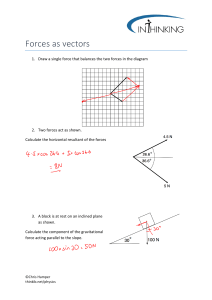
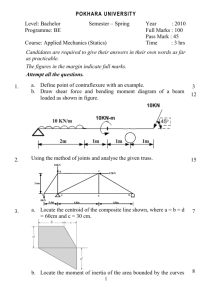
QUESTION BANK DESCRIPTIVE TYPE: Mar ks CO PO BTL A List two practical applications of Parabola. 2 1 1 2 Construct an ellipse, with distance of the focus from the directrix B as 50mm and eccentricity as 2/3. Also, draw normal and tangent to the curve at a point 40mm from the directrix.. 5 1 1 1,6 C Construct a cycloid, given the diameter of the generating circle as 40mm. Draw tangent to the curve at a point on it, 35 from the line 5 1 1 1,6 A Construct a regular hexagon of side 40 mm using inscribing circle method. 2 1 1 2 Construct a parabola, with the distance of the focus from the B directrix as 50mm. Also, draw normal and tangent to the curve, at a point 40mm from the directrix. 5 1 1 1,6 Draw an epi-cycloid of a circle of 40mm diameter, which rolls on another circle of 120mm diameter for one revolution clock-wise. C Draw a tangent and a normal to it at a point 90 from the centre of the directing circle. 5 1 1 1,6 A Distinguish epicycloid from hypocycloid. 2 1 1 1 Draw, a hypo-cycloid of a circle of 40mm diameter which rolls inside another circle of 160mm diameters, for one revolution B counter clock-wise. Draw a tangent and a normal to it at a point 65mm from the centre of the directing circle 5 1 1 1,6 Construct a hyperbola, with the distance between the focus and C the directrix as 50mm and eccentricity as 3/2. Also, draw normal and tangent to the curve at a point 30mm from the directrix 5 1 1 1,6 A When eccentricity is greater than 1, then the curve is called? 2 1 1 1 UNIT-I 1 2 3 4 5 6 The area of a field is 50,000 sq m. The length and the breadth of the field, on the map is 10 cm and 8 cm respectively. Construct a B diagonal scale which can read up to one meter. Mark the length of 235 meters on the scale. What is the R.F. of the scale? 5 1 1 1,6 Construct a hyperbola with its foci, 70mm apart and the major C axis 45mm. Draw tangent to the curve at a point 20mm from the focus. Also, determine the eccentricity of the curve. 5 1 1 1,6 A1. What are steps involved in construction of scale. 2 1 1 1 2. On a map, the distance between two points is 14 cm. The real B distance between them is 20 km. draw a diagonal scale of this map to read kilometers and hectometers and to measure up to 25 km. Show a distance of 17.6 km on this scale An area of 144 sq cm on a map represents an area of 36 sq km on the field. Find the R.F. of the scale of this map and draw a C diagonal scale to show kilometers, hectometers and decameters and to measure up to 10 kilometers. Indicate on the scale a distance of 7 kilometers, 5 hectometers and 6 decameters 5 1 1 1,6 5 1 1 1,6 A Define Representative factor. 2 1 1 2 On a building plan, a line 20 cm long represents a distance of 10 m. Devise a Diagonal scale for the plain to read up to 12 m, B showing meters, decimeters and Centimeters. Show on your scale the length 6.48 m and 11.14 m. 7 1 1 1,6 A room of 1728 m3 volume is shown by a cube of 216 C cm3volume. Find R.F. and construct a plain scale to measure up to 42 m. Mark a distance of 22 m on the scale. 7 1 1 1,6 A Construct a regular hexagon of side 40mm 2 1 1 2 A 3.2 cm long line represents a length of 4 meters. Extend this B line to measure lengths up to 25 meters and show on it units of meter and 5 meters. Show the length of 17 meters. 7 1 1 1,6 Construct a parabola, with the length of base as 60mm and axis C 30mm long. Also, draw tangent to the curve at a point 25mm from the base 8 1 1 1,6 A Divide a line of 88mm into 7 parts by acute angle method. 2 1 1 7 8 1 Construct a scale of 1.5 cm = 1dm to read up to 1 meter and show on it a length of 0.6 meters 5 1 1 Construct a rectangular hyperbola, when a point P on it is at distances of 18mm and 34mm from two asymptotes. Also, draw a C tangent to the curve at a point 20mm from an asymptote. 5 1 1 1,6 10 1 1 1,6 9 A Circle of 50mm diameter rolls on a horizontal line for half a revolution clock-wise and then on a line inclined at 900 to the horizontal for another half, clock-wise. Draw the curve traced by a point P on the circumference of the circle, taking the top-most point on the rolling circles the initial position of the generation point. 10 1 1 1,6 10 A stone is thrown from a 4 m high building and at its highest flight, the stone just crosses the top of a 10 m high tree from the ground. Trace the path of the projectile, if the horizontal distance between the building and the tree is 5 m. Find the distance of the point from the building where the stone falls on the ground B 1,6 UNIT-II S.No Question Mark CO PO BTL A Define orthographic projection. 2 2 2 2 B State the quadrants in which the following points are situated: 5 2 3 1,6 5 2 3 1,6 C A point P is 15 mm above the H.P. and 20 mm in front of the V.P. Another point Q is 25 mm behind the V.P. and 40 mm below the H.P. Draw projections of p and Q keeping the distance between their projectors equal to 90 mm. Draw straight lines joining (i) their top views and (ii) their front views. A Explain 1st angle method of projection. 2 2 2 2 5 2 3 1,6 B The top view of a 75 mm long line AB measures 65 mm, while the length of its front view is 50 mm. it’s one end A is in the H.P. and 12 mm in front of the V.P. draw the projections of AB and determine its inclinations with the H.P. and the V.P. 5 2 3 1,6 C A line AB, 65 mm long, has its end A 20 mm above the H.P. and25 mm in front of the V.P. The end B is 40 mm above the H.P. and 65 mm in front of the V.P. Draw the projections of AB and shows its inclinations with the H.P. and the V.P. A A point ‘P’ is 20mm behind V.P and 30mm above H.P. Draw its projections. 2 2 2 1 5 2 3 1,6 B Draw the projections of a line AB, 90 mm long, its midpoint M being 50 mm above the H.P. and 40 mm in front of the V.P. The end A is 20 mm above the H.P. and 10 mm in front of the V.P. Show the traces and the inclinations of the line with the H.P. and the V.P. (a) A point P; its top view is 40 mm above x-y; the front view, 20 mm below the top view. (b) A point Q, its projections coincide with each other 40 mm blow x-y. 1 2 3 5 2 3 1,6 C A pentagonal plane with a 30mm side rests on HP on an edge such that the surface is inclined at 45ᵒ to the HP and the edge on which its rests is inclined at 30 ᵒ to the VP. Draw its projections? A What is the principle of 3rd angle projection. 2 2 2 1 10 2 3 1,6 B The front view of a line AB measures 65 mm and makes an angle of 45 with xy. A is in the H.P. and the V.T. of the line is 15 mm below the H.P. The line is inclined at 30 to the VP. Draw the projections of AB and find its true length and inclination with the H.P. Also locate its H.T 3 2 2 3 A A hexagonal plate with a 30 mm side negligible thickness has its surface perpendicular to the H.P and inclined at 45ᵒ to the VP. Draw its projections when one of the sides of the plane is parallel to and 15 mm in front of the VP. 9 2 3 1,3 B A hexagonal plane with a 30mm side has a corner in the VP and its surface is inclined at 45ᵒ to the VP. Draw its projections when the front view of the diagonal through the corner in the VP is inclined at 30ᵒ with the HP. A Draw the symbol of 1st angle projection 2 2 3 1,3 10 2 3 1,6 B A plate having the shape of an isosceles triangle has base 50 mm long and altitude 70mm. it is so placed that in the front view is seen as an equilateral triangle of 50mm sides and one side inclined at 45° to XY draw its top view? A pentagonal ABCDE with a 35mm side AB in the VP and inclined at 30ᵒ to the HP. and corner A is 15mm above the HP and the corner D is 30mm in front of the VP. Draw the projections of the plane and find its inclination with the VP. 12 2 3 1,6 Draw the projection of a circle of 75mm diameter having the end A of the diameter AB in the HP the end B in the VP and the surface inclined at 30° to the HP and at 60° to the VP. 12 2 3 1,6 4 5 6 7 8 UNIT –III S.No Mark CO PO BTL 2 3 3 2 1. A hexagonal pyramid, base 25mm side and axis 50 mm long, has B an edge of its base on the ground. Its axis is inclined at 30 to the ground and parallel to the V.P. Draw its projections A Distinguish between frustum and truncated solid. 10 3 3 1,6 2 3 3 2 10 3 3 1,6 B A square prism, base 40 mm side and height 65 mm, has its axis inclined at 45 to the H.P. and has an edge of its base, on the H.P. and inclined at 30 to the V.P. Draw its projections. A Draw the cone of 40 mm base in simple position. 2 3 3 1 10 3 3 1,6 B Draw the projections of a cube of 25 mm long edges resting on the H.P on one of its corners with a solid diagonal perpendicular to the V.P. A What are the different types of solids. 2 3 3 1 10 3 3 1,6 B A cylinder of 40 mm diameter, 60 mm height and having its axis vertical, is cut by a section plane, perpendicular to the V.P., inclined at 45 to the H.P. and intersecting the axis 32 mm above the base. Draw its front view, sectional top view, sectional side A What are the different types of section planes. 2 3 3 1 10 3 1 1,6 B A hexagonal pyramid, base 30 mm side and axis 65 mm long, is resting on its base on the H.P. with two edges parallel to the V.P. It is cut by a section plane, perpendicular to the V.P. inclined at 45 to the H.P. and intersecting the axis at a point 25 mm above the base. Draw the front view, sectional top view, sectional side view and true shape of the section. A Define sectional plane and sectional view. 2 3 3 1 A 1 2 3 4 5 6 Question Define and classify the solid. B 7 8 A 9 A pentagonal pyramid has is base on the H.P. and the edge of the base nearer the V.P., parallel to it. A vertical section plane, inclined at 45 to the V.P., cuts the pyramid at a distance of 6 mm from the axis. Draw the top view, sectional front view and the auxiliary front view on an A.V.P. parallel to the section plane. Base of the pyramid 30 mm sides; axis 50 mm long 10 3 1 1,6 A cube of 35 mm long edges is resting on the H.P. on one of its faces with a vertical face inclined at 30 to the V.P It is cut by a section plane, perpendicular to the V.P., inclined at 45 to the H.P. and passing through the top end of the axis. (i) Draw its front view, sectional top view and true shape of the section. (ii) Project another top view on an auxiliary plane, parallel to the section plane. 10 3 1 A cone, base 75 mm diameter and axis 80 mm long is resting on its base on the H.P. It is cut by a section plane perpendicular to the V.P., inclined at 45 to the H.P. and cutting axis at a point 35 mm from the apex. Draw it front view, sectional top view, sectional side view and true shape of the section. 10 3 1 A cube of 65 mm long edges has its vertical faces equally inclined to the V.P. It is cut by a section plane, perpendicular to the V.P., so that the true shape of the section is a regular hexagon. Determine the inclination of the cutting plane with the H.P. and draw the sectional top view and true shape of the section. 10 3 1 Mark CO PO BTL 1,6 1,6 1,6 UNIT-IV S.No A What is development of surface and classify them. 2 4 3 2 10 4 3 1,6 B A hexagonal prism base 20mm, axis 40 mm long is resting on HP with an edge of the base parallel to VP. It is cut by two section planes; one is perpendicular to VP and inclined at 300to HP and cuts left longer edge and upto the centre of prism. Another section plane perpendicular to VP and inclined at 600 to HP cuts the prism from centre of prism to extreme right. Draw the development of the lateral surface of the hexagonal prism A What is lateral surface development. 2 4 3 2 1 2 Question 10 4 3 1,6 B A cylinder of base 50 mm diameter and axis 60 mm long is resting on its base on HP. It is cut by section plane perpendicular to VP and Inclined at 450 to HP and cuts all the generators from extreme left generator. Develop the lateral surface of the truncated cylinder A What are the applications of developments of surface. 2 4 3 2 A cone of base diameter 50mm and axis 60mm is resting on its base on the HP. a section plane perpendicular to VP. And inclined at 45ᵒ to HP, bisects the axis of the cone. Draw the development of its lateral surface. 10 4 3 1,6 A What is frustum of a solid. 2 4 3 2 10 4 3 1,6 B A square hole of side 25mm is cut in a cylindrical drum of diameter 50mm and height 70mm. the faces of the hole are inclined at 45 °to the HP. and axis interacts with that of the drum at right angles. Draw the developments of its lateral surface. A What is truncated solid. 2 4 3 2 10 4 3 1,6 2 4 3 2 3 B 4 5 B 6 A A square pyramid of base 30 mm, axis 45 mm is resting on HP on its base with an edge is parallel to VP. It is cut by a section plane perpendicular to VP and inclined at 450 to HP and cuts the axis 20 mm below the apex. Draw the development of the lateral surface of the square pyramid. Draw the lateral surface development of a sqaure pyramid. Draw the development of cylinder as per figures given below. 10 4 3 6 Draw the development of a cone as per figure given below. 12 4 3 6 B 7 UNIT-V S.NO 1 QUESTION Mark CO PO BTL A Distinguish between isometric view and orthographic view. 2 5 1 2 10 5 1 1,6 B Draw the isometric view of a frustum of a Hexagonal Pyramid when it is resting on its base on the H.P with two sides of the base parallel to the V.P. The side of the base is 20 mm and top 8 mm. The height of the frustum is 55 mm 2 A 1. Compare isometric view with isometric projections 2 5 1 2 10 5 1 1,6 3 2. Draw the Isometric View of a Cylinder of diameter 46 mm and height 60 mm when it is resting on one of its B ends on the H.P. It is cut by a plane perpendicular to the V.P and inclined at 450 to the H.P. The plane passes through a point on the axis located at 15 mm form the top A 3. What is non isometric plane? 2 5 1 1 Draw the elevation, top view and side view of the objects shown in figures. 10 5 1 1,6 What do you mean by isometric drawing ? 2 5 1 B 4. 4 A 1 10 5 1 1,6 2 5 1 2 10 5 1 B 5 A B List out the advantages of isometric over orthographic projections. 1,6 15 5 1 1,6 15 5 1 1,6 6 7 15 5 1 1,6 15 5 1 1,6 15 5 1 1,6 8 9 Two views of a casting are shown in the figure 2 below. Draw the isometric view of the Casting 10