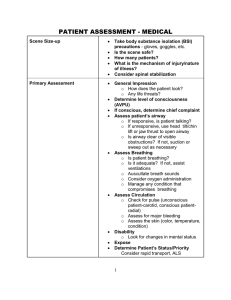
NREMT PARAMEDIC REVIEW EXAM-496 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 2024 Intracellular - answer Fluid inside of a cell Extracellular - answer Fluid outside of a cell Interstitial - answer Around a cell Mydriasis - answer Dilated pupils Can be caused by a CNS stimulant (like cocaine) or lack of oxygen to the brain Miosis - answer Constricted pupils Anisocoria - answer Unequal pupils Nystagmus - answer Rapid, involuntary eye movement Subcutaneous Emphysema - answer Air under the skin Ecchymosis - answer Bruising Ataxic respirations - answer Also known as Biot's respirations Anoxia - answer Without oxygen Apnea - answer Without breathing Eupnea - answer Normal breathing pattern + rate Osmosis - answer Fluid movement from a lower concentration to a higher concentration Diffusion - answer Gas movement from a higher concentration to a lower concentration Erythrocytes - answer Red blood cells; transports oxygen and carbon dioxide Leukocytes - answer White blood cells; fight infection Thrombocytes - answer platelets; blood clotting Homeostasis - answer The body's ability to maintain stability in spite of changes MAP/Mean Arterial Pressure - answer Average arterial pressure during a single cardiac cycle Aphasia - answer Lack of or altered speech Dysarthria - answer Difficulty speaking, slurred speech Thrombus - answer Blood clot that forms in a vein Embolus - answer Intravascular particle that moves and becomes lodged in a vessel Thromboembolus - answer Small pieces of a blood clot that break off; potentially becoming an embolus Photophobia - answer Sensitivity to light Syncope - answer Brief loss of consciousness due to lack of blood to the brain Neoplasm - answer Tumor, new growth Encephalitis - answer Inflammation of the brain Diplopia - answer Double vision Exophthalmos - answer Protruding eyeballs Hemoptysis - answer Coughing up blood or blood-stained sputum Hemophilia - answer Blood clotting disorder that can lead to uncontrolled bleeding Leukocytosis - answer Too many WBCs Leukemia - answer Cancer of blood cells Lymphoma - answer Cancer of the lymphatic system Thrombocytosis - answer Too many platelets Thrombocytopenia - answer Destruction of platelets Polycythemia - answer Increase in RBCs Epistaxis - answer Nosebleed Otitis externa - answer External ear infection Otitis media - answer Middle ear infection Ataxia - answer Loss of control of body movements Menarche - answer Onset of menses; first period Menopause - answer End of menses Mittelschmerz - answer Abdominal pain during ovulation Cor Pulmonale - answer Enlargement of the right side of the heart due to disease Hepatomegaly - answer Enlarged liver Splenomegaly - answer Enlarged spleen Apneustic - answer Characterized by long deep breaths with periods of apnea. Typically occurring with CNS injury/stroke Biot's (Ataxic) - answer Irregular periods of breathing or gasping with apnea. Typically occurring in cases of increased ICP Cheyne Stokes - answer An increase in rate and depth, then a decrease and so on, with periods of apnea. Typically seen in neurological conditions Kussmaul - answer Rapid and deep breathing, usually seems in DKA If you hear rales and crackles when auscultating a patients lungs; what can you infer? answer Fluid is present in the smaller airways/alveoli If you hear rhonchi when auscultating a patients lungs; what can you infer? - answer mucus or fluid is present in the larger airways/bronchi Audible wheezing is caused by? - answer Bronchoconstriction secondary to edema What organs (or portion of an organ) are located in the RUQ? - answer Liver, stomach, gallbladder, kidneys What organs (or portion of an organ) are located in the LUQ? - answer Liver, stomach, spleen, pancreas, kidneys What organs (or portion of an organ) are located in the RLQ? - answer Male/Female reproductive organs, appendix, kidneys What organs (or portion of an organ) are located in the LLQ? - answer Male/Female reproductive organs, kidneys What organs are located in all 4 abdominal quadrants? - answer Large and small intestines, kidneys What should you expect if you have a patient complaining of LUQ pain that radiates to his/her back? - answer Pancreatitis Peritonitis - answer Inflammation of the abdominal lining What is visceral pain and what can it indicate? - answer Pain is usually vague, the site of pain cannot be pointed to specifically. described as a dull pressure. It can indicate organ injury . What is somatic pain and what can it indicate? - answer Pain is typically sharp and localized. It can indicate peritoneal lining irritation. What is referred pain? - answer Pain that is perceived in other parts of the body. Cullen's sign - answer Bruising around the umbilicus; indicates abdominal cavity bleeding. Grey Turner's - answer Bruising on the flanks; indicates bleeding from the kidneys and may present with hematuria. Kehr's - answer Referred pain to shoulder; indicates injury to the spleen or blood under the diaphragm. Murphy's - answer RUQ pain associated with cholecystitis What is the difference between a persons systolic and diastolic blood pressure known as? answer Pulse pressure What do narrowing pulse pressures indicate? - answer Shock What do widening pulse pressures indicate? - answer Increased ICP Characteristics of Cushing's Triad include? - answer Increased systolic blood pressure, decreased respiratory rate and pulse rate. Normal Blood Glucose Range BGL - answer 80-140 mg/dL When should you check a patients BGL? - answer In all patient with AMS, seizures, head trauma and history of diabetes. Normal Pulse Ox range - answer 95-100% What does a Pulse Ox measure? - answer It measures the O2 saturation of hemoglobin Normal ETCO2 range - answer 35-45 mmHg Carboxyhemoglobin - answer A compound of carbon monoxide and hemoglobin that forms in RBCs, causing CNS depression, headache, dizziness, confusion, seizures, coma, and cardiac ischemia, eventually death by ventricular fibrillation Hemoglobin - answer Molecules that carry O2 on red blood cells Normal hemoglobin ranges - answer Male 14-17.4 g/dL Female 12-16 g/dL Methemoglobin - answer Hemoglobin with oxidized iron that cannot bind to oxygen. What can cause Methemoglobin and what are the effects? - answer Amyl nitrate, benzocaines, nitrates, nitroglycerin and cyanide. Changes include skin color changes from grey to cyanotic, CNS changes, delirium and eventually death. What it comes to cardiac enzyme tests done in hospitals, the enzyme Creatine Kinase (CK) is found where? - answer In muscle Where can the enzyme CK-I be found upon blood testing? - answer In the brain and smooth muscle Where can the enzyme CK-II be found upon blood testing? - answer In the heart muscle Where can the enzyme CK-III be found upon blood testing? - answer In skeletal muscle Elevated CK can indicate what? - answer MI myocardial infarction or skeletal muscle trauma What is the first enzyme to elevate in myocardial infarction? - answer Creatine Kinase Where can the enzyme Lactic Dehydrogenase (LD) be found upon blood testing? - answer In heart and skeletal muscle but can also be found in the liver, kidneys and RBC's Elevated Lactic Dehydrogenase (LD) indicates what? - answer Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) The enzyme Myoglobin can be found where upon blood testing? - answer In striated muscle Elevation of Myoglobin can indicate what? - answer Damage to cardiac or skeletal muscle The enzyme Troponin can be found where upon blood testing? - answer In cardiac muscle Elevation of what enzyme is very specific to cardiac injury/ischemia? - answer Troponin What are positively charged ions called? - answer Cations What are negatively charged ions called? - answer Anions What is the chemical abbreviation for calcium? - answer Ca++ What is the chemical abbreviation for chloride? - answer Cl What is the chemical abbreviation for magnesium? - answer Mg++ What is the chemical abbreviation for potassium? - answer K+ What is the chemical abbreviation for sodium? - answer Na+ What is the most common extracellular anion? - answer Chloride What is the most common intracellular cation? - answer Potassium What is the most common extracellular cation? - answer Sodium What what determines blood pH levels? - answer The amount of hydrogen ions in blood Normal blood pH range - answer 7.35-7.45 What is a blood pH of less than 7.35 considered? - answer Acidotic What is a blood pH greater than 7.45 considered? - answer Alkalotic PCO2 measures what? - answer The partial pressure of CO2 in blood Normal PCO2 range - answer 35-45 What is a PCO2 reading of less than 35 indicate? - answer Respiratory Alkalosis Respiratory Alkalosis can be caused by what type of breathing? - answer Kussmaul respirations, Hyperventilating, Hypocarbia (breathing too fast) If you suspect respiratory alkalosis, what should your treatment involve? - answer Decreasing their respiratory rate or your ventilation rate What is a PCO2 reading greater than 45 indicate? - answer Respiratory Acidosis Respiratory Acidosis can be caused by what type of breathing? - answer Decreased tidal volume and respiration rate, Hypercarbia (breathing too slow) If you suspect respiratory acidosis, what should your treatment involve? - answer Increasing your ventilation rate, Intubation What is the fluid of choice in cases of hemorrhaging? - answer Blood What are colloid solutions? - answer Solutions with large particles and proteins that do not leak out of blood vessels What are some examples of Colloid solutions? - answer Albumin, Dextran, Hespan and Blood Plasma What are crystalloid solutions? - answer All other solutions NOT used in fluid replacement, but when giving medications What are some examples of crystalloid solutions? - answer Normal Saline, D5W, Lactated Ringers What is used for fluid replacement in the field? - answer Isotonic fluids Why are isotonic fluids used for fluid replacement in the field? - answer Fluid stays in the blood vessels longer Examples of isotonic fluids - answer Normal Saline and Lactated Ringers Example of hypertonic fluids - answer 10% Dextrose (D10) Example of hypotonic fluids - answer 1/2 Normal Saline Whats another name of RBCs? - answer Erythrocytes What are hemoglobin? - answer Molecules that contain iron that transport O2 What is Hematocrit? - answer The percentage of RBCs in whole blood Average hematocrit - answer 45% Another name of WBCs and what are their functions? - answer Leukocytes // Fight infection Another name of Platelets and what are their functions? - answer Thrombocytes // Promote clotting in hemorrhage What blood type is the universal donor? - answer O Negative What blood type is the universal recipient? - answer AB Positive Dose for fluid replacement in adults and children - answer 20 mL/kg Dose for fluid replacement in newborns - answer 10 mL/kg What chemical is released when the parasympathetic nervous system is activated? - answer Acetylcholine What chemical is released when the sympathetic nervous system is activated? - answer Norepinephrine The RAAS system is activated when what physiological change occurs? - answer A fall in blood pressure The kidneys release Renin into the bloodstream which converts the plasma protein Angiotensin to what? - answer Angiotensin I Enzymes in the lungs convert Angiotensin I to what? - answer Angiotensin II What are the effects of the RAAS system/Angiotensin II? - answer Vasoconstriction which increases blood pressure and restricts blood flow to the kidneys decreasing the kidneys ability to excrete water When the RAAS system is activated, the adrenal cortex is stimulate to release what hormone? - answer Aldosterone Hypovolemic shock - answer Loss of blood/fluid due to trauma, burns, dehydration, vomiting (non-hemorrhagic) 3 types of Distributive shocks - answer Neurogenic, Anaphylactic, Septic shock Examples of Obstructive shock - answer Pulmonary embolism, Cardiac tamponade, Tension Pnuemothorax Drugs such as LSD and heroin are Schedule I drugs because? - answer They have a much higher abuse potential with no recognized medical necessity Drugs such as cocaine, PCP and morphine are Schedule II drugs because? - answer They have a high potential for abuse but have some accepted medical uses in the US Narcotics will do what to a persons pupils? - answer Constricted pupils Stimulants will do what to a persons pupils? - answer Dilated pupils Examples of Narcotics - answer Opium, heroin, fentanyl, morphine, codeine. Examples of Stimulants - answer Cocaine, methamphetamines. Narcotics have what effect on the user? - answer CNS and Respiratory depression A person who has taken a stimulants will most likely present with what kind of behavior? answer Restlessness and agitation Physiological effects of stimulant usage - answer Increased B/P, HR and RR Treatment for Tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) overdoses - answer Sodium Bicarbonate Treatment for Organophosphate poisoning - answer Atropine in high doses Basic treatment for Carbon Monoxide poisoning - answer Remove the patient from the scene immediately, SpO2 and CO2 monitoring A medication would be classified in Pregnancy Category A if; - answer It presents no risk to the fetus A medication would be classified in Pregnancy Category X if; - answer Research has proven it to cause fetal abnormalities and in using it, the risks far outweigh the benefits Examples of Catecholamines (Sympathomimetics) - answer Epinephrine, Dopamine, Norepinephrine Alpha medications cause - answer Vasoconstriction Beta 1 medications cause - answer Beta 1 works on the heart causing vasodilation Beta 2 medications cause - answer Beta 2 works on the lungs causing bronchodilation A medication with an inotropic effect will do what? - answer Effect the strength of contraction A medication with an chronotropic effect will do what? - answer Effect the rate of contraction A medication with an dromotropic effect will do what? - answer Effect the rate of conduction 5 rights for medicarion administration - answer 1) Right dose 2) Right drug 3) Right patient 4 ) Right route 5) Right time 1mg is equal to how many mcg? - answer 1,000mcg 1mcg is equal to how many mg? - answer 0.001mg Drugs given enteral are given via what route? - answer Via the GI tract; Orally, Sublingually, NG tube, Rectally What conditions can be directly attributed to chronic unresolved stress? - answer Impotence What is an evidence-based decision making model? - answer Care provided based on medical research findings What critical body functions does Cortisol do? - answer Gluconeogenesis, Promotes gastric ulcer formation in times of chronic stress, Decreases bone function, Enhances urine excretion Cortisol levels rise during times of; - answer Stress, maintaining normal vitals signs and helping to control emotions Evidence-based research focuses on; - answer Improving medical practices Clinical research focuses on; - answer Improving patient outcomes What is the function of the Trigeminal cranial nerve? - answer Assist with chewing control and facial sensation The fifth cranial nerve is also known as? - answer Trigeminal What is the function of the oculomotor cranial nerve? - answer Eye movement The third cranial nerve is also known as? - answer Oculomotor When transferring a patient with Hep A, what statement is most accurate? - answer Wear gloves when assisting the patient with a urinal When a cell experiences changes in osmotic pressure and begins losing water, shrinking in size, this process is referred to as? - answer Crenation Example of being a patient advocate - answer Notifying social services at the hospital that an elderly patient living alone can no longer adequately take care of themselves. Define patient advocate - answer The healthcare provider "speaks" for the patient and the patients well being when the patient cannot do so. What services as the initial barrier to an organism invading the body? - answer The body's production of mucus works to trap and expel the organism What is the body's best barrier to prevent the cross-contamination of diseases? - answer Integumentary system A widespread proliferation of atypical cells is defined as; - answer Cancer What is a goiter? - answer Swelling of the thyroid gland due to thyroid abnormality Types of abuse - answer Emotional, Physical, and Sexual What is best described as pandemic? - answer H1N1 virus To meet pandemic criteria, a disease must; - answer Affect many people across a large region and it must be infectious in nature What document identifies the structure and guidelines for teaching EMS programs? - answer National EMS Education Standards What should you suspect when the alveolar plateau appears reversed in waveform capnography? - answer Emphysema The majority of carbon dioxide transported in the blood is carried; - answer As Bicarbonate In a patient with pneumonia, where would you most likely hear adventitious lung sounds (crackles, rhonchi) - answer Right middle posterior chest If you are properly ventilating through port #2 of a dual lumen ETC, where is the tip of the device? - answer In the trachea If you are properly ventilating through port #1 of a dual lumen ETC, where is the tip of the device? - answer Occluding the esophagus and ventilations are exiting the tube through perforations near the trachea What role do central chemoreceptors play? - answer To detect carbon dioxide and hydrogen levels in the bloodstream to aid in the negative feedback control of breathing tPa (Alteplase) is only effective within how many hours of coronary ischemia? - answer 6 hours Per NREMT any onset of Hemiparesis is indicative of what? - answer Stroke What is a Grand Mal seizure? - answer A generalized seizure What is status epilepticus? - answer A prolonged generalized seizure What is the most common cause of seizures in children? - answer A fast spike in body temperature What is Hydrocephalus? - answer A buildup of fluid in the ventricles of the brain The purpose of an NG tube is to do what? - answer Relieve gastric distention Prerenal - answer A decrease in blood flow to the kidneys Intrarenal - answer Disease or damage within the kidneys Postrenal - answer Blockage to the urine collecting system Acute renal failure - answer A sudden loss of kidney function due to trauma, illness or toxin Chronic renal failure - answer A long, slow process of the kidneys inability to function End stage renal disease (ESRD) - answer A complete and permanent loss of kidney function Hyperthyroidism is also called what? - answer Graves Disease Exophthalmos - answer Protrusion of the eyeballs Another name for untreated hyper-thyrotoxicosis - answer Thyroid storm A patient presenting with "Moon Face" most likely has what type of condition? - answer Hypothyroidism Function of the Thymus - answer Located between the sternum and the heart, it produces Tlymphocytes to help fight infection Function of the adrenal glands - answer Located on the superior portion of the kidneys, produces epinephrine and norepinephrine An adrenal insufficiency is also known as; - answer Addison's disease An overproduction of adrenal hormones - answer Cushing's syndrome Insulin - answer Produced in the beta cells of the Islets of Langerhans, decreasing blood glucose Glucagon - answer Produced in alpha cells, increasing blood glucose NIDDM - answer Non Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Treatment for Hypoglycemia in the field - answer Oral Glucose or 50% Dextrose (0.5-1 g/kg) slow IV, or Glucagon (0.5-1 mg) SQ or IM Hyperglycemia-Diabetic Ketoacidosis DKA - answer Gradual onset, usually over a number of days. Skin will appear dry and hot, patient may have a fever and be dehydrated. The patient may also appear tired/unconscious. Other S&S include abdominal pain, N+V, Kussmaul respirations Polyuria - answer Production of abnormally large volumes of dilute urine. Polydipsia - answer Abnormally great thirst as a symptom of disease Polyphagia - answer Excessive hunger also known as hyperphagia Hypoglycemia - answer Sudden onset, usually over a couple of hours. Skin will appear pale and clammy. The patient may exhibit bizarre behavior or experience seizures. Other S&S include headache, shaking, dizziness and tachycardia Most common cause of anaphylaxis - answer Penicillin Injections Second most common cause of anaphylaxis - answer Hymenoptera (Bee, wasp) stings Systemic Lupus - answer An autoimmune disease occurs when the immune system attacks the body because it confuses it for something foreign. Scleroderma - answer A chronic connective tissue disease generally classified as one of the autoimmune rheumatic diseases, causing hardening and tightening of the skin and connective tissues. Most common STD - answer Chlamydia 2nd most common STD - answer Gonorrhea Cause of Hantavirus - answer Contact with contaminated rodent waste Cause of West Nile Virus - answer Mosquito bite Cause of Lyme Disease - answer Deer tick bite Cause of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever - answer Tick bites Tonic seizure - answer a sudden stiffening and contracting of the muscles Clonic seizure - answer a rhythmic jerking of one or several muscles Tonic-Clonic seizure - answer Also known as a Grand Mal seizure, a type of generalized seizure that is a combination of Tonic and Clonic seizing in a specific pattern What is necessary when restraining a patient? - answer Use 4-5 people, move fast, tie one arm above the patients head and the other arm to their side with the ankles places together, monitor the patients circulation while they are restrained and ONLY remove the restraints if you need to obtain access or their circulation becomes compromised. Alcoholism is common among what age group? - answer Geriatrics/elderly Delirium Tremens are possible side effects of what condition? - answer Alcohol withdrawal S&S of TCA overdose - answer Blurred vision, altered mental status, seizures, heart blocks, wide QRS on EKG, torsades de pointes, V-tach Treatment for TCA overdose - answer Sodium Bicarbonate S&S of Salicylates-aspirin overdose - answer Hyperventilation, tachycardias, fever, sweating, ringing in the ears. Tinnitus - answer Ringing in the ears Treatment for Aspirin overdose - answer Large amounts of IV fluids, patient may require dialysis S&S of Organophosphate poisoning - answer SLUDGE; Salivation, Lacrimation, Urination, Diarrhea, GI problems, Emesis Treatment for Organophosphate poisoning - answer Large amounts of Atropine Otitis Externa - answer External ear infection Otitis Media - answer Middle ear infection Proliferative Phase of the menstrual cycle - answer First 2 weeks of the cycle, Estrogen levels increase Secretory Phase of the menstrual cycle - answer Time of ovulation Ischemic Phase of the menstrual cycle - answer Estrogen and Progesterone levels decrease if fertilization does not occur The ovaries secrete what two important hormones? - answer Estrogen and progesterone Role of estrogen - answer Aids in the development of breasts and regulates the menstrual cycle in females. Maintains healthy libido and maturation of sperm in males. Role of progesterone - answer Necessary for the implantation of a fertilized egg in the uterus, also for maintaining pregnancy. In late pregnancy, progesterone levels fall. Uterine contractions are stimulated by what hormone? - answer Oxytocin Menarche - answer Onset of Menses, First period Menopause - answer End of Menses Mittelschmerz - answer Abdominal pain during ovulation AB - answer Number of abortions or miscarriages Bloody show - answer Blood-tinged mucus from the cervix, occuring during cervical dilation Cephalic Delivery - answer Head first delivery Lightening - answer Fetus is moving down into the birth canal Braxton Hicks Contractions - answer Irregular contractions "False Birth" Gravida - answer Number of times pregnant Primigravida - answer First pregnancy Para - answer Number of deliveries (Multiples, like twins count as one delivery) Primipara - answer First delivery Postpartum - answer After birth Prenatal and Antepartum - answer Conception until birth; Before birth Where does fertilization of the egg take place? - answer Fallopian tubes Where does the fertilized egg implant? - answer Uterine wall Embryo - answer Up to 8 weeks Fetus - answer Up to delivery Newborn / Neonate - answer From birth to one month Role of the Placenta - answer Provides nutrients to the fetus and gets rid of waste products Umbilical Cord - answer Connects the fetus to the placenta, consists of 2 arteries and 1 vein Normal pregnancy period - answer Nine months; 40 weeks In pregnancy, a drop in blood pressure is common in what trimester? - answer 3rd Trimester What questions are important to ask any OB patient? - answer Past medical history. Is she having any bleeding/spotting? When is her due date? If she is in active labor ask when was the onset. How far apart are her contractions? Did her water break? If so, what color was the fluid? Does she feel like pushing? S&S of abortion/miscarriage - answer Bilateral lower abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding that is bright red in color and may contain clots/tissue S&S of ectopic pregnancy - answer Unilateral lower abdominal pain, spotting, shock Abruptio Placenta - answer Occurs when the placenta tears away from the uterine wall S&S of abruptio placenta - answer Trauma/MOI, Tearing abdominal pain, Dark red vaginal bleeding Placenta Previa - answer Occurs when the placenta implants partially or completely over the cervical opening S&S of placenta previa - answer The patient may have no pain at all but will present with bright red vaginal bleeding Preterm Labor - answer Labor occuring before 38 weeks gestation Another word for Toxemia - answer Preeclampsia Preeclampsia - answer Hypertension during pregnancy; before seizure Eclampsia - answer Hypertension during pregnancy; after seizure Treatment of Eclampsia - answer Magnesium Sulfate FIRST if seizing, Valium if seizing continues Hyperemesis Gravidarum - answer Excessive vomiting during pregnancy Rh- Mother + Rh+ Baby - answer The mother produces antibodies that attack the baby's RBC's 1st stage of labor - answer Complete dilation 2nd stage of labor - answer Delivery of the baby; expulsion 3rd stage of labor - answer Delivery of the placenta Procedure for an amniotic sac intact delivery - answer Pinch the amniotic sac open and remove it from the babies face Procedure for Breech (Buttocks first) presentation - answer Using a sterile, gloved hand, reach into the vagina with your palm towards the baby's face, creating a "V" shape with your fingers to provide an airway for the baby Limb (arm/leg protruding) presentation procedure - answer DO NOT try to delivery, rapid transport, position mom in the knee-chest position with her pelvis elevated How much blood loss within 24 hours is considered postpartum hemorrhage? - answer 500 mL You've just delivered a newborn in the back of your ambulance, the newborn's body is pink but extremities are cyanotic, heart rate is below 100, you hear no sounds coming from the newborn with little to no limb movement, respirations are slow and irregular. What APGAR score does this newborn currently have? - answer 3 After birth, an APGAR score should be taken when? - answer At one and five minutes Order of resuscitation in a newborn - answer Warm, position, dry, clear airway, stimulate to breath / Supplemental O2 / BVM / Intubate / Chest compressions / Medications Most common problems in newborns - answer Respiratory distress and hypothermia If a newborn is bradycardic, what is your first action - answer Look for signs of hypoxia, provide O2 Average weight of a newborn - answer 7 lbs Average weight of a 6 month old - answer 14 lbs (weight doubles) Average weight of a 1 year old - answer 21 lbs (weight triples) Law of inertia - answer A body in motion (or at rest) will remain in motion (or at rest) unless acted upon by an outside force Law of conservation of energy - answer Energy cannot be created or destroyed but can be changed from one form to another Kinetic energy - answer Energy an object has while in motion, with speed being the most important factor. Formula for Kinetic Energy - answer Mass(weight) x Velocity(speed)^2 / 2 What injuries would you suspect a patient to have in a MVC with frontal impact who went up and over the dashboard? - answer Injuries to the head, neck and chest What injuries would you suspect a patient to have in a MVC with frontal impact who went down and under the dashboard? - answer Injuries to the knees, femur, hip and pelvis What injuries are most common in rear-end collisions? - answer Neck and back injuries Calcaneus - answer Heel bone Example of a weapon used in low velocity penetrating injuries - answer Knife Example of a weapon used in medium velocity penetrating injuries - answer Handgun, Shotgun Example of a weapon used in high velocity penetrating injuries - answer Military weapon Primary phase in blast injuries - answer Pressure waves, hollow and air-filled organs are affected Secondary phase of blast injuries - answer Struck by shrapnel Tertiary phase in blast injuries - answer Injuries due to patient being thrown into the air Quaternary Injuries - answer All other injuries resulting from a blast; crush, asphyxia, burns, toxic exposure Compensatory Hypovolemic Shock - answer Perfusion is able to be maintained, Blood pressure will be normal for patient, delayed cap refill. Patient may appear anxious, restless, combative, weak, have dilated pupils, etc Decompensated (uncompensated) shock - answer Decrease in blood pressure is a late sign. Decreased level of consciousness or may be unconscious, unable to feel pulses Irreversible shock - answer Damage to vital organs. Bradycardia is a terminal sign Layers of the skin - answer Epidermis (outermost layer), Dermis (connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves), Subcutaneous (adipose tissue) Superficial partial thickness burns - answer Red, painful, but with no blisters Deep partial thickness burns - answer Red, painful and with blisters Full thickness - answer Black, yellow or white. No pain and no blisters Ohm's Law - answer Role of voltage and resistance Joule's Law - answer Relationship between heat production, current and resistance Abduction - answer To move away from Adduction - answer To move towards the body Dislocation - answer Bones end is displaced from joint Flexion - answer Angle of a joint decreases Extension - answer Angle of a joint increases Ligament - answer Connects bone to bone Medial - answer Position closer to the midline of the body Lateral - answer Position further away from the midline of the body Sprain - answer Injury to a ligament Strain - answer Injury to a muscle Subluxation - answer Partial displacement of a bone at a joint Tendon - answer Connects bone to muscle 6 P's in fractures and dislocations - answer Pain, pallor, paresthesia, paralysis, pressure, pulse Paresthesia - answer Numbness Principles of Splinting - answer Assess PMS before and after applying the splint, immobilize the joint above and below, cover any wounds before splinting, pad splint. Function of the Cerebrum - answer Personality, Intelligence, Eyesight in occipital area Function of the Cerebellum - answer Fine motor movement, balance, coordination Function of the Brain Stem (Medulla Oblongata) - answer All vital functions; blood pressure, heart rate, breathing, consciousness The Meninges cover the brain and spinal cord and are made up of what layers? - answer Dura mater (outermost layer) Arachnoid, Pia mater Afferent Nerves - answer Ascending, sensory nerves bring messages from the body to the brain Efferent Nerves - answer Descending, motor nerves take messages from the brain to the body Difference between aqueous and vitreous humor - answer Aqueous humor can be replenished Hyphema - answer blood in the anterior chamber of the eye usually from a direct blow to the eye Battle Signs and Raccoon eyes are a sign of what? - answer Basilar skull fracture How do you calculate Cerebral perfusion pressure? - answer CPP = MAP - ICP Epidural Hematoma - answer Bleeding between the Dura mater and the skull Subdural Hematoma - answer Bleeding between the Dura mater and the arachnoid Coup/contracoup - answer Injury to tissues under the site of impact as well as injury to the opposite side of impact Normal ICP - answer 2-12 mmHg In increased ICP, Cushing's response presents with - answer Increased blood pressure, decreased pulse rate and irregular respirations Early signs of increased ICP - answer Vomiting without nausea, headache, altered mental status Treatment for increased ICP - answer Spinal precautions, assist ventilations to maintain PO2 of 90 mmHg Flail Chest - answer Multiple ribs fractured in several places, Paradoxical respirations Treatment for a Flail Chest - answer Positive pressure ventilations Treatment for hypovolemic shock - answer C-spine, O2, airway control, bleeding control, keep them warm, Isotonic crystalloids- 20 mL/kg, may repeat twice more for a total of 60 mL/kg, rapid transport Difference between a Tension Pneumothorax and a Hemothorax - answer A tension pneumo will present with JVD and a hemothorax will present with flat neck veins Position of Pleural Decompression - answer 2nd intercostal space midclavicular above the 3rd rib, 5th intercostal space midaxillary above the 6th rib Beck's Triad in Cardiac Tamponade - answer Muffled heart sounds, JVD, Decreased blood pressure Commotio Cordis - answer Direct blow to the chest causing a disruption in heart rhythm, CPR and Defibrillation Solid organs - answer Kidneys, liver and spleen Hollow organs - answer Stomach, bowels and bladder Grey-Turner's Sign - answer Bruising/hematoma in the flanks Most common cause of trauma in the elderly - answer Falls Role of the Hypothalamus - answer Controls body temperature Treatment for Hypothermia - answer Remove from the cold, rewarm slowly, remove any wet clothing, O2, cover in blankets, hot packs in groin and armpits Treatment for Frostbite - answer Remove any wet clothing, thaw in warm water that is less than 106 degrees, do not massage frozen parts Structures of the upper airway - answer Nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx (epiglottis and vallecula), larynx (vocal cords) Structures of the lower airway - answer Trachea, bronchi, alveoli, etc Smallest area of the adult airway - answer Glottic opening at the vocal cords Alveoli - answer Where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged Anoxia - answer Without oxygen Apnea - answer Without breathing Atelectasis - answer Lack of surfactant causing alveoli to collapse Carina - answer Distal end of the trachea where bronchi split into the left and right main stem. Angle of Louis is located at this level Dyspnea - answer Difficulty breathing Eupnea - answer Normal breathing Hemoptysis - answer Coughing up blood Hering-Breuer - answer Reflex that prevents overexpansion of the lungs Hypercarbia - answer Increased CO2 in the blood Hypoxemia - answer Decreased oxygen in the blood Hypoxia - answer Decreased oxygen to the tissues Minute Volume - answer Amount of air inhaled or exhaled in one minute Formula for Minute Volume - answer MV = TV(tidal volume) x RR Orthopnea - answer Difficulty breathing while lying supine The Phrenic nerve innervates what? - answer The diaphragm Surfactant - answer Chemical in alveoli that keeps them from collapsing Tidal Volume - answer Amount of air taken in, in one breath What is the body's main stimulus to breathe? - answer An increase in CO2 detected by the brainstem (medulla) Purpose of your airway assessment - answer Identify an inadequate, unstable or potentially difficult airway. Yankauers/Rigid suction - answer Insert only as far as you can see French/Soft - answer Measure from the tip of the nose to the ear lobe or from the corner of the mouth to the ear lobe Suctioning time - answer Less than 10 seconds in adults, then ventilate for 2 minutes. Less than 5 seconds in infants and children, while only suctioning on the way out. Per NREMT, a gurgling sound indicates; - answer The need to suction; always look for "suction when necessary" Steps for verifying tube placement - answer Visualize the tube passing between the vocal cords, misting present in the tube, positive lung sounds, absent epigastric sounds, capnography Shark-fin Capnography indicates; - answer Asthma, COPD Anatomical structures in order in reference to Cricothyrotomy - answer Thyroid cartilage, Cricothyroid membrane, Cricoid cartilage Induction agents in RSI - answer Etomidate, Midazolam, Ketamine, Propofol Paralytics in RSI - answer Succinylcholine, Rocuronium, Vecuronium Ventilations ratio for adults - answer 12-20 BPM Ventilation ratio for children - answer 15-30 BPM Ventilation ratio for infants - answer 25-30 BPM Artificial ventilation device - answer BVM Purpose of PEEP; Positive end-expiratory pressure - answer Increases the amount of air that remains in the lungs with each ventilation following expiration, keeping the alveoli open When should you use an oxygen delivery device? - answer Signs of shock, SpO2 less than 94% Anatomical airway differences between pediatrics and adults - answer Smaller nose and mouth become easily obstructed, Larger tongue takes up more space in the airway, Narrow trachea that should not be hyperextended at risk of closing off the airway Pediatrics are "Belly Breathers", what does that mean? - answer They use their diaphragms to breath, less chest rise. Smallest structure of the pediatric airway - answer Cricoid ring Up to what age should an uncuffed ET tube be used? - answer 8 years of age What is the most common cause of cardiac arrest in infants and children? - answer Hypoxia If a patient is referred to as a "Pink Puffer" what chronic disease do they most likely have? answer COPD/Emphysema Forms of COPD - answer Emphysema, Chronic Bronchitis S&S of Emphysema - answer Pursed lips/Puffing, Barrel chest, JVD S&S of Chronic Bronchitis - answer Cyanosis, green mucus, cough, rhonchi, JVD If a patient is referred to as a "Blue Bloater" what chronic disease do they most likely have? answer Chronic Bronchitis Last resort medications in cases of Status Asthmaticus - answer Epinephrine and Magnesium Sulfate Pneumonia - answer Infection in the lungs; bacterial viral, and fungal S&S of Pneumonia - answer SOB, high fever, tachypnea, dyspnea, productive cough with yellow/green mucus, crackles or rhonchi Pneumonia is most common in what age groups? - answer The elderly and children S&S of Pulmonary Embolism - answer Sudden onset, chest pain, JVD, cyanosis from the nipple line and up, shock and respiratory distress Hyperventilation - answer Respiratory Alkalosis You would most likely hear stridor in; - answer Partial upper airway obstruction Laryngotracheobronchitis-Croup (Upper Airway) - answer Viral, seal bark cough, no fever, slow onset, KEEP CALM Epiglottitis (Upper Airway) - answer Bacterial, drooling, high fever, rapid onset, transport in a position of comfort, do not put anything in mouth Pertussis-Whooping Cough (Lower Airway) - answer Highly contagious, whooping sound when coughing Cystic Fibrosis - answer Genetic, thick mucus production, life threatening If a patient with cystic fibrosis is on a ventilator that is not adequately breathing for the patient, what should you do? - answer Increase the volume on the ventilator Valves on the right side of the heart - answer Tricuspid and Pulmonary Valve Valves on the left side of the heart - answer Bicuspid and Aortic Valve Layers of the heart - answer Endocardium, myocardium, epicardium/pericardium Intrinsic firing rate of the SA node - answer 60-100 BPM Intrinsic firing rate of the AV node - answer 40-60 BPM Intrinsic firing rate of the Purkinje Fibers - answer 20-40 BPM Stroke Volume - answer Amount of blood pumped with each contraction Cardiac Output - answer Amount of blood pumped in one minute. CO = SV x HR Preload - answer Blood (pressure) coming back to the right side of the heart Afterload - answer Pressure the left ventricle had to pump against Frank-Starling Law - answer The further the heart muscle is stretched, the harder it will contract More than 1 mm of elevation in the inferior leads - answer Check V4R Changes on the EKG in cases of Hyperkalemia - answer Tall, peaked T-waves 5 H's - answer Hypovolemia, hypothermia, hypoxia, hydrogen ion acidosis, hyper/hypokalemia 5 T's - answer Pulmonary/Cardiac Thrombus, tension pneumothorax, cardiac tamponade, toxins/overdose Pediatric Joule settings for Defibrillation - answer 1st; 2 joules/kg. 2nd; 4 joules/kg What makes a patient considered unstable? - answer CASH; Chest pain, Altered mental status, SOB, Hypoperfusion (shock) Cor Pulmonale - answer Abnormal enlargement of the right side of the heart Sudden Infant Death Syndrome usually occurs during what age? - answer 4-6 months When was the EMS White Paper published? - answer 1966 by the National Academy of Sciences What is a paramedics primary role in public health? - answer Preventing diseases, education and vaccination Offline medical control - answer protocols, standing orders Online medical controls - answer calling for orders by phone or radio Stages of Stress - answer Alarm, resistance, exhaustion Death and Dying stages in order - answer Denial, anger, bargaining, depression, acceptance Critical Incident Stress Management - answer A system used to deal with stress on the job by educating and providing resources What is the most effective way to control disease transmission? - answer Proper hand washing Standard Precautions - answer Assumes all body fluids are contaminated Ryan White Act - answer Requires notification of EMS personnel if they are exposed to a patient with a communicable/infectious disease NHTSA and DOT require a minimum data set on PCR including; - answer Chief complaint, Initial assessment with vitals, age, sex, race, times, unit number Facilitation - answer Encourages the patient to give you informations. "Go on, I'm listening" Reflection - answer Repeating what the patient says Scope of Practice - answer State law defining the role of prehospital providers Standard of Care - answer Following laws, rules, protocol, national curriculum Plaintiff must have these 4 things to prove negligence - answer 1) paramedic had a duty to act 2)there was a failure to act/breach of duty 3) injury occured 4) injury was directly caused by the provider Res ipsa loquitur - answer The act speaks for itself Sources of Errors - answer Skills based, Rules based, Knowledge based Libel - answer False writing injuring one's reputation Slander - answer False verbal statements injuring one's reputation Landing zone size at night - answer 100 feet by 100 feet When approaching air medical transport, you should; - answer Approach from the front after being cleared by the pilot or crew. In a Hazmat situation, the hot zone is; - answer A contaminated area In a Hazmat situation, the warm zone is; - answer The decontamination area In a Hazmat situation, the cold zone is; - answer The safe zone, prehospital workers work in this area. Multi Casualty Incident - answer any incident that put excessive demands on EMS workers Sections of NIMS - answer Command, Finance/Admin, Logistics, Operations, Planning Staging sector - answer where emergency vehicles wait to be assigned In simple triage, a patient would be considered "Red" if; - answer Their airway is not open requiring an NPA/OPA, respirations over 30, No radial pulses or delayed cap refill, cannot follow simple commands In an MCI, you are assigned to triage and come across a 34 year old female with a visible fracture to her left femur, what would you categorize her as? - answer Priority 2 Yellow In an MCI, a patient actively in cardiac arrest receives what color tag? - answer Black, cardiac arrests are not treated in MCI Using JUMP START Triage, a pediatric is considered "Red" if; - answer Their airway is not open requiring an NPA/OPA, respirations less than 15 or over 45 (if not breathing, give 5 rescue breaths, if breathing resumes; red tag. If breathing does not resume; black tag. No peripheral pulses.