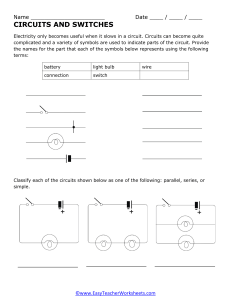
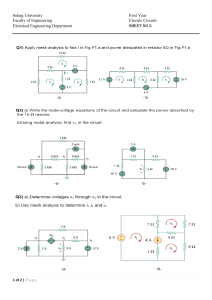
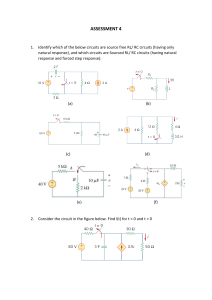
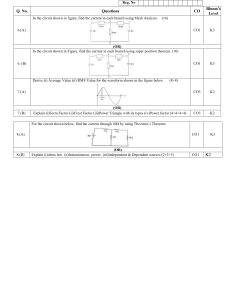
WORLD UNIVERSITY OF BANGLADESH DEPARTMENT OF MECHATRONICS ENGINEERING PROGRAMS B. Sc. in Automobile Engineering & Mechanical Engineering COURSE TITLE: BASICS OF ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY COURSE CODE: AM 07131211 Prepared byPROTIK BARUA Lecturer OVERVIEW Teacher’s Introduction Introduction to Basics of Electrical Technology Rationale Course Learning Outcomes (CO) Program Outcomes (PO) CO Vs PO Marks Distribution Grading System Reference Books TEACHER’S INTRODUCTION Course Teacher: PROTIK BARUA Designation: Lecturer Department: Department of Mechatronics Engineering (MTE) Contact Number: 01875792837 E-mail: protik.barua@mte.wub.edu.bd INTRODUCTION TO BASICS OF ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY An electrical circuit is an interconnection of some electrical elements. This interconnection provides at least one complete path in which current can flow. Electrical elements are the basic building block of a circuit. They are of two typesActive Elements Passive Elements Generators Resistors Batteries Capacitors Operational Amplifiers Inductors RATIONALE An electric circuit is composed of electrical components that form a continuous conducting path connected to the terminals of a power source. Electrical circuits are basically used to transport and convert electrical energy to any other kind of energies. Generally Electric current flows in two ways as an alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). This course demonstrates the analysis and applications of different technologies relevant to electrical circuits. COURSE LEARNING OUTCOMES (COs) On the successful completion of the course, students will achieve CO1, CO2, and CO3. CO1 • Identify the fundamental components relevant to electrical technology CO2 • Apply circuit laws and theorems to the analysis of electrical circuits CO3 • Construct electrical circuits and calculate the response of electrical energies Program Outcomes (PO) PO1 Engineering Knowledge PO2 Problem analysis PO3 Apply knowledge of mathematics, science and engineering. Identify, formulate, research and analyze complex engineering problems and reach substantiated conclusions using the principles of mathematics, natural sciences and engineering sciences. Design/ Design solutions for complex engineering problems taking in to development of consideration to safety, health and welfare of the public and solutions environment. PO4 Investigation Make investigations of complex problems, conducting experimental design and interpret data to provide valid conclusions. PO5 Modern tool usage Create, select and apply appropriate modern tools to complex engineering activities with an understanding of their limitations. PO6 The engineering Apply reasoning informed by contextual knowledge to assess societal, and society health, safety and cultural issues and consequent responsibilities relevant to professional engineering practices. Program Outcomes (POs) PO7 Environment and sustainability PO8 Ethics PO9 Individual work and teamwork PO10 Communication Communicate effectively about complex engineering activities with the engineering community in particular and with society at large. PO11 Project planning and finance Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of project identification, selection, formulation, implementation, monitoring, evaluation, management and financing. PO12 Identify the impact of sustainable engineering solutions in a global, economic, environmental and societal context. Identify professional and ethical values, principles and responsibilities. Function effectively as an individual and as a member or leader of diverse teams and in multidisciplinary settings. Life-long learning Recognize the need for and have the preparation and ability to engage in independent, life-long learning in the broadest context of technological changes. CO VS PO PO1 CO1 PO2 √ CO2 √ CO3 √ PO3 PO4 PO5 PO6 PO7 PO8 PO9 PO10 PO11 PO12 MARKS DISTRIBUTIONS Evaluation Criteria Weekly quizzes based on reading and video lesson reflections. There will be several quizzes in the whole semester. Discussion Forums to ensure class participation and reflect learning. There will be several forum discussion throughout the semester. Depending on the topic taught, several assignments will be provided to all students. Marks 15% 10% 10% Attendance/Class Performance 10% Midterm Examination 15% At end of the semester, a comprehensive evaluation in the form of final exam or research paper or research presentation needs to be done. 40% GRADING SYSTEM Letter Grade Marks Range Grade Point Remarks A+ 80 - 100% 4.00 Outstanding A 75 - 79% 3.75 Excellent A- 70 - 74% 3.50 Very good B+ 65 – 69% 3.25 Quite Good B 60 – 64% 3.00 Good B- 55-59% 2.75 Above average C+ 50-54% 2.50 Average C 45-49% 2.00 Satisfactory D 40 - 44% 1.00 Bad F Below 40% 0.00 Fail W — — Withdrawn I — — Incomplete IP — — In Progress REFERENCE BOOKS Alexander Sadiku; “Fundamental of Electric Circuits”; McGraw-Hill Education; 5th edition. Boylestad; “Introductory Circuit Analysis”; Prentice Hall; 10th edition. B. L. Thereja & A. K. Theraja; “A textbook of Electrical Technology Volume-1”; S. Chand Publisher, 2008 Joseph A. Edminister & Mahmood Nahvi; “Theory and Problems of Electric Circuits”, Schaum’s Outline; McGraw-Hill Education; 3rd edition.