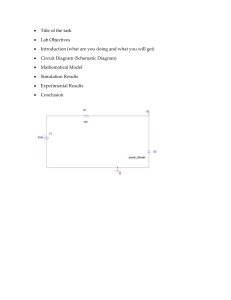
1 ENGG 112.02: Electronics II Laboratory Activity 1 Characterization of a Junction Field-Effect Transistor (JFET) Objectives 1. Characterize an n-channel junction field-effect transistor (JFET). 2. Compare simulation program with integrated circuit emphasis (SPICE) results to experimental circuits with field-effect transistors (FET). Theoretical Background 1. A field-effect transistor (FET) is a three-terminal device that largely matches the operation and the applications of a BJT. The most important difference between the two is, while a BJT is current-controlled, a FET is voltage-controlled. The electric field established in a FET controls the circuit conduction without direct contact, which is the case for BJTs. The “field effect” comes from this phenomenon. 2. A junction field-effect transistor (JFET) is a type of FET. The major part of its structure is an n-type material, which serves as a channel between layers of p-type material. The top of the ntype material connected through an ohmic contact to a terminal is the drain (D). The other end connected the same way is the source (S). The p-type material layers on both sides are connected together through ohmic contacts to the gate (G) terminal. Materials Equipment/Material 1. Power supply with at least two channels No. _____________ 2. Breadboard No. _____________ 3. Wires and connectors 4. Digital multimeter (DMM) No. _____________ 5. n-channel JFET (2N5458) [functionality tested Functional Pre-Activity? (✔ if working, ✘ if defective; date and time of check) Functional Post-Activity? (✔ if working, ✘ if defective; date and time of check) Remarks (Relevant details, especially if defective or damaged) 2 through the activity itself] We, the undersigned students, have physically examined the equipment and materials listed above and have reported any defects. We attest to this through the checklist above. We understand that we can be held responsible for the repair or replacement of the equipment and materials if we damage them during the conduct of the laboratory activity. Signature above printed name of each student and date: Activity I. Experiment 1. Construct the circuit in Fig. 1 using the power supply to generate the DC voltages. 2. Sweep 𝑉𝐷𝐷 from 0 to 10 V with an increment of 0.2 V. Do a secondary sweep of 𝑉𝐺𝐺 from 0 to −5 V with an increment of −1 V. This step results in a plot of the drain characteristics (𝑉𝐷𝐷 vs. 𝐼𝐷 ) of the JFET. 3. Obtain the transfer characteristics of the JFET by another sweep of 𝑉𝐺𝐺 from −3 to 0 V with an increment of 0.2 V. This step results in a plot of the transfer characteristics (𝑉𝐺𝐺 vs. 𝐼𝐷 ) of the JFET. 2N5458 Fig. 1. Network used to obtain the characteristics of the n-channel 2N5458 JFET II. Simulation 1. Construct and simulate the circuit in Fig. 1 in LTspice XVII. 2. Follow the same procedure as in step I-2 in the simulation. 3. Follow the same procedure as in step I-3 in the simulation. III. Post-measurement 1. Find the pinch-off voltage and the 𝐼𝐷𝑆𝑆 of the n-channel 2N5458 JFET. 3 2. Using the obtained plots, check whether both of the obtained quantities in step III-1 are accurately defined by the experimental and simulation characteristics. Submission Requirements • Laboratory report 1. The laboratory report should be in IEEE conference article format with the following standard structure: title, author/s and affiliation, abstract, introduction (problem formulation and theoretical background), methods or models, results (discussion), conclusion, and references. 2. Submission is through Canvas with a deadline a week after the date of the laboratory activity. Source [1] R. L. Boylestad and L. Nashelsky, Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 11th edition. Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2013.