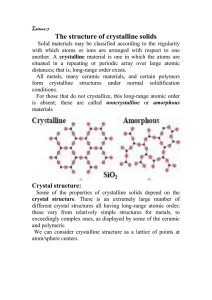
Unit 1 - Crystal physics Objectives ❖ Importance of Crystals in the current world ❖To describe the arrangements in crystalline solids based on lattice, basis, and crystal structure ❖Different crystal systems Infromation Revolution Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer(ENIAC) First Computer Today Semiconductor crystals made the possible information Revolution today and lead to development of modern electronic systems and devices Crystals : germanium, silicon, gallium arsenide and many others Infromation Revolution Crystals made possible the information in hand .... Digital revolution Information (world) at Hand Infromation Revolution An example for infromation revolution .... 1990 •Cell phone subscribers: 12.5 million (0.25% of world population in 1990 •internet users: 2.8 million (0.05% of world population in 1990) 2000 Cell phone subscribers: 1.5 billion (19% of world population in 2002) Internet users: 631 million (11% of world population in 2002) 2010 Cell phone subscribers: 4 billion (68% of world population in 2010) Internet users: 1.8 billion (26.6% of world population in 2010) 2020 Cell phone subscribers: 4.78 billion (62% of world population in 2020) Internet users: 4.54 billion (59% of world population in 2020) What is the point of studying crystal physics ? Silicon crystal ingots and 200 mm Si wafers A multipurpose Si Photonics Process Core Crystals in Optics Ruby crystal ❖ Many Crystals are used in optical conversions, Lasers, Displays, optical communications .... Nd- YAG crystals Name a two crystals used in Lasers ... Ruby laser Nd- YAG Lasers Crystals in Different Fields Industrial communications Telecommunications Mobile, Radio Aviation , Marine Instrumentation Computers, Disk drives Automotive Engine control, sterio, clock, GPS Military & Aerospace communications Navigtion Radar Sensors Electronic warfare Research & Metrology Atomic clocks Instruments Space tracking Celestial navigation Quatrz crystal is one of the crystal used in the all mentioned applications Crystals found are Everywhere ! Some common crystals found in the human body .... Calcium phosphate Uric acid crystals- found in joints Calcium oxalate crystals Calcium carbonate crystals What is the point of studying solid state physics ? Understanding the electrical properties of solids is right at the heart of modern society and technology. The entire computer and electronics industry relies on tuning of a special class of material, the semiconductor, which lies right at the metal-insulator boundary. Solid state physics provide a background to understand what goes on in metals, semiconductors and insulators What is the point of studying solid state physics ? Solid state physics(SSP) is the applied physics • New technology for the future will inevitably involve developing and understanding new classes of materials. What does a crystal consist of at the microscopic level? (or) How do atoms assemble into solid structures? STRUCTURE OF ATOM - +++ + + - - - Atom 1 Atom 2 Proton Electron Neutron - - +++ + + - Repulsive force - - - +++ + + + - +++ + + - - Atom 3 FORCE VS DISTANCE FOR MANY ATOMS Kasap – Principles of electronic materials Matter Liquid Solid Gas On the basis of arrangement of atoms Solid Crystalline solids Single crystalline Amorphous solids Polycrystalline CRYSTALLINE SOLIDS • The atoms or molecules are arranged in a definite, repeating pattern in three dimension i.e., throughout the entire volume of the material • The atoms possess perfect long range order • Sharp melting point • They are anisotropic An example of long range periodic order Single Crystal What will be microscopic picture ? Single Crystal Periodical across the entire volume Single Crystal Single Crystals, ideally have a high degree of order, or regular geometric periodicity, throughout the entire volume of the material Si (110) Polycrystalline Solids ❑ The grains are usually 100 nm - 100 microns in diameter ❑ Polycrystals with grains that are < 100 nm in diameter are called nanocrystallites AMORPHOUS SOLIDS • The atoms or molecules are not arranged in a regular pattern in three dimension i.e., throughout the entire volume of the material • The atoms possess perfect short range order • No sharp melting point. • They are isotropic. • They don’t show all characteristics of solids. Crystals • The periodic array of atoms, ions, or molecules that form the solid is called Crystal Structure Crystal Structure = Lattice + Basis ( Motif) • Space Lattice is a regular periodic arrangement of points in space • Basis is an atoms (group of atoms) placed in the points of the space lattice A Two-Dimensional (Bravais) Lattice with Different Choices for the Basis Lattice Basis + Crystal = A Two-Dimensional (Bravais) Lattice with Different Choices for the Basis Lattice Basis + Crystal = A Two-Dimensional (Bravais) Lattice with Different Choices for the Basis Lattice Basis + Crystal = Unit Cell: A unit cell is the smallest portion of a crystal lattice, which can generate the entire crystal by repetition through lattice translations Unit Cell: A region of space which can generate the entire cystal by repetition through lattice translations Unit Cell: A region of space which can generate the entire cystal by repetition through lattice translations Unit Cell (3D) The unit cell is the smallest structural unit or building block that can describe the crystal structure. ➢ Repetition of the unit cell generates the entire crystal FCC Unit Cell Primitive Cell A primitive cell of a particular crystal structure is the smallest possible unit cell one can construct ❑ One lattice point ( one atom) Primitive Cell: Lattice points only at the corner of the cell Non-Primitive Cell: Lattice points at its corner and extra lattice points Parameters of a unit cell • A unit cell is characterized by six parameters. These parameters are three edges (a, b and c) and angles between them (α, β and γ). • Dimensions along the edges of a unit cell is represented by a, b and c. • Edges of unit cell may or may not be mutually perpendicular. • The angle between b and c is represented by α, between between a and b by γ. by and Seven crystal system and Seven crystal system and Seven crystal system and What different you noticed in the seven cystal system ? Primitive Cell Unit Cell Seven crystal system and Why there is only 14 Bravais lattices ? Symmetry restricts only 14 different lattices in three dimensions Symmetry operations : Translations, Rotation, Reflection, Inversion Is this Scanning electron microscopic figure polycrstalline or single crystalline ? Zinc Oxide Semiconductor Thin film Is this Scanning electron microscopic figure polycrstalline or single crystalline ? • Polycrystalline Zinc Oxide Semiconductor Thin film