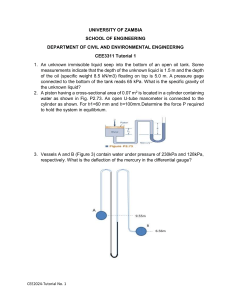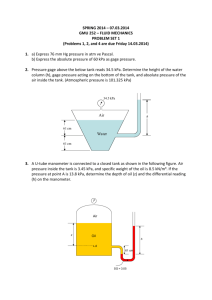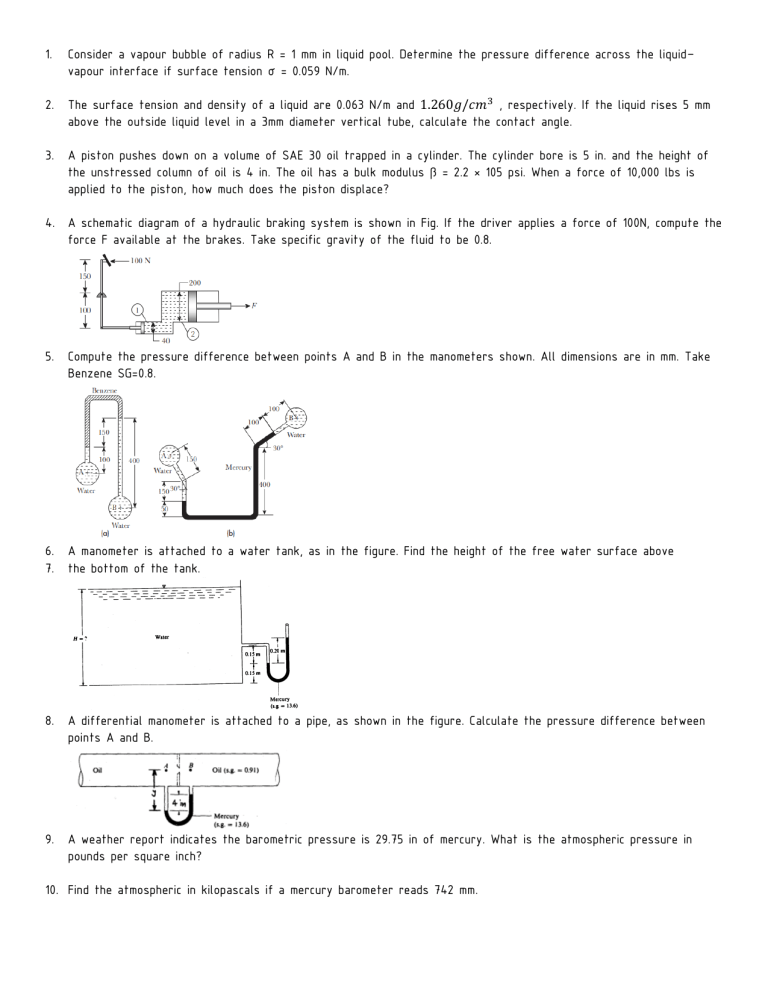
1. Consider a vapour bubble of radius R = 1 mm in liquid pool. Determine the pressure difference across the liquid– vapour interface if surface tension σ = 0.059 N/m. 2. The surface tension and density of a liquid are 0.063 N/m and 1.260𝑔/𝑐𝑚3 , respectively. If the liquid rises 5 mm above the outside liquid level in a 3mm diameter vertical tube, calculate the contact angle. 3. A piston pushes down on a volume of SAE 30 oil trapped in a cylinder. The cylinder bore is 5 in. and the height of the unstressed column of oil is 4 in. The oil has a bulk modulus β = 2.2 × 105 psi. When a force of 10,000 lbs is applied to the piston, how much does the piston displace? 4. A schematic diagram of a hydraulic braking system is shown in Fig. If the driver applies a force of 100N, compute the force F available at the brakes. Take specific gravity of the fluid to be 0.8. 5. Compute the pressure difference between points A and B in the manometers shown. All dimensions are in mm. Take Benzene SG=0.8. 6. A manometer is attached to a water tank, as in the figure. Find the height of the free water surface above 7. the bottom of the tank. 8. A differential manometer is attached to a pipe, as shown in the figure. Calculate the pressure difference between points A and B. 9. A weather report indicates the barometric pressure is 29.75 in of mercury. What is the atmospheric pressure in pounds per square inch? 10. Find the atmospheric in kilopascals if a mercury barometer reads 742 mm. 11. An open tank contains 5.7 m of water covered with 2.8 m of kerosene (𝛾 = 8.0 𝑘𝑁/𝑚3 ), Find the pressure at the interface and at the bottom of the tank. 12. If the absolute pressure in a gas is 40 psia and the atmospheric pressure is 846 mbar, find the gage pressure in a.) 𝑙𝑏/𝑖𝑛2 ; (b) kPa; (c) bar. 13. Calculate the density. specific weight and volume of chloride gas at 25 °C and pressure of 600000 𝑁/𝑚2 abs. Take R =118j/kg k 14. (a) Calculate the density, specific weight, and specific volume of oxygen at 20 °C and 40 kPa abs. (b) If the oxygen is enclosed in a rigid container, what will be the pressure if the temperature is reduced to -100 °C? 15. What depth of oil, sp gr 0.750, will produce a pressure of 40.0 psi? What depth of water? 16. Vessels A and B contain water under pressures of 276 kPa and 138 kPa, respectively. What is the deflection 17. of the mercury in the differential gage in the figure? 18. If water vapor (R=85.7 ft/°R) in the atmosphere has a partial pressure of 0.60 psia and the temperature is 80°F, what is its specific Weight? 19. If the atmospheric pressure is 0.900 bar and a gage attached to a tank reads 390 mmHg vacuum, what is the absolute pressure within the tank in kPa? 20. A differential gage is attached to two cross sections A and B in a horizontal pipe in which water is flowing. The deflection Of the mercury in the gage is I .92 ft. the level nearer A being the lower one. Calculate the difference in pressure in psi between sections A and B.