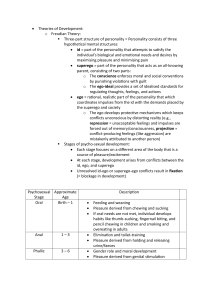
5Chapter 6: Human Development • Know the basic events of the prenatal periods Zygote Period: conception to 2 weeks, during this period the zygote take place in the uterus, takes about a day or two for cells to begin dividing, cells divide slowly at first “pass fail option” Embryo Period: 2 weeks to 8 weeks, cluster of cells now, these clusters divide to create different areas of the body, embryo is about an inch long, by the end of this period the heart is fully formed, most crucial period because of rapid growth of organs, teratogens will affect the most during this period Fetus Period: 8 weeks to birth, lots of growth this period (mass) • Know what teratogens are and how they affect the developing organism Teratogens are any environmental agent that causes damage during the prenatal period Teratogen Affect Alcohol Intellectual disability; impaired motor coordination, attention, memory and language; Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS)(leads to major underdevelopment) Tobacco Low birth weight and increased chances of prematurity, impaired breathing during sleep, miscarriage, infant death, and cancer later in childhood Prescription + nonprescription drugs Illegal drugs “I can go ahead and say, illegal drugs, maybe not a good idea” - Dr. Wryan Leonard ● ● Aspirin linked to low birth weight Caffeine linked to miscarriage + irritability Cocaine, heroin, or methadone linked to prematurity, low birth weight, physical defects, breathing problems, and death around the time of birth (cocaine can bind to sperm cells this usually only results in the failure to conceive a child) • Know what reflexes are and their importance Reflexes are inborn, automatic response to a particular form of stimulation, some reflexes have survival value, lack of reflexes signify neurological problems • Know the developmental trends associated with motor and physical development Cephalocaudal Trend: an organized pattern of physical growth and motor control that proceeds from head to tail; growth of the head and chest occurs before that of the trunk and legs, “head to toe” development Proximodistal Trend: a pattern of physical growth and motor control that proceeds from the center of the body outward; growth of the arms and legs occurs before that of the hands and feet, from the center outward so like shoulders before arms etc. • Know Piaget and his four stages of cognitive development Piaget believed children move through 4 stages of development between infancy + adolescent, also believed children “are not just small dumb adults”, his thinking was scientifically based, apparently he was wrong about a lot of stuff but the info he was researching was valuable enough for other people to be interested in it 4 Piagetian Stages : Sensorimotor, Pre-operational, Concrete operational, and Formal operational • Know Freud’s theory: Freud’s theory proposed that childhood sexuality and unconscious motivations influence personality, a lot of what we are is below our conscious, believed any problems dealing with anxiety or depression were just a battle between your conscious and unconscious • Know the iceberg analogy of personality: The ego represents the top of the iceberg because it is the part of the personality that we can see. The part above the water represented the conscious mind. The part under the water represented the unconscious- id and superego • Know the 3 components of personality and how they develop & interact with each other: ● Id: Strives to satisfy basic sexual and aggressive drives, operates on the pleasure principle, demanding immediate gratification. ● Ego: the largely conscious, “executive” part of personality, mediates among the demands of the id, superego, and reality, operates on the reality principle, satisfying the id’s desires in ways that will realistically bring pleasure rather than pain. The ego is the conscious mind, has to balance between the id and superego ● Superego: the part of personality that presents internalized ideals (the conscience) develops around age 7 • Know the psychosexual stages of development and how they determine Personality: ● Fixation: a lingering focus of pleasure-seeking energies at an earlier v v psychosexual stage, where conflicts were unresolved ● Oedipus Complex: a boy’s sexual desires toward his mother and feelings of jealousy and hatred for the rival father ● ^i don’t think this is what this is asking for • Know the fixations associated with each stage: ● Oral (0-18 months): Pleasure centers on the mouth-sucking, biting, and chewing ● Anal (18-36 months): Pleasure focuses on bowel and bladder elimination; coping with demands for control ● Phallic (3-6 years): Pleasure zone is the genitals; coping with incestuous sexual feelings ● Latency (6 to puberty): Dormant sexual feelings ● Genital (puberty on): Maturation of sexual interests • Know the pros & cons of Freudian theory Pros: Cons: not scientific so you can’t exactly prove him wrong, sexist Key Terms: - zygote: first period of prenatal development, conception to 2 weeks - embryo: second period of prenatal development, 2 weeks to 8 weeks - fetus: third period of prenatal development, 8 weeks to birth - teratogen: any environmental agent that causes damage during the prenatal period - reflex: inborn, automatic response to a particular form of stimulation - cephalocaudal: an organized pattern of physical growth and motor control that proceeds from head to tail; growth of the head and chest occurs before that of the trunk and legs - proximodistal: a pattern of physical growth and motor control that proceeds from the center of the body outward; growth of the arms and legs occurs before that of the hands and feet - scheme: organized ways of making sense of experience, Piaget believed a child’s schemes change with age - at first, schemes are motor action patterns and later move to mental level - assimilation: new experiences are readily incorporated into existing schemes - accommodation: existing schemes must be changed to incorporate new information - sensorimotor: in this period, intelligence is demonstrated through motor activity without the use of symbols. Knowledge of the world is limited (but developing) because it's based on physical interactions/experiences. Children acquire object permanence at about 7 months of age (memory). Believed this is when people learn cause-and-effect - object permanence: knowing an object still exists when it is out of vision - pre-operational: in this period (which has two stages), intelligence is demonstrated through the use matures, and memory and imagination are developed, but thinking is done in a non logical, non reversible manner. Egocentric thinking predominates, when language develops, around age 2 - symbolic thought - egocentric: thinking everyone thinks and knows what you do - concrete operational: in this stage (characterized by conservation), intelligence is demonstrated through logical and systematic manipulation of symbols related to concrete objects. Operational thinking develops (mental actions that are reversible). Egocentric thought diminishes - logical thought: - conservation - formal operational: in this stage, intelligence is demonstrated through the logical use of symbols related to abstract concepts - abstract thought: thoughts that are not tied to physical concepts. Things like love, justice, and pride. - moral thought - Electra complex: essentially the oedipus complex but for girl’s feelings for their father and resenting their mother - id: strives to satisfy basic sexual and aggressive drives, operates on the pleasure principle, demanding immediate gratification, we have this from birth, component of our personality, keeps the species alive (animalistic impulses), as it develops it becomes the largest part of our personality, “devil on your shoulder” - ego: the largely conscious, “executive” part of the personality, mediates among the demands of the id, superego, and reality, operates on the reality principle, satisfying the id’s desires in ways that will realistically bring pleasure rather than pain, makes decisions, has to balance between the id and the superego -superego: the part of personality that presents internalized ideals (the conscience), tells us what’s right from wrong, wants us to be a good person, part conscious - part unconscious, morality principle - unconscious: according to Freud, a reservoir of mostly unacceptable thoughts, wishes, feelings, and memories - fixation: a lingering focus of pleasure-seeking energies at an earlier psychosexual stage, where conflicts were unresolved, if failed challenge at this stage a fixation will develop and person is “trapped” at this stage until fixed by therapy - identification - oral stage - anal stage - phallic stage - latency stage - genital stage - Oedipus complex: a boy’s sexual desires toward his mother and feelings of jealousy and hatred for the rival father. It is found in both children, and it describes when a child has sexual desires/falls in love with the opposite-sex parent and feels jealous/hate/sees the same-sex parent as competition. - anal-expulsive: type of personality developed when parents are too relaxed about potty training leading to someone is sloppy, messy, or uncaring - anal-retentive: type of personality developed when parents are too overbearing about potty training leading to someone who is strict about rules, obsessive with cleanliness Stage Focus Mistake Fixation Oral (0-18 months) Pleasure centers on the mouth - sucking, biting, chewing Weaning process: letting a child breastfeed too long or stopping before they’re ready Smoking, chewing pens, sucking thumb. overeating Anal (18-36 months) Pleasure focuses on bowel and bladder elimination; coping with demands for control During potty training: ● Parents being too overbearing ● Parents being too loose or relaxed Anal-retentive (overbearing) or anal-expulsive (relaxed) Phallic (3-6 years) Pleasure zone is the genitals; coping with incestuous sexual feelings The children need to “identify” with the parent of the same sex to fix the fixation Oedipus complex for boys Electra complex for girls (also penis envy) Latency (6 to puberty) Dormant sexual feelings (No corresponding erogenous zones) Not repressing your memory and remembering all of the stages before this. Genital (puberty on) Maturation of sexual interests