Catalysis Tasks: Reactor Design & Performance Problems
advertisement

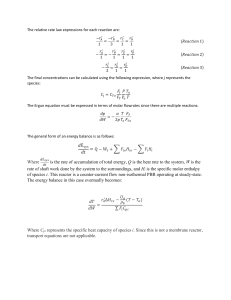
CATALYSIS TASKS TASK #1 In an experimental mixing reactor reactor filled with catalyst particles of 1.2 mm and a total mass of 10 g, the first-order reaction A B takes place at a pressure of 1 atm and a temperatura of 336ºC. The feed volumen velocity of pure A is 4 cm3/s , achieving 80% conversión. The experimental reactor operates in the absence of external and internal resistance. Based on the experiments of the experimental reactor, we want to design a comercial reactor that operates at 80% conversion. We choose between a fluidized bed reactor (dp = 1mm) and a PBR reactor (dp = 1.5 cm), where the external resistance on the catalyst side can be neglected. Use the same model equation for the fluidized bed as for the stirred reactor. Choosing which of the reactors provides the minimum need for a catalyst? Other data: 𝜌𝑝 = 2000 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3 De = 1*10^6 m2/s TASK #2 • In the PBR reactor, the reaction A 2B (k = 4 m^3/(m^3s)) takes place in an aqueous solution, which is limited by internal difusión. Calculare the mass of catalyst for 90% conversión if the molar Flow of reactant A at the inlet FA0 = 1*10^4 mol/h. • Other data: 𝜌𝑝 = 2000 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3 De = 4*10^8 m2/s, dp = 6 mm, cA0 = 1 mol/L. TASK #3 • The heterogeneously catalyzed reaction A B takes place in a porous spherical catalyst with an initial concentration of A of 100 mol/m^3. By how much is the velocity in the grain of the catalyst fue to internal resistance lower than the reaction velocity on the Surface. a) At the entrance to the reactor. b) At the exit from the reactor at 80% conversion? The reaction rate is written in the form Other information: De = 1*10^-6 m2/s, dp= 6mm TASK #4 • The first-order reaction A B takes place in a PBR reactor on a porous catalyst at a atemperature of 1173 K and a pressure of 101.3 kPa. Pure component A flows through a pipe of raiud 2,54 cm with a volumen Flow rate of 1*10^6 m^3/s. Calculare the mass of catalyst for 99.8% conversión of reactant A. • Other data: K= 2.34*10^-7 m3/gs Gas : 1.53*10^-8 m^2/s DAB = 2*10^-8 m^2/s Catalyst: De = 1.82*10^-8 m^2/s, 𝜌𝑝 = 2800 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3, 𝜀𝐵 = 0.5 , 𝑑𝑝 = 6𝑚𝑚 𝜀𝑝 ∗ 𝑑𝑗 = 0.357 ∗ 𝑅𝐸 −0,359 TASK #5 • The first-order reaction A 4B takes place in the gas pase in a PBR reactor. The feed rate of pure reactant A is 2 kmol/h at a pressure of 3 bar and a temperatura of 160ºC. The reaction rate is written in the form: • Determine the volumen of the catalyst bed for a 60% conversión of component A if the mass permeability coefficient kc = 2 m/h Other information: De = 6.56*10^-7 cm^2/s, 𝜌𝑝 = 2.24 𝑔/𝑐𝑚3, 𝜌𝐵 = 0.50 𝑔/𝑐𝑚3 dp= 1mm TASK #6 • In the PBR reactor, the first-order reaction A B takes place. In the case of using a spherical catalyst with a diameter of 9 mm, the chemical reaction takes place under the high influence of internl difusión, with a conversión of 63.2% achieved. How does increasing the diameter of the catalyst grain to 18 mm affect the conversión? TASK #7 • How large grains should we use to make the internal resistance negligible? • Other information: TASK #8 • The PBR reactor is filled with porous catalyst particles 1.2 cm in diameter. In the reactor at a temperatura of 336ºC and a pressure of 1 atm, the Elementary reaction A+B C+D ( k=0.01m^6/mol*kg*s) takes place with a gas Flow rate of 1 m^3/s (1/3, 1/3B, 1/3l). What is the mass of the catalyst to achieve 80% conversión? • External material resistance is negligible. • Other information: De = 2*10^-6 m^2/s , 𝜌𝑝 = 2000 𝑘𝑔/𝑚3, dp = 1.2 cm TASK #9 • The catalytic reaction of the first order is carried out in a mixing with baskets. By changing the speed of rotation of the baskets, we have achieved conditions where the external resistance can be neglected. With grains of two different sizes, we determined the following values of reaction rates: • Determine the Thiele modulus and effectiveneness factor for both grains. TASK #10 • The speed of the first order catalytic reaction aB is studieed in the absence of external material resistance at different sizes of spherical catalyst grains. At the reactant concentration on the catalyst surface Cas=0.025 mol/L, the following apparent reaction rate values were measured: • a) Determine the true rate of a chemical reaction and the reaction rate constant. • b) Determine 𝜃 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝜂 for a grain with a diameter of 5 mm. • c) Determine the value of the effective diffusivity De. TASK #11 • The first-order catalytic reaction A B is carried out at a temperatura of 630ºC and a pressure of 1 bar in a PBR reactor with spherical particles of diameter dp = 0.176 cm. At a feed rate of 0.2 mol/cm^3 , 50% conversión was achieved. Calculate the value of the efficiency factor 𝜂. Other information: De=8*10^-8 m^2/s TASK #12 • Heterogeneous catalyzed reaction with reaction rate equation: Is carried out in a PBR reactor in the presence of a solid catalyst with spherical particles. Entrance the concentration of reactant A is 2.5 mol/L. At this concentration, the Thiele modulus is 8.0 for 80% conversión of reactant A, determine the value of the quotient TASK 13 • The reaction A B was carried out in a differential packed bed catalyst reactor at different temperaturas, molar flows and particle sizes. The results are shown in the graph. • a) Determines the operating conditions where the reaction rate is limited by external material transport. • b) Determine the operating conditions where the reaction rate is limited by the chemical reaction. • c) Determine the operating conditions where the reaction rate is limited by internal difussion. • d) Calculate the effiency factor for a temperatura of 400 K and a catalyst particle diameter of 0.8 cm. TASK #14 • The heterogeneously catalyzed irreversible dimerization reaction 2 A A2 was studied in a basket reactor at a rotating speed where the external resistance can be neglected. Each of the 4 baskets contained 40 g of catalyst. Pure reactant A was fed into the reactor at a pressure of 8.2 atm. At a temperature of 227 ºC, • the following experiments were performed at a temperature of 237ºC, • the following experiments was performed FT0 = 9 mol/min. And yA = 0.097. The reaction is limited by internal difussion. • A) Apparent order of the reaction and the apparent activation energy. • B) Determine the correct order of the reaction and the correct activation energy. Fraction of A at oulet, yA TASK #15 • The exothermic reaction A + B C was performed with two different catalyst particle sizes. The reaction took place under conditions where the externla resistance on the catalyst side can be neglected. The following global reaction rate data were obtained at a different temperatures. • A) Calculate the activation energy • B) Calculate the efficiency factor at each of the temperaturas for particles with a diameter of 8 mm. TASK #16 • The exothermic reaction A B (10% A, 90% I) takes place in a PBR reactor and is limited by external mass transport, internal difusión and Surface reaction, for which we can write: • At a certain point in the reactor, the pressure and temperatura in the main stream are 0.05 bar and 500 K, the efficiency is 0.08, and the mass Flow per empty cross-section of the reactor is 0.8 kg/m^2s. At this point in the reactor, • A) Calculate the global reaction rate at this point • B) Calculate the external concentration gradient • C) Calculate the temperatura gradient. • Other information: • Gas: • Catalyst: • Reaction: where: TASK #17 • The endothermic catalytic reaction AB takes place in a differential PBR reactor and is limited by external mass transport, internal difusión and Surface reaction, for which we can write: • A reaction mixture of 50% A and 50% I enters the reactor at a total pressure of 1 bar and a temperature of 750 K. Mass Flow (G) to empty. Calculate the global gradient, if the conversion reaction rate, efficiency factor, external concentration and temperature cross section of the reactor is 1 kg/m^2s differential PBR reactor is 3.6 %. • Other data: • Gas: • Catalyst: • Reaction: