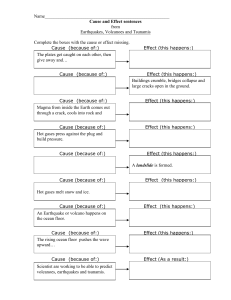
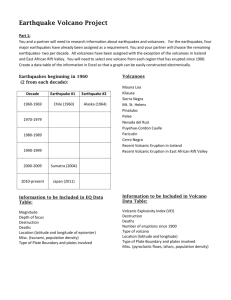
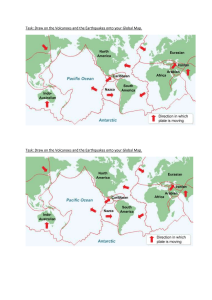
GEOGRAPHY SE1 PREP EARTHQUAKES: CAUSES AND IMPACTS. 1) What are earthquakes? A. When 2 plates move together, apart or against each other it leads to build up of pressure which creates an earthquake when it is released. Epicenter: The center of the earthquake, on the surface of the earth. Focus: The location where the build up of pressure occurs in the crust. Richter Scale: The strength of the earthquake is measured on this scale. Seismometer: The device used to measure the strength of seismic waves spreading from the focus. The CLOSER to the epicenter the HIGHER is the intensity of the earthquake. 2) Consequences: Significant damage to infrastructure. (ST, LT) Injury and Death. (trapped in remains of buildings) (ST) Diseases in the aftermath of the earthquake. (ST) Spread of fire, landslides, and flooding. (ST) Inc. in crime levels as ppl will start stealing because of poverty caused by the damage of the earthquake. (ST) Rebuilding of damaged places. (LT) 3) Response and Action: Immediate search and rescue operation. Demolish, repair, patch up and planning phase. Rebuild, replace, restore and improve. 4) How they can be reduced. 3 Ps: PREDICT PROTECT PREPARE. VOLACNOES CAUSES AND IMPACTS: 1) What are volcanoes? A. Volcanoes are openings in the ground where magma from deep inside the earth makes its way to the surface B. When magma erupts it become lava, oozing out of the ground. When it cools it forms rock. BASIC INFO AND TERMS: They tend to occur on Convergent and Divergent boundaries. RING OF FIRE: belt of freq. volcanic eruption around the edge of Pacific Ocean. Volcanoes and earthquakes usually occur in the same places and are found in zones of activity. Main zones of activity: West American Ocean, Indian and Pacific Oceans Volcanoes might be dormant, active or extinct. 2) SHORT-TERM IMPACTS OF VOLCANOES: Eruptions and Lava Flows Ash Clouds and Pyroclastic Flows Immediate Loss of Life and Property. 3) LONG-TERM IMPACTS OF VOLCANOES: Soil Fertility New Landforms Climate Impact Economic Impact 4) TYPES OF VOLCANOES: Shield Volcano: - Broad, gently sloping volcano. - Formed by low-viscosity lava flows. - Eruptions are generally non-explosive. - Commonly found at divergent plate boundaries. - E.g.: Mauna Kea and Mauna Loa in HAWAII Cinder Cone Volcano: - Steep-sided, conical volcano. - Formed from ejected volcanic fragments (cinders). - Eruptions are typically short-lived and explosive. - Smaller in size compared to other types. - e.g.: Paricutin in Mexico Composite Volcano: - Tall, symmetrical volcano with steep sides. - Built up by alternating layers of lava flows, ash, and volcanic rocks. - Eruptions can be both explosive and effusive. - Found at convergent plate boundaries. - e.g.: Mount Fuji in Japan. Dome Volcano: - Volcano with a dome-shaped appearance. - Formed by the slow extrusion of highly viscous lava. - Eruptions are characterized by the building of the dome. - Can result in explosive activity if the dome collapses. - e.g.: The Yellowstone Caldera in Western US 5) Why is the ring of fire situated where it is right now? The abundance of volcanoes and earthquakes around the ring of fire is caused by the amount of movement of tectonic plates in the area. Along much of the Ring of Fire, plates overlap at convergent boundaries called subduction zones. TSUNAMIS CAUSES AND IMPACTS: 1) What is a tsunami? A. A tsunami is a series of ocean waves that sends surges of water, sometimes reaching heights of over 100 feet (30.5 meters), onto land. CAUSES OF TSUNAMIS: Underwater earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, or landslides. Displacement of ocean water due to sudden vertical movement of the seafloor. Generates powerful ocean waves with long wavelengths. High-speed tsunami waves travel across deep ocean basins. Can inundate coastal areas upon reaching shallower waters. 2) SHORT TERM IMPACTS OF TSUNAMIS: Immediate flooding of coastal areas. Rapid destruction of infrastructure and homes. High casualties and loss of life. Displacement of populations. 3) LONG-TERM IMPACTS OF TSUNAMIS: Economic downturn due to damaged infrastructure. Ongoing psychological trauma for survivors. Environmental changes affecting ecosystems. Rebuilding and recovery efforts extend over years. PREPARATION AND MANAGEMENT 1) FACTORS INFLUENCING THE IMPACT OF A NATURAL DISASTER: Wealth And Level of Development Time Population Weather And Climate