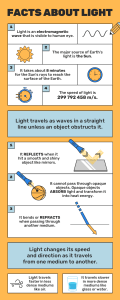
Lesson 14.1 How Light Travels 1 describe how light travels; 2 infer that light travels in a straight line; 3 describe how light travels in different kinds of materials; Objectives At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: Objectives At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: 4 explain how shadows are formed; and 5 classify objects as transparent, translucent, and opaque. Learn about It! Sun as the Main Source of Light Sun is the main source of light on Earth. It is about one hundred fifty million kilometers from Earth. Sun’s distance from earth. Learn about It! Speed of Light Light travels fast. It moves at a speed of three hundred million meters per second in a vacuum. Light travels faster than sound. This is the reason why you see the lightning first before hearing the thunder clap during a thunderstorm. Learn about It! Speed of Light Sun’s light can reach Earth in just around eight minutes. Light travels faster than sound. This is the reason why you see the lightning first before hearing the thunder clap during a thunderstorm. Learn about It! The Path of Light Light travels in a straight line. This behavior of light can be observed by putting an obstacle to the light source. Sun’s light passes through the hole on top of the cave in a straight path. Learn about It! What is a shadow? A shadow is a dark area or pattern that is formed on a surface when light rays are blocked by an object. The shadow usually appears on the side of the object that is blocking the light. Shadows are dark areas formed on surfaces when objects block the light. Learn about It! How Light Travels Through Different Materials An opaque material does not allow light to pass through. Objects made from wood, metal, cloth, plastics and concrete are opaque. Wooden furnitures are opaque materials. Learn about It! How Light Travels Through Different Materials Translucent materials allow some light to pass through. Some examples of translucent objects are wax paper and stained glass windows. Stained glass windows are translucent materials. Learn about It! How Light Travels Through Different Materials Objects that allow light to pass through completely are described as transparent. Clear materials are usually transparent. Clear glass bottles are transparent materials. Learn about It! How Light Travels Through Different Materials Therefore, the speed of light changes as it travels, depending on the material where it passes through. Learn about It! How Light Travels Through Different Materials The pencil appeared to be broken inside the glass of water as the speed of light changes as it travels through the different states of matter. Key Points 1 Light travels from its source in a straight path. 2 Light interacts with different materials. ● Opaque materials do not allow light to pass through. ● Transparent materials allow all light to pass through. ● Translucent materials allow some light to pass through. 3 Light travels at different speeds as it passes through solids, liquids, and gases. Check Your Understanding Supply the word that will make each statement true. 1. Light travels in a __________ path. 2. Some light can pass through __________ objects. 3. Light cannot pass through __________ objects. 4. The __________ of light changes as it passes through different states of matter. 5. Light travels fastest in __________ where there are no obstacles. Challenge Yourself Can shadows be formed in a completely dark place? Why or why not? Bibliography Jones, Mary, Geoff Jones, and Phillip Marchington. Physics. 2nd ed. Coordinated Science. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2000. Dobey, Daniel C., Robert J. Beichner, and Sharon Lee Raimondi. Essentials of elementary science. 2nd ed. Essentials of Classroom Teaching Series. Boston: Allyn and Bacon, 1999. Hackett, Dr. Jay, Dr. Richard Moyer, Dr. Joanne Vasquez, Mulugheta Teferi, M.A., Dinah Zike, M.Ed, Dr. Dorothy Terman, and Dr. Gerald Wheeler. 2013. Science A Closer Look 6. Quezon City: McGraw-Hill Education (Asia) and Phoenix Publishing House. Heat Transfer. Accessed August 23, 2017. http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/thermo/heatra.html. "Temperature System." How does heat move? Accessed August http://www.qrg.northwestern.edu/projects/vss/docs/thermal/1-how-does-heat-move.html. Group, ACEPT W3. "The Path of Light." Pinhole Reading. Accessed https://www.asu.edu/courses/phs208/patternsbb/PiN/rdg/lightpath/lightpath.shtml. August The Propagation of Sound. Accessed August 24, 2017. http://pages.jh.edu/~virtlab/ray/acoustic.htm. 23, 23, 2017. 2017.