before dose) GRAM POSITIVE OR GRAM NEGATIVE: LIST WHAT IT DOES TO THE CELL: Bactericidal Carbapenems OVERVIEW: broad-spectrum antibiotics against (+, -) and anaerobic bacteria PROTOTYPE: penem NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: Lab tests: C&S prior to therapy Monitor: liver and kidney function and seizures Bacteria & Resistance to antibiotics - Bacteria adapts to their environment by changing the cell wall leading to resistance Use only when necessary Result in superinfection or overgrowth of resistant pathogens Superinfections occurs because antibiotics destroying bacteria and in the normal flora o Ex: fungi or yeasts resulting in yeast infections and candidiasis MOA: inhibit protein synthesis. Irreversibly binding to bacteria ribosomes leading to misreading of the genetic code INDICATIONS: serious infections susceptible to penicillin when penicillin is contraindicated Ex: E. coli, pseudomonas aeruginosa CONTRAINDICATIONS: R & H disease, hearing less, myasthenia gravis or Parkinson’s, active herpes, or mycobacterial infections DRUG-DRUG: diuretics, neuromuscular blocking agents (muscle relaxer) SIDE/ADVERSE EFFECT: Ototoxicity: BLACK BOX WARNING, hearing loss, loss of balance Nephrotoxicity: BLACK BOX WARNINIG, proteinuria, urine casts, dilute urine, elevated BUN, elevated creatinine Intense neuromuscular blockade, hypersensitivity MOA: inhibits cell membranes synthesis in susceptible bacteria causing death INDICATIONS: intra-abdominal (peritonitis), urinary tract, skin, gynecological infection, pneumonia CONTRAINDICATIONS: allergy to PCN or cephalosporins, seizure, lactation, meningitis, & pts younger than 18 (ertapenem & meropenem) History of hypersensitivity and if it occurs discontinue drug GRAM POSITIVE OR GRAM NEGATIVE: LIST WHAT IT DOES TO THE CELL: Bactericidal Cephalosporins OVERVIEW: broad-spectrum, effective +, - bacteria GENERATIONS: 1. CEPHalexin, CEFazolin 2.CEFaclor, CEFaclor, CEFprozil 3.CEFotaxime (claforan), CEFtriazone (Rocephin) 4.CEFepime, CEFditoren, CEFtaroline NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: Take with food 2 Cross-allergy with penicillin Avoid ETOH Obtain C & S before 1st dose May give false positive for proteinuria & glycosuria GRAM POSITIVE OR GRAM NEGATIVE: LIST WHAT IT DOES TO THE CELL: Bactericidal & Bacteriostatic (depends on the dose used & drug) Fluoroquinolones OVERVIEW: broad-spectrum to treat infection caused by +, - bacteria PROTOYPE: Ciprofloxacin (cipro) NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: C & S before therapy start - Do not take with food (slows absorption), 1 hr before meals or 2 hr after meals - Do not take with iron preps or antacids - Can take with probenecid (gout meds.) - Cipro must be given alone if IV GRAM POSITIVE OR GRAM NEGATIVE: LIST WHAT IT DOES TO THE CELL: Bactericidal Penicillin & Penicillinase Resistant Antibiotics: PCN: first antibiotic introduced for clinical use. PROTOTYPE: CAUTIONS: pregnancy, renal dysfunction DRUG-DRUG: valproic acid (Depakote) SIDE/ADVERSE: GI Toxicity: monitor dehydration, electrolyte imbalances Superinfection CNS: dizziness, H/A, & AMS, seizures MOA: interferes with the cell wall building ability when diving preventing the bacteria from biosynthesizing INDICATIONS: UTI, postop infection, pelvic infections, meningitis CONTRAINDICATIONS: allergies to penicillin SIDE/ADVERSE: GI effects, CNS effect, Nephrotoxicity, superinfections, DRUG-DRUG: aminoglycosides, oral anticoagulants, ETOH MOA: using passive diffusion enters the bacterial cell to interfere the action of DNA enzyme needed to for reproduction INDICATIONS: - Urinary and respiratory tract, G, skin infection - Prevention of anthrax infection (1q12h60d) - Typhoid fever CONTRAINDICATIONS: pregnancy, lactation & uncomplicated infection CAUTION: renal dysfunction SIDE/ADVERSE: Musculoskeletal: tendinitis, tendon rupture, peripheral neuropathy, exacerbated muscle weakness, BLACK BOX WARNING GI: N/V/D/ D, dry mouth Superinfection (C. Diff) Phototoxicity, CNS, liver toxicity, BM suppression DRUG-DRUG: antacids, warfarin, theophylline (lung diseases, asthma & COPD) MOA: prevent bacteria from building cells wall when dividing causing cells to weaken becoming swell and burst from osmotic pressure PCNs: Penicillin Penicillinase-Resistant Antibiotics: Nafcillin, Oxacillin NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: Risk of allergic reaction, MUST check for hypersensitivity. Take 1 hr before or 2 hrs after meals with 8 oz of water (except amoxicillin and penicillin with meals) Cross allergy with cephalosporins Monitor liver functions: AST, ALT, Renal function: BUN, urine output GRAM POSITIVE OR GRAM NEGATIVE: LIST WHAT IT DOES TO THE CELL: Bactericidal INDICATIONS: PNA, meningitis, infectious endocarditis, pharyngitis, syphilis, prophylaxis against bacterial endocarditis prior to dental procedures CONTAINDICATIONS: allergies to PCN or cephalosporins, renal disease SIDE/ADVERSE: GI, ABD pain, glossitis, stomatitis, gastritis, sore mouth, superinfections, renal impairment, hypersensitivity DRUG-DRUG: tetracyclines, parenteral aminoglycosides, PO contraceptives Sulfonamides MOA: block para-aminobenzoic acid to prevent the synthesis of folic acid in bacteria that synthesize their own folates INDICATIONS: trachoma (leading case of blindness), nocardiosis (causes PNAs, brain abscesses, inflammation), UTIs, STIs, ulcerative colitis, RA CONTRAINDICATIONS: allergy to sulfonylureas or thiazides diuretics, pregnancy/lactation CAUTION: renal disease, history of kidney stones, elderly SIDE/ADVERSE: GI (ABD pain, anorexia, stomatitis), hepatic injury, renal (crystalluria, hematuria, proteinuria, nephrotic syndrome), CNS, BM suppression, blood dyscrasias, photosensitivity DRUG-DRUG: warfarin, phenytoin, sulfonylurea and hypoglycemics, oral hormonal contraception (decrease effects), cyclosporine, (high risk of nephrotoxicity) MOA: inhibits protein synthesis leading to the inability of bacteria to multiply INDICATIONS: acne; GU infections caused by chlamydia trachomatis; periodontal disease; rocky mountain spotted fever; brucellosis; Lyme disease, pneumonia; anthrax, GI infections from H. pylori & when PCN is contraindicated CONTRAINDICATIONS: allergy to tartrazine, pregnancy/lactation, ocular infections (ophthalmic preparations), hepatic dysfunction SIDE/ADVERSE: GI (ABD pain, glossitis, esophageal ulceration, dysphagia), yellow/brown tooth discoloration, hypoplasia of tooth enamel, hepatotoxicity DRUG-DRUG: penicillin G, oral contraceptives, digoxin, iron, charcoal OVERVIEW: Treat infections caused by +, - bacteria PROTOYPE: sulfadiazine NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: Take with meals Encourage fluids (3000 ml/day) Good oral care (stomatitis risk) CBC; BS; PT; BUN; Creatine GRAM POSITIVE OR GRAM NEGATIVE: LIST WHAT IT DOES TO THE CELL: bacteriostatic Tetracyclines OVERVIEW: broad spectrum, against +, - bacteria Based on the structure of soil mold, composed of 4 rings “tetra” PROTOTYPE: demeclocycline, doxycycline, tetracycline NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: Take on empty stomach with 8 oz of water, 1 hr before meals or 2 hr after meals can take with food if GI distress, do not take before lying down Note the expiration date; might cause toxicity Monitor renal function Avoid sunlight or use sunscreen GRAM POSITIVE OR GRAM NEGATIVE: LIST WHAT IT DOES TO THE CELL: Bacteriostatic Antimycobacterial OVERVIEW: classifies by the basis of their ability to hold stain even in the presence of a destaining agent such as acid TUBERCULOSIS 1ST: ethambutol, INH, pyrazamide TUBERCULOSIS 2ND: bedaquiline, capreomycin, cycloserine LEPROSY: dapsone NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: Monitor for hepatic side effects. Monitor for CNS effects as numbness and tingling of the extremities. Collect sputum specimens as directed by healthcare provider checking for acid fast bacteria. Establish infection control measures based on extent of disease condition and established protocol. Establish therapeutic environment to ensure adequate rest, nutrition, hydration, & relaxation Monitor for dietary compliance (foods high in tyramine) Monitor client’s ability and motivation to comply with therapeutic regimen. To be taken 1 hour before meals or 2 hrs after GRAM POSITIVE OR GRAM NEGATIVE: LIST WHAT IT DOES TO THE CELL: Ketolides OVERVIEW: PROTOTYPE: telithromycin (ketek) NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: GRAM POSITIVE OR GRAM NEGATIVE: LIST WHAT IT DOES TO THE CELL: Bactericidal Lincosamides OVERVIEW: similar to macrolides but more toxic PROTOTYPE: clindamycin (cleocin), lincomycin (lincocin) NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: GRAM POSITIVE OR GRAM NEGATIVE: MOA: act on the DNA/RNA of the bacteria that prevents synthesis of mycolic acid in the cell wall leading to lack of growth & eventual bacterial death INDICATIONS: mycobacterium tuberculosis, mycobacterium leprae, mycobacterium aviumintracellular CONTRAINDICATIONS: renal & hepatic failures, pregnancy SIDE/ADVERSE: peripheral neuropathy, hepatotoxicity hyperglycemia, discolored body fluids (orange urine, saliva, sweat, tear with rifampin (treat tuberculosis), pseudomembranous colitis. DRUG-DRUG: INH inhibits metabolism of phenytoin; rifampin decreases effectiveness of oral contraceptives and warfarin MOA: blocks protein synthesizes by binding to ribosome subunits INDICATIONS: mild to moderate communityacquired pneumonia CONTRAINDCIATIONS: heart condition, bradycardia, hypokalemia, MS (BLACK BOX WARNING- RISK OF FATAL RESPIRATORY FAILURE) CAUTIONS: renal or hepatic impairment, pregnancy & lactation ADVERSE EFFECT: GI, superinfections, hypersensitivity, anaphylaxis DRUG-DRUG: Statins, pimozide, digoxin, metoprolol, rifampin (treat tuberculosis), phenytoin, carbamazepine (control seizures), phenobarbital, theophylline (lung disease asthma & COPD) MOA: bind to the subunit of the ribosome, interfering with protein synthesis preventing cell division depending on the drug INDICATIONS: use to severe infection when a less toxic antibiotic cannot be used CAUTIONS: hepatic or renal impairment, pregnancy & lactation LIST WHAT IT DOES TO THE CELL: bactericidal & bacteriostatic Lipoglycopeptides OVERVIEW: semisynthetic derivatives of vancomycin PROTOTYPE: telavancin (vibativ) NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: GRAM POSITIVE OR GRAM NEGATIVE: LIST WHAT IT DOES TO THE CELL: bactericidal Macrolides OVERVIEW: PROTOTYPE: thryomycin NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: GRAM POSITIVE OR GRAM NEGATIVE: LIST WHAT IT DOES TO THE CELL: bactericidal & bacteriostatic Oxazolidinones OVERVIEW: PROTOTYPE: erythromycin (Eryc) NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: GRAM POSITIVE OR GRAM NEGATIVE: LIST WHAT IT DOES TO THE CELL: Bactericidal ADVERSE EFFECT: GI: fatal colitis Pain, skin infections, BM suppression MOA: inhibit cell wall synthesis by interfering with the polymerization and cross-linking of peptidoglycans binding to cell membrane and disrupt barrier function INDICATIONS: complicated skin and skin structure infections (IV use only) CONTRAINDICATIONS: pregnancy/lactation (BLACK BOX WARNING-FETAL RISK), women of childbearing age CAUTIONS: renal impairment ADVERSE EFFECT: GI, infusion site irritation Nephrotoxicity: foamy urine Red man syndrome: flushing, sweating, hypotension (occur from rapid infusion) DRUG-DRUG: nephrotoxic drug, drugs that prolong QT interval MOA: bind to the subunit of the ribosome interfering with protein synthesis preventing cell division or cell death deponing on the concentration of the drug INDICATIONS: pelvic inflammatory disease, upper respiratory infection, intestinal amebiasis, prophylaxis for endocarditis before dental work in pts with valvular heart disease if allergic to PCN CONTRAINDICATIONS: eye infections (ocular preparations) CAUTIONS: hepatic & renal impairment, pregnancy & lactation ADVERSE EFFECT: GI (ABD cramping, anorexia, diarrhea, vomiting, colitis) AMS, superinfections Hypersensitivity: ranges from rash to anaphylaxis DRUG-DRUG: Digoxin, oral anticoagulants, theophylline, carbamazepine, corticosteroids, cycloserine (treat tuberculosis TB) MOA: interfere with protein synthesis on the bacterial ribosome and act as monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) INDICATIONS: Vancomycin-resistant strains of enterococci (VRE) Methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Penicillin-resistant pneumococci Diabetic foot infections; Pneumonia Skin and skin structure infections Monobactam OVERVIEW: PROTOTYPE: aztreonam (azactam) NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: GRAM POSITIVE OR GRAM NEGATIVE: LIST WHAT IT DOES TO THE CELL: Bactericidal CONTRAINDICATIONS: MAOIs, hepatic impairment, pheochromocytoma, HTN, hyperthyroidism, BM suppression ADVERSE EFFECT: CNS: H/A, insomnia, dizziness GI: N, V, D, dry mouth, colitis Thrombocytopenia (tumor in adrenal gland) HTN DRUG-DRUG: meds that increase BP & bleeding, NSAIDs, serotonergenic drugs (drugs that alter the serotonin in the body) DRUG-FOOD: Tyramine containing food. - Aged cheese, chicken liver, summer sausage, red wine, soy sauce MOA: disrupts bacterial cell wall synthesis which promotes leakage of cellular contents INDICATIONS: urinary tract, skin, intra-abdominal, and gynecological infections, septicemia CONTRAINDICATINS: Hx of allergy to PCN or cephalosporins, renal & hepatic impairment, pregnancy & lactation ADVERSE EFFECT: GI, elevated hepatic enzymes, injection site irritation, & anaphylaxis DRUG-DRUG: nafcillin, cephradine, metronidazole CH 51: DIURETIC AGENTS Kidney Function Review - Regulate fluid balance Regulate electrolyte composition Acid-base balance of body fluids Secrete renin (regulates BP) & erythropoietin (Stimulates RBC production) Produce calcitriol (active of Vit D to help maintain bone homeostasis) Renal failure - - - - - Renal Failure Treatment - - Treatment: manage the cause of the dysfunction Diuretics: increase urine output Cardiovascular: treat underlying HTN or heart failure Dietary management: prevent worsening of renal impairment o Need protein restriction o Reduction of Na+, K +, phosphorus, Mg intake Moderate to severe renal failure decreased drug dosages - Decrease in the kidney ability to maintain electrolyte & fluid balance & to excrete waste products Primary treatment goal is to maintain blood flow through the kidneys and adequate urine output Need to diagnose the degree of kidney failure Urinalysis: look for proteinuria and albuminuria Acute: immediate treatment to reverse retention of nitrogenous waste that result in death caused by renal hypoperfusion Chronic: period of months or year that may go undiagnosed for many years gradual development & nonspecific symptoms End-stage renal disease (ESRD): dialysis, kidney transplant Diuretic Overview Increased the amount of urine produced by the kidneys Increase sodium & water excretion Indications o Edema associated with congestive heart failure o Acute pulmonary edema o Liver disease (including cirrhosis) o Renal disease o Hypertension o Decrease intraocular pressure (glaucoma) o Condition that cause hyperkalemia Classes of diuretics - Thiazide & Thiazide- lie diuretics Loop Diuretics Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors Potassium-Sparing Diuretics Osmotic Diuretics Thiazide & Thiazide- Like Diuretics Loop Diuretics MOA: -Action is to block the chloride pump -prevents reabsorption of water -slight increase in the volume of urine produced -urine that is excreted will be rich in sodium -promote reabsorption of calcium -works with renal function is not impaired INDICDATIONS: -treatment of edema associated with CHF, liver, or renal disease -drug of choice for essential HTN PROTOTYPES: Thiazide Diuretics: hydrochlorothiazide, chlorothiazide, hydroflumethiazide Thiazide-Like Diuretics: chlorthalidone, indapamide, metolazone CONTRAINDICATIONS: Allergy to thiazides or sulfonamides, fluid & electrolyte imbalances, renal impairment CAUTION: Lupus, glucose intolerance/DM, liver disease, hyperparathyroidism, bipolar disorder, pregnancy/lactation DRUG-DRUG: Digoxin, lithium, antihypertensives, NSAIDs ADVERSE EFFECTS: Hypotension, dehydration, increased LDL cholesterol Hypokalemia: weakness, muscle cramps, arrhythmias Hypo/natremia, chloremia Hyper/glycemia, uricemia NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: Monitor electrolytes K+, Na+, CI-, Mg Monitor BUN, serum creatinine, uric acid, glucose. Cholesterol levels Assess for dysrhythmias Take in the AM- may take with food Monitor weight, BP MOA: -block the chloride pump in the ascending loop of Henle -production of a copious amount of sodium-rich urine -Decreased reabsorption of sodium, chloride, & water -Works to cause extensive diuresis in the presence of severe renal impairment. INDICATIONS: -used in emergent need for rapid mobilization of fluid -acute CHF, acute pulmonary edema, hypertension, hypercalcemia, PROTOTYPE: called loop bc work in the loop of Henle -Furosemide (lasix): most commonly used, less powerful than new drugs, larger margin of home safety -Bumetanide (bumex) & Torsemide (Demadex): new drugs, more powerful than Lasix -Ethacrynic acid (edecrin): first loop diuretic introduced, used less frequently in the clinical setting CONTRAINDICATIONS: Electrolyte depletion, anuria (severe renal failure). Hepatic coma, pregnancy CAUTION: Lupus, glucose intolerance/DM, gout, children older than 18 years DRUG-DRUG: Digoxin, lithium, antihypertensives, NSAIDS, anticoagulants ADVERSE EFFECTS: Dehydration, alkalosis, ototoxicity, Decreased HDL cholesterol, increased LDL cholesterol Hypokalemia: weakness, muscle cramps, arrhythmias Hypocalcemia: muscle twitching, cramps, tingling of hands & feet Take K+ supplements as directed & rich foods: bananas, potatoes, dried fruits, nuts, spinach, & citrus fruits Report tenderness or pain in joints Hypomagnesemia: weakness, tremors, muscle twitching Hyper: glycemia, uricemia Hypo: natremia, chloremia, tension, NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: -monitor electrolytes: k+, Na+, CI-, Ca+, Mg -Monitor BUN , serum creatinine, uric acid, glucose, cholesterol levels -assess for dysrhythmias & hearing loss -Take in the AM- may take with food, -Change position slowly -Monitor weight, BP -Take with K+ supplements as directed and rich foods -Reports symptoms of hypokalemia -Report tinnitus or hearing loss Potassium-Sparing Diuretics CARBONIC ANHYDRASE INHIBITORS MOA: -blocks the action of aldosterone in the distal tubule & collecting tubule -causes excretion of sodium & water while retaining potassium -therapeutic effect can take 12-48 hrs INDICDATIONS: -adjuncts with thiazide or loop diuretics for potassium sparing effects to treat HTN and edema -Heart Failure -patients who are at risk for hypokalemia PROTOTYPES: Amiloride (Midamor) Spironolactone (Aldactone) Triamterene (dyrenium) CONTRAINDICATIONS: Hyperkalemia, severe renal failure anuria DRUG-DRUG: antihypertensive, potassium supplements, salicylates ADVERSE EFFECTS: Hyperkalemia: lethargy, confusion, ataxia, muscle cramps, arrhythmias, dyspnea Endocrine effects: deepened voice, impotence, menstrual cycle irregularities, Drowsiness Metabolic acidosis: drowsiness, restlessness NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: -monitor electrolytes K+, Na+ -monitor BUN, serum creatinine, glucose -Assess for dysrhythmias -take in the am- may take with food -monitor weight, BP MOA: -Blocks the effects of carbonic anhydrase preventing formation of carbonic acid in the proximal tubule -More sodium and bicarbonate are lost in the urine INDICDATIONS: -adjuncts to other diuretics when a more intense diuresis is needed -open angle glaucoma decreasing secretion of the aqueous humor of the eye PROTOTYPES: Acetazolamide (diamox) Methazolamide (generic) CONTRAINDICATIONS: Allergy to sulfonamides or thiazides DRUG-DRUG: -salicylates -lithium ADVERSE EFFECTS: -acid-base & electrolyte imbalances -metabolic acidosis -hypokalemia: weakness, muscle, cramps, arrhythmias, fatigue -paresthesia of extremities, confusion, drowsiness -report symptoms of hyperkalemia -Avoid k+ based salt substitutes -Avoid excess amounts of high K+ foods OSMOTIC DIURETICS MOA: -pull water into the proximal tubule & loop of Henle without Na+ loss -prevent Na+ & H2O reabsorption In the blood the gradient allows fluid to be drawn from the intracellular into intravascular spaces INDICDATIONS: -increase intracranial pressure -prevents renal failure due to shock, drug overdose, trauma, or severe hypotension PROTOTYPES: Mannitol (Osmitrol) sugar, given continuous IV infusion, often used in acute situations CONTRAINDICATIONS: renal failure & anuria, pulmonary edema, intracranial bleeding, dehydration, CHF CAUTION: DRUG-DRUG: ADVERSE EFFECTS: related to drop in fluid levels (hypotension, N/V, light-headedness, confusion, H/A) heart failure, pulmonary edema, rebound increased intracranial pressure, fluid & electrolyte imbalances, metabolic acidosis NURSING CONSIDERATIONS: - Nursing Considerations Assess daily weight (report increase of 3 lbs or more/day), Adequate intake (1500 mL/day) & output (report urine <30 mL/hr) Skin turgor/moisture Vital signs Breath sounds Presence of edema Safety CH 43: DRUS AFFECTING BLOOD PRESSURE Hypertension Risks of Coronary Artery Disease rt HTN Conditions RT Untreated HTN Treating HTN Antihypertensive Agents Diuretics: Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors Angiotensin III receptor blockers (ARBs) Beta-adrenergic antagonists Calcium channel blockers Direct-acting vasodilators ACE Inhibitors MOA: INDICATIONS: CONTAINDICATIONS: ADVERSE EFFECTS: DRUG-DRUG: PROTOYPE: INDICATIOS: ADVERSE EFFECT: THERAPEUTIC CLASS: PHARMACOLOGIC CLASS: PREGNANCY CATERGORY: Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBS) MOA: CONTRAINDICATIONS: CAUTION: ADVERSE EFFECTS: DRUG-DRUG: Calcium Channel Blockers MOA: INDICATIONS: CONTAINDICATIONS: ADVERSE EFFECTS: DRUG-DRUG: PREGNANCY CATERGORY: PROTOYPE: INDICATIOS: ADVERSE EFFECT: THERAPEUTIC CLASS: PHARMACOLOGIC CLASS: PROTOYPE: INDICATIOS: ADVERSE EFFECT: THERAPEUTIC CLASS: PHARMACOLOGIC CLASS: PROTOYPE: INDICATIOS: ADVERSE EFFECT: THERAPEUTIC CLASS: PHARMACOLOGIC CLASS: Direct Vasodilators MOA: INDICATIONS: CONTAINDICATIONS: ADVERSE EFFECTS: DRUG-DRUG: PREGNANCY CATERGORY: Diuretics Hypotension Nursing Considerations: Anti-hypotensive Agents OVERVIEW: MOA: INDICATIOS: CONTRAINDCIATIONS: CAUTION: ADVERSE EFFECT: DRUG-DRUG: Ch 46: ANTANGINAL AGENTS Coronary Artry Disease Definitions Types of Angina Nitrates Actions of Antianginal Drugs PROTOYPE: OVERVIEW: INDICATIONS: ADVERSE EFFECT: CONTRAINDICATIONS: CAUTION: DRUG-DRUG: Beta Blockers OVERVIEW: PREVENTION: ADVERSE EFFECTS: CONTRAINDICATIONS: CAUTIN: DRUG-DRUG: Calcium Channel Blockers OVERVIEW: CONTRAINDCIATIONS: CAUTION: ADVERSE EFFECTS: DRUG-DRUG: THERAPEUTIC CLASS: PHARMACOLOGIC CLASS: PREG CAT: PROTOYPE: THERAPEUTIC CLASS: PHARMACOLOGIC CLASS: PREG CAT: PROTOYPE: TERAPEUTIC CLASS: PHARMACOLOGIC: PREG CAT: Nursing Considerations