Uploaded by
tericleveland85
Sulfonamide Antibiotics: Indications, Action & Nursing Considerations
advertisement

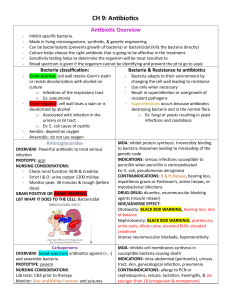
Class: Sulfonamide Antibiotics Indications Examples: Urinary tract infection (often combined with Bacteriostatic, broad-spectrum antibiotic that interferes with the bacterial synthesis of folic acid. trimethoprim to become Bactrim) Targets gram + / gram - Sulfamethoxazole Respiratory infection Mechanism of Action MRSA Prophylaxis and treatment of opportunistic infections in HIV patients The Adverse Effects Contraindications photosensitivity, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, rash, epidermal necrolysis, anemia, thrombocytopenia, hepatoxicity, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, headache, urticaria, cough, convulsions, crystalluria, toxic nephritis, peripheral neuritis Known Drug allergy Pregnancy Mechanism of Action can lead to adverse effects Infants under 2 months of age Nursing Considerations Monitor for hypoglycemia if taking oral sulfonylureas for DMII. Increase fluid intake by 2-3 L/day to prevent crystalluria. The nurse should take steps to prevent or treat adverse reactions Monitor for rash because it could be a reaction. Give medication with full 8 oz. glass of water. Give medication with food if GI upset occurs. Monitor for increased toxicity if patient is taking phenytoin. Monitor for increased anticoagulant effects if patient taking warfarin. Reference: Lilley, Collins, Harrington, Snyder. (2011). Pharmacology and the Nursing Process. St. Louis, MO: Mosby, Elsevier Inc. Educate patient about photosensitivity. I