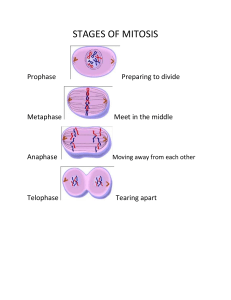
DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA is a large molecule found inside the cells of living things. It is made up of different elements that carry genetic information. DNA is made up of four basic building blocks called nucleotides. A = adenine T C G = thymine The order of nucleotides within a strand of = cytosine DNA forms a special genetic code. This code provides instructions for the development, = guanine growth and functioning of all living things. CHROMOSOMES A segment of DNA that carries the instructions for making a specific protein is called a gene. NUCLEOTIDES Humans have a total of 46 DNA molecules. These are organised into long, coiled-up structures called chromosomes. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus (control centre) of the cell. They are responsible for the genetic information that is passed down from parents to children. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes in each of their cells. THE STRUCTURE OF A PLANT CELL NUCLEUS VACUOLE A double-membraned organelle that contains the genetic material required for all cellular processes. A fluid-filled membrane-bound organelle that helps with water balance and waste management. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM A membrane-bound organelle for cell transport and protein synthesis. GOLGI COMPLEX VESICLES CELL MEMBRANE Membrane-bound spheres used for transporting material in and out of the cell. Semi-permeable lipid bilayer that separates the inside and outside of the cell. CHLOROPLAST Converts light energy into chemical energy through the process of photosynethesis. A membrane-bound organelle that modifies and packages proteins for distribution. CELL WALL Structural layer that provides support for plant growth and defence against pathogens. MITOCHONDRIA Use aerobic respiration to generate energy for all metabolic functions. Types of Cells Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Lack a defined nucleus Defined nucleus Prokaryotic Dispersed genetic material in the cytoplasm. Plant Cellulose cell wall; chloroplasts and vacuoles. Cell Basic and fundamental unit of life, it possesses a highly organized structure that enables it to carry out its vital functions. Animal Rigid cell wall; may have flagella. Protist They can have a cell wall, without differentiated tissues. Fungal Chitin Cell Wall; they are heterotrophs. ANIMAL CELL Nucleolus Nucleus Lysosome Nuclear Membrane Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Golgi Apparatus Vacuole Mitochondrion Centrioles ORGANELLES Mitochondrion Lysosome They are the powerhouse of a cell as they play an important role in releasing energy. They are round organelles surrounded by a membrane and comprising digestive enzymes. Nucleus It also contains DNA and other genetic materials. Golgi Apparatus Centrioles Vacuole Centrioles are barrel-shaped organelles which lives within the centrosome. It is involved in maintaining shape and storing water, food, wastes, etc. It is involved in manufacturing, storing, packing, and transporting the particles throughout the cell. UNICELLULAR ORGANISMS MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS Cell division allows unicellular organisms to replicate & reproduce. Cell division allows multicellular organisms to grow & repair. GROWTH Cells divide and make new cells to build tissues and organs. CELL DIVISION AND GROWTH REPAIR Cells divide to repair tissue and replace cells as they die. CELL CYCLE REPRODUCTION A series of events that take place in a cell as it grows and divides. Cell division produces reproductive cells (sperm cells and egg cells). THE PROCESS OF MEIOSIS Prophase I Chromosome condense and undergo crossover as tetrads, the nuclear membrane breaks down, and the spindle begins to form. Tetrad Microtubule Condensed chromosomes Meiotic spindle Metaphase I Chromosome tetrads are lined up in the middle of the cell by microtubules from the spindle, forming the metaphase plate. Anaphase I Chromosome tetrads are broken apart by the spindle and sister chromatids are pulled to opposite ends of the cell. Prophase II Chromosomes recondense, the nuclear membrane is broken down, and meiotic spindle is formed in each of the new cells. Sister chromatids Telophase I Nuclear membranes form around the two sets of chromosomes and the cell undergoes cytokinesis, forming two haploid daughter cells. Nuclear membrane Metaphase II Metaphase plate Pairs of sister chromatids are lined up in the middle of cell by the meiotic spindle, forming the metaphase place in both cells. Anaphase II Sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite ends by the microtubules of the meiotic spindle of each cell. Chromatid Telophase II Gametes! Nuclear membranes form around the halved sets of DNA and the cells undergo cytokinesis, forming four haploid daughter cells. The twisted ladder shape is called a double helix. DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid Sugar macro-molecule [ stores the genetic material ] nitrogen Bases Adenine Thymine Cytosine Guanine THE PROCESS OF MITOSIS Mitosis is the process by which a single parent cell divides to make two identical daughter cells. Unicellular organisms undergo mitosis to reproduce asexually. Multicellular organisms undergo mitosis to create new cells for growth and repair old cells. INTERPHASE The cell grows, replicates its DNA to prepare for cell division. This stage occurs before mitosis commences. PROPHASE The chromosomes (genetic material) condense (coil tightly) and the nucleolus disappears. METAPHASE The chromosomes align in the centre of the cell and attach to microtubules in preparation to split apart. ANAPHASE Chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. This stage ensures that each cell contains identical chromosomes after splitting. TELOPHASE Two new nuclei form around each set of chromosomes. Chromosomes decondense and the cells begin to split from each other. CYTOKINESIS The cytoplasm of the parent cell splits to form two identical daughter cells. TWO TYPES OF CELL DIVISION Mitosis vs. Meiosis A cell dividing into two or more cells is the process of cell division. Organisms divide and replenish their cells all the time and in different ways. The two most common process of cell division is mitosis and meiosis. What is mitosis? Mitosis is the process wherein a cell divides and produces two new cells. Its goal is to produce a new cell identical to its parent cell. It has 5 phases: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. At the end of the 5 phases of mitosis, two new cells are created. What is meiosis? Meiosis is a type of cell division used in organisms that sexually reproduce. The goal is to produce the sperm and the eggs (gametes) that have half of the DNA of the parent cell. It has 4 stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. The process of cell division occurs two times during meiosis and can produce a total of four gametes.