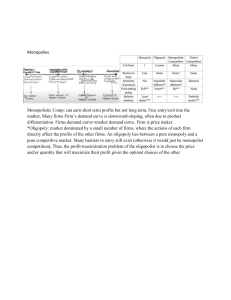
Chapter 14 Economics Notes What is Oligopoly? - Lies between perfect competition and monopoly Natural or legal barriers prevent the entry of new firms A small number of firms compete Duopoly: an oligopoly market with two firms - Ex. two taxi companies, two car rental firms - In part a, one firm produces the efficient scale of 30 rides a day, so two firms can satisfied the market demand - This market is a natural oligopoly with two firms, a natural duopoly In part b, the efficient scale of one firm is 20 rides per day, so three firms can satisfy the market demand at the lowest possible price, the natural oligopoly has three firms Legal oligopoly arises when a legal barrier to entry protects the small number of firms in a market Because barriers to entry exist, oligopoly consists of a small number of firms - Interdependence: with small number of firms in market, each firm’s actions influence the profits of all other firms - - - - Temptation to Cooperate: when a small number of firms share a market, they can increase their profits by forming a cartel and acting like a monopoly - Cartel: group of firms acting together, colluding, to limit output, raise price and increase economic profit HHI or Herfindahl-Hirschman Index divides oligopoly from monopolistic competition is generally taken to be 2500 - HHI < 2500 is an example of monopolistic competition - HHI > 2500 is an example of oligopoly Oligopoly Games - Game Theory: set of tools for studying strategic behaviour - All games share four common features - Rules - Strategies - Payoffs - Outcome - Art and Bob steal a car, receive 2 years each for their crime - How does the judge extract a confession to a crime she thinks they committed prior to this one? Prisoners game - If both confess to larger crime, each will receive 3 years for both crimes - If one alone confesses, he will receive only 1 year will other will receive 10 years - Art and Bob have two possible actions 1. Confess to the bank robbery 2. Deny having committed the bank robber - There are four possible outcomes 1. Both confess 2. Both deny 3. Art confesses and Bob denies 4. Bob confesses and Art denies - Payoff Matrix: table that shows the payoffs for every possible action by each player for every possible action by each other player - Nash Equilibrium: player A takes best possible action given the action of player B, and player B takes the best possible action given the action of player A → Bob’s Choices - CONFESS: Art confesses (3 years vs 10 years) DENY: Art confesses (1 year vs 2 years) → Art’s Choices - - CONFESS: Bob confesses (3 years vs 10) - DENY: Bob confesses (1 year vs 2 years) Thus, each player’s best action is to confess Nash equilibrium for prisoners’ dilemma is called Dominant-Strategy Equilibrium: equilibrium in which the best strategy of each player it to cheat (confess) → The Dilemma - Dilemma arises as each prisoner contemplates the consequences of his decision and puts himself in the place of his accomplice Each knows that it would be best if both denied, but each also knows that if he denies, it is in the best interest of the other to confess - Each considers whether to deny and rely on his accomplice to deny or confess hoping his accomplice denies but expecting him to confess → A Bad Outcome - For the prisoners, the equilibrium of the game, with each confessing, is not the best outcome If neither of them confesses, each gets only two years for the lesser crim Each player can put himself in the other’s player’s place, and so each player can figure out that there is a best strategy for each of them Each knows that he can serve 2 years ONLY if he can trust the other to deny Each player also knows it is not in best interest of other to deny → An Oligopoly Price-Fixing Game - Cost and Demand Conditions - Two firms A and B have identical costs - Two firms can produce this good at a lower cost than either one firm or three firms can - If they enter a collusive agreement (agreement between two or more producers to form a cartel to restrict output, raise the price and increase profits) - The firms in a cartel can pursue two strategies, comply or cheat - A firm that complies carries out the agreement - A firm that cheats breaks agreement to own benefit and cost to other firm - There are four possible combinations 1. Both firms comply 2. Both firms cheat 3. Trick complies and Gear cheats 4. Gear complies and Trick cheats - Only thing firms in duopoly must do beyond what a monopoly does is to agree on how much of the total output each of them will produce - MC1 is the industry marginal cost curve if each firm produces the same quantity of output - Curve is constructed by added together outputs of two firms at each level of marginal cost - Because the two firms are the same size, at each level of marginal cost, the industry output is twice the output of one firm - The curve MC1 in part B is twice as far to the right as the curve MC in part A - To maximize industry profit, firms in duopoly agree to restrict output to the rate that makes the industry marginal cost and marginal revenue equal LOOK AT TEXTBOOK TO EXPLAIN SPECIFIC CASE A Game of Chicken - Not all games have a unique equilibrium, and one that does not is a game called “chicken” LOOK AT TEXTBOOK TO EXPLAIN SPECIFIC GAME