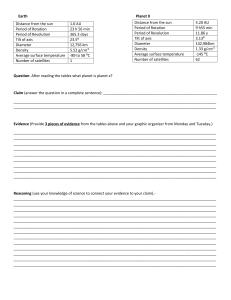
Relationship of the sun to Earth Solar energy and the Earth’s seasons The sun radiates heat and light in all directions The sun is a star. It is the closest star to Earth, which is why it looks so big relative to other starts we see in the night sky. The light and heat from the sun radiate in all directions. The heat doesn’t reach Earth which is 150 million km away, but the light does. Think of a fire burning. It radiates heat and light energy in all directions. We can see the glow of the flames and we can feel the heat even if we stand some distance from the fire. But we can see the flame from much further than we can feel the heat. The light energy is transferred to us by radiation. Remember that we learnt that radiation is the transfer of the sun’s energy to Earth via electromagnetic waves. When the radiation reaches Earth, it is absorbed by matter on Earth and gets converted to heat. The sun is the main source of radiation, but a fire and light bulbs also release radiation. The sun is a huge ball of gas that’s very hot. The surface temperature of the sun is around 5500°C. It radiates a lot of heat and light. The heat and light travel through space in all directions from the sun’s surface. Earth gets a small portion of that light radiation. Earth receives energy from the sun There are different types of radiation that the sun emits. Radiation is actually light waves. For example there is visible light which is the radiation that we see as colour. We are blind to all the other light waves. This is not because they don’t have colour, but because our eyes and brains cannot process them. For example there is ultraviolet radiation which is also a light wave. This light wave can cause our skin to burn. There is also infrared radiation, which again is a light wave. Again, we cannot see it, but we feel infrared as heat. © e-classroom www.e-academyonline.co.za www.e-classroom.co.za Earth gets hot due to: 1. The infrared radiation coming from the sun which is felt as heat and absorbed by gases and objects on Earth, warming them up. 2. Other light waves that are absorbed by gases and objects on Earth, and the light energy gets converted into heat energy. Each of these account for 50% of the heating of the Earth. Earth spins on its axis once a day Earth has an imaginary line going through its centre from North Pole to South Pole. This imaginary line is known as the axis of the Earth. The axis is not vertical, but tilted. It is tilted at an angle of 23.5°. Earth spins on its axis once a day. It spins from west to east. This spinning movement around the axis is called __________________. This rotation is responsible for the night and the day. See the diagram below. The half of the Earth that’s facing the sun experiences day, the half that’s facing away from the sun experiences night. Every planet’s rotation is different. You do not need to learn the diagram below, but it’s interesting to see the tilts of the different planets in relation to the sun, the direction of the spin and the duration of a rotation. © e-classroom www.e-academyonline.co.za www.e-classroom.co.za Which planet has the smallest tilt relative to the sun? __________________________________________________________________ Which planets, like Earth, spin from west to east? __________________________________________________________________ Earth’s day is 24 hours. Which other planet has a similar day duration to us? __________________________________________________________________ Which planet has the longest day? __________________________________________________________________ This means that Venus has the slowest rotation. Which planet has the fastest rotation? __________________________________________________________________ Earth orbits the sun creating seasons Earth revolves around the sun every _____________________. We refer to this as a year. When you have your birthday, you have completed another full _______________ around the sun! Earth (as well as all the other planets) revolves around the sun in an anticlockwise direction. Again, you don’t need to learn the picture below, but it’s really interesting to note how long it takes other planets to revolve around the sun. © e-classroom www.e-academyonline.co.za www.e-classroom.co.za Which planet has the shortest year? __________________________________________________________________ Which planet has the longest year? __________________________________________________________________ One year on Neptune is 165 years on Earth. This means that it takes 165 Earth years for Neptune to complete a full rotation around the sun.As you can see from the picture below, as the Earth orbits the sun, the angle of the tilt does not change. Look at the diagram below. It shows four different seasons as Earth orbits the sun. © e-classroom www.e-academyonline.co.za www.e-classroom.co.za As you can see, the intensity of the sun’s radiation at different places changes throughout the year. This happens because the tilt of the axis does not change. What is intensity in this context? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ When the hemisphere is tilted towards the sun, what can you say about the intensity? Explain. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ When the hemisphere is tilted away from the sun, what can you say about the intensity? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Because different intensities of light reach the northern and southern hemispheres at different times of year, we get different seasons. When a hemisphere is tilted towards the sun, what season will it be? ______________. When a hemisphere is tilted away from the sun, what season will it be? ______________. It is because of that tilt towards the sun in summer that makes summer days longer than winter days. When it’s winter in the northern hemisphere, it’s summer in the southern hemisphere. When it’s summer in the northern hemisphere, it’s winter in the southern hemisphere. In between winter and summer it is spring and autumn (fall). The equator hardly experiences any seasonal changes. © e-classroom www.e-academyonline.co.za www.e-classroom.co.za