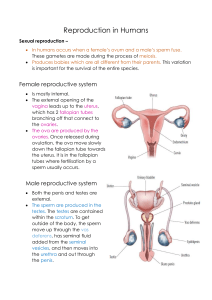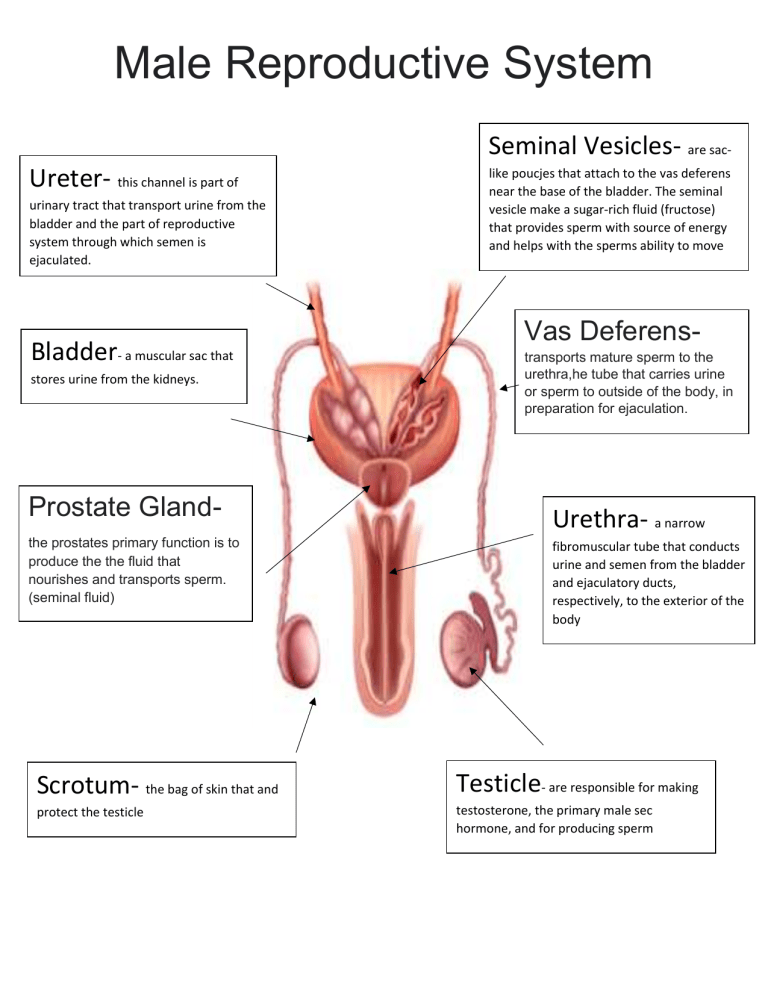
Male Reproductive System Seminal Vesicles- are sacUreter- this channel is part of urinary tract that transport urine from the bladder and the part of reproductive system through which semen is ejaculated. Bladder- a muscular sac that stores urine from the kidneys. Prostate Glandthe prostates primary function is to produce the the fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. (seminal fluid) like poucjes that attach to the vas deferens near the base of the bladder. The seminal vesicle make a sugar-rich fluid (fructose) that provides sperm with source of energy and helps with the sperms ability to move Vas Deferenstransports mature sperm to the urethra,he tube that carries urine or sperm to outside of the body, in preparation for ejaculation. Urethra- a narrow fibromuscular tube that conducts urine and semen from the bladder and ejaculatory ducts, respectively, to the exterior of the body Scrotum- the bag of skin that and Testicle- are responsible for making protect the testicle testosterone, the primary male sec hormone, and for producing sperm Female Reproductive System Cervix- The cervix is the lower portion of the uterus, an organ of the female reproductive tract. . It connects the vagina with the main body of the uterus, acting as a gateway between them. Fallopian Tube- are the female structures that transport the ova from the ovary to the uterus each month. In the presence of sperm and fertilization, the Fallopian tubes transport the fertilized egg to the uterus for implantation. Uterus- organ that receives the Ovary-produce, store, and release eggs into the fallopian tubes in the process called ovulation fertilized egg and supports its development during pregnancy. Vagina- a canal that joins the cervix (the lower part of uterus) to the outside of the body. It also is known as the birth canal. Give the functions of the following below: 1. Testosterone- is a hormone produced by the human body. It's mainly produced in men by the testicles. Testosterone affects a man's appearance and sexual development. It stimulates sperm production as well as a man's sex drive. It also helps build muscle and bone mass. 2. Estrogen- to regulating the menstrual cycle, estrogen affects the reproductive tract, the urinary tract, the heart and blood vessels, bones, breasts, skin, hair, mucous membranes, pelvic muscles, and the brain. 3. Progesterone- Progesterone prepares the endometrium for the potential of pregnancy after ovulation. It triggers the lining to thicken to accept a fertilized egg. It also prohibits the muscle contractions in the uterus that would cause the body to reject an egg. Medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone. It is a progestogen and is used in combination with estrogens mainly in hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and low sex hormone levels in women. 4. FSH- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is a gonadotropin, a glycoprotein polypeptide hormone. FSH is synthesized and secreted by the gonadotropic cells of the anterior pituitary gland, and regulates the development, growth, pubertal maturation, and reproductive processes of the body. 5. LH- LH is made by your pituitary gland, a small gland located underneath the brain. LH plays an important role in sexual development and functioning. In women, LH helps control the menstrual cycle. It also triggers the release of an egg from the ovary. This is known as ovulation. 6. Menstrual Cycle- The menstrual cycle is the regular natural change that occurs in the female reproductive system that makes pregnancy possible. The cycle is required for the production of oocytes, and for the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy. The menstrual cycle occurs due to the rise and fall of estrogen.