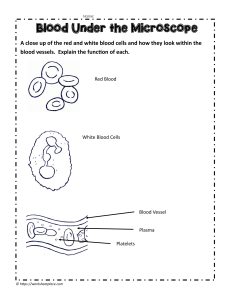
BLOOD CELLS Laboratory Exercise Background The function of the circulatory system is to transport materials through out the body. Materials are transported in a fluid called blood. Blood transports nutrients, gases, enzymes, hormones, and waste products. The blood also regulates body temperature, pH , and electrolytes, and protects the body from foreign invaders. The fluid portion of blood is called plasma, and the cellular portion of the blood includes several types of highly specialized cells and cell fragments. These cells are the red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets. Purpose To examine and identify the blood cells of human and frog blood. Relate their structure to their function. Procedure 1. Place a prepared slide of human blood on the stage of a compound light microscope. Focus on high power. 2. Sketch the cells as they appear in your field of view. Label red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets (if visible). 3. Answer the questions that follow. 4. Repeat steps 1 – 3 using the preparation of frog blood. Data: Sketch and Label blood cells. Figure 1 – HUMAN BLOOD Figure 2 - FROG BLOOD Analysis 1. Is there a nucleus visible in the human red blood cells? Why or why not? 2. What is hemoglobin and what is its function? In which blood cell would it be found? 3. Red blood cells have a shape called biconcave. Explain how this shape is beneficial for its function(s). 4. Do frog red blood cells have a nucleus? Why or why not? 5. List the human blood cells you examined in order from the most numerous to the least numerous. 6. List the human blood cells you examined in order from the largest to smallest in size. 7. What general shape is a white blood cell? How does its shape aid in its function? 8. If this were a slide of a person with a disease, such as pneumonia, what would be different about the white blood cell count? 9. Describe the shape of a platelet from the pictures in your book. Does it look like a typical “cell” to you? Why or why not? 10. What would happen if there were no platelets in the blood? 11. Hemophiliacs actually have platelets. Why is that they have blood that won’t clot? 12. MYSTERY DISEASES. Look at the mystery disease slides. For each one, state the suspected disease and the microscopic evidence that supports your hypothesis. #1 : #2 : #3 : #4 :