Ex/PGlInt-B/SWE/06/199/20 13
M.E. (Water Resources & Hydraulic Engineering) Examination, 2013 (Evening)
(1 sl Semester)
PRINCIPLE
OF WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING
,
(Paper - IV)
Time: Three Hours
Full Marks: 100
Answer Q. (1) and anyfour from the remaining
I.
i)A hydraulic structure has been designed for a 50-year flood. The probability that exactly one flood of
design capacity will occur in 75 year life of the structure is
.
(a)0.02
(b)0.220
(c) 0.336
(d) 0.780
ii)A 6-h storm had 6 cm of rainfall and the resulting runoff was 3 cm. If the <I>-indexremains at the same
value the runoff due to 12 cm of rainfall in 9 h in the catchment is
(a)9.0cm
(b)4.5 cm (c) 6 cm (d) 7.5 cm
iii)Astorm hydrographwas due to 3 h effective rainfall. It contained 6 cm of direct runoff. The ordinate of
DRHofthis storm'
.
(a)when divided by 3 gives the ordinate of a 6-h unit hydrograph
(b)when divided by 6 gives the ordinate of a 3-h unit hydrograph
(c)when divided by 3 gives the ordinate of a 3-h unit hydrograph
(d)when divided by 6 gives the ordinate of a 6-h unithydrograph
= ""' ~
'!I"!Oiio;
~~~
c=",,,,
"'~~
~,
~=
~'" ~
~~
E~
- iv) For a return period of 100 years the Gumbel's reduced variate is
.
.
(a)-4.600 (b)4.600
(c)0.517
(d) 1.2835
v)A mean annual runoff of ffi3/Sfrom a catchment of area 31.54 sq. km represents an effective rainfall of
(a)IOOcm (b)lcm (c) 100 mm (d) 3.17cm
vi)A 25 gll solution of a fluorescent tracer was discharged into stream at a constant rate of 10 cm3/s. The
background concentration of the dye in the stream water was found to be zero. At a downstream section
sufficiently far away, the dye was found to reach an equilibrium concentration of 5 ppb. Estimate the stream
discharge.
(a) 30 m3/s
(b)
45 m3/s (c)
50 m3/s(d)
60 m3/s
vii)A triangular DRH due to a storm has a time base of 80 hrs and a peak flow of 50 m3/s occurring at 20 hrs
from the start if the catchment area is 144 km2,the rainfall excess in the storm was
a) 20 cm
b) 7.2 cm
c) 5 cm
d) none of these
viii) The 12-hr unit hydrograph of a catchment is triangular in shape with a base width of 144 hours and a peak
discharge value of23 m3/s.This unit hydrograph refers to a catchment of area
a) 756 km2
b) 596 km2
c) 1000 km2
d) none of these
ix) The soil has a coefficient of permeability of 0.51 cm/s. If the kinematic viscosity of water is 0.009 cm2,the
;,wrinsioperrrrcatriliryliToarcy"s ISa60ut
a)5.3xl04
b) 474
c)4.7xI07
d) 4000
Ex/PG/lnt-B/SWE/06/199/20
13
x) Darcy's law is valid in a porus medium flow if the Reynold's no. is less than unity. This Reynold's no. is
defined as
a) (Discharge velocity x maximum grain size)/fl
b) (Actual velocity x Average grain size)/y
c) (Discharge velocity x Average grain size)/y
d) (Discharge velocity x Pore size)/y
2x10= 20
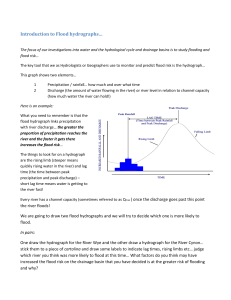
2 (a)Discuss briefly the various abstractions that take place from the precipitation
b)Estimate the average depth of precipitation over an area of 1600 sq.km. due to a storm. The
isohyetsf~xthe stormwith the area enclosedis givenbelow:
Isohyets
(mm)
Enclosed area (sq.km)
21
20
19
18
17
16
.
15
14
13
12
530
1300
2030
2500
2900
3200
3500
3710
3800
3910
(6+ 14)
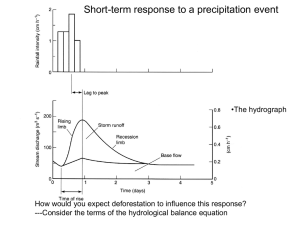
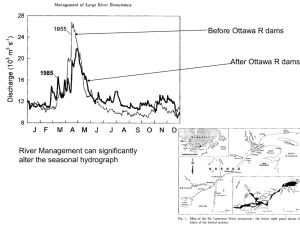
J.a)Wi~h the help or typical hydrographs describe the saliel)t features .of (i) perennial, (ii) intermittent and
(iii)ephemeral streams
(b)Discharges in a river are considered in 10 class intervals. Three consecutive years or data of the discharge in
the river arc givell below. Draw the /low duration curve f()r
/low
-. th~ river and determine the 75'% dependable ----540100I
5()-250-'25>J50
Disch;~~ Range (~ume~) ..
'<i) -, 6.010- - I
39
99
149
249
349
.
9.9
14.()
2 4.9
12"
169
121
60
]0
20
1.17 I IRl
2
137
6
'!
I
l Nil. ofocnrrrcllccs
~_.
,~
-
u
(6+ 14)
the scope and limitations of
4.(a)Write down the gcnerall.'«lIalioll lix hydrological li'cqucney analysis .Discuss
flood frequency studies.
(b)The 1100d data or a rivn was allalyscd I<u' the prediclion or extreme values by I,og -Pearson Type III
Distrihlltion .1!sillg the variall' / log () .whne () 1100ddischarge in the river,it was J(Hllld thai /. lIIean =2.51, z
s.d. 0.1 ()2 ami eo-dfieicllt or sknv ('s 0.7
(i )I':slillialc th~' 1100ddisl'h;III!.l' wilh rdllf'll pniods or )0, I00,200 and 1000 years ill this river.
(ii)Whal would hl' the ('oITespollding lood discharge il' Log normal distrihutioll was used? COIIIIIICillOil thc
two sels or resulls.
(6+14)
5.a) Distinguish between hydrologic storage and hydrologic channel routing
.h)Route the following flood through a reach for which K= 22 hand x=O.25. Plot the inflow and outflow
hydrographs alld dclerlllille Ihe peak lag and attelluatioll. 1\t t=-O,lheouUlow discharge is 40 cumec.
- ----
Time(h)
0
12
24
36
48
60
72
Inflow
40
65
165
250
240
205
170
84
130
96
115
(cumec»
(2+ 18)
108
85
120
70
132
144
60
54
-
20/3
'.
Ex/PG/Int-B/SWE/a6/199/2a 13
IS
6.a)Whatare the guidelines to select the number of segments in case of area-velocity method of stream flow
j
measurement? Describe in details the stream flow measurement by area-velocity method?
,I
b)Describe in details the stream flow measurement
ultrasonic method of stream flow measurement?
by Ultrasonic
method?
What are the advantages
of
c) List the qualities of a good tracer for use in dilution technique of flow measurement.
d)What is the method to measure the velocity of a river in case of a shallow river and also in case of a
moderately deep stream?
tl
(9+6+2+3)
7. a) The ordinate of the unit hydrograph (OUH) of a basin are given in table below
16
18
10.
12
14
a
2
4
6
8
Time(h)
OUH(mJ/s)
a
25
10.0. 160.
190.
170.
11a
70.
30.
20.
20.
22
6
0.
Calculate the following:
.
(i)
The ordinates of the S-curve hydrograph
(ii)
The ordinates of the 4 hour unit hydrograph of the basin.
b) The ordinates of a hydrograph of surface runoff resulting from 4.5 cm of r3.;infallexcess of duration 8 h in a
catchment are as follows:
Time(h)
--
Disc_hatg.
a
5
13
21
28
_O '" .40.... 2JO-" ..40.0.. 600
32
35
41
82Q.. ....11$0. }44a
45
55
1510. ..1420.
61
91
98
115
138
1190.
650.
520.
290.
a
(m3/s)
Determine the ordinates of the 8-h unit hydrograph for this catchment.
12+8=20.
8. a) The flood of a small stream is given bellow. Analyze the recession limb of the hydrograph and determine
the recession coefficients. Neglect interflow.
Time
(days)
Discharge
(m3/s)
90.
66
34
20.
a
0..5
La
1.5
r
I
I
Time
(days)
2.0.
2.5
3.0.
3.5
4.0
Discharge
(m3/s)
13
9.0.
4.5
3.0.
6.7 .
5.0.
.JoB
Time
(days)
5.5
6.0.
6.5
7.0.
Discharge
(m3/s)
2.2
1.8
1.6
1.5
I
5.0.
2.6
Estimate the groundwater storage at the end of day-3 from the occurrence of peak.
b) List the factors affecting a flood hydrograph. Describe the analysis of the recession limb of a flood
hydrograph.
14+6=20.
Ex/PG/Int-B/SWE/06/199/2013
9. (a) Develop the equation relating the steady state discharge from a we)) in a confined aquifer. State clearly all
the assumptions involved in your derivation.
(b) A confined stratified aquifer has a total thickness of 12 m and is made up of three layers. The bottom layer
has a coefficient of permeability of 30 mid and a thickness of 5.0 m. The middle and top layers have
permeability of 20 mid and 45 mid respectively and are of equal thickness. Calculate the transmissibility of the
confined aquifer and the equivalent permeability, if the flow is along the stratification.
10+10=20