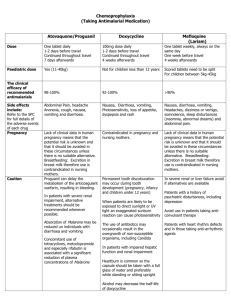
MIDWIFERY II PRESENTATION MUGABE JOSHUA Hyperemesis gravidarum(HG) Definition Signs and symptoms Investigations Management Complications Definition Excessive nausea and vomiting in the first half of pregnancy not responding to simple measures and destabilizing pregnancy or/and the mother’s life. It is most common in the first three months of pregnancy, molar or multiple pregnancy. Signs and symptoms Severe nausea and feeling faint and dizzy when standing(postural hypotension) Persistent vomiting which can lead to dehydration Dehydration, fatigue, light-headedness. Morning sickness, anxiety, hyper salivation, ketosis, weight loss(>5% of prepregnancy weight). Diagnosis Period of amenorrhoea History of nausea and excessive vomiting not responding to simple measures The woman has difficulty in performing normal daily duties Weak, dehydrated, tachycardia Differential Diagnosis Malaria Urinary Tract Infection (Pyelonephritis and Cystitis) Gastrointestinal disorder Hepatitis Pancreatitis Central nervous system disease Investigations Blood for: Haemogram Urea and electrolytes Malarial parasites Urinalysis Ultrasound scan to confirm pregnancy and rule out molar or multiple pregnancy Management Immediate Treatment • Take history, review past records and examine the mother • If the mother is dehydrated, start IV fluids (normal saline alternating with 5% dextrose OR Ringer’s Lactate). Treat with antiemetics: • Metoclopramide (Plasil) IM (10 mg 8-hourly) • OR Phenogan (promethazine hydrochloride) IM (12.5 mg 8-hourly for 24 hours). • OR Prochlorperazine (Buccastem, Stemetil) IM (12 mg once 12hourly) Cont. Note: If vomiting subsides, give antiemetics orally. In addition to any of the above antiemetics, give Vitamin B complex, 2ml in 500mls of Normal Saline or Ringer’s Lactate, single dose If condition doesn’t improve within 24 hours, consult or refer to higher level facility. • Use of ginger can help reduce hyperemesis. • If patient improves, encourage oral and frequent fluid intake at least three litres in 24 hours. Counsel on the following • Possible aggravating factors like if the pregnancy is not wanted/planned, family problems and complications that may arise if the condition continues • Avoid nauseating drugs e.g. Metronidazole, Ferrous Sulphate, (Iron), sweetened drinks, fatty foods • Encourage the mother to eat dry foods like roasted cassava, popcorns, hard corns which should be taken in the morning before any meal • Brush the teeth at night at least one hour after a meal Note: Avoid brushing the teeth in the morning or immediately after meals • Mother should come out of bed very slowly in the morning Follow-up • Review after 1 week. Then resume subsequent visits as per antenatal schedule. • Identify appropriate social support for the mother during the course of treatment. Note: Excessive vomiting can result to reduced levels of vitamin B complex. Use of vitamin B complex prevents Wernicke’s encephalopathies COMPLICATIONS Dehydration Electrolyte imbalance Weight loss Preterm labor Maternal morbidity such as micronutrient deficiency, GI bleeding Low birth weight(LBW) Preterm birth(PTB) Small-for-gestational age(SGA) Perinatal death References Essential Maternal and Newborn Clinical Care Guidelines for Uganda Uganda Clinical Guidelines 2020 https://bmcpregnancychildbirth.biomedcentral.co https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov 22 January, 2023
![Questionnaire used in the study Demographics GENDER: M [ ] F](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006712173_1-21c851410b04058d524e1b79e54e32b0-300x300.png)