Information Systems: Types, Levels, and Decision Support
advertisement
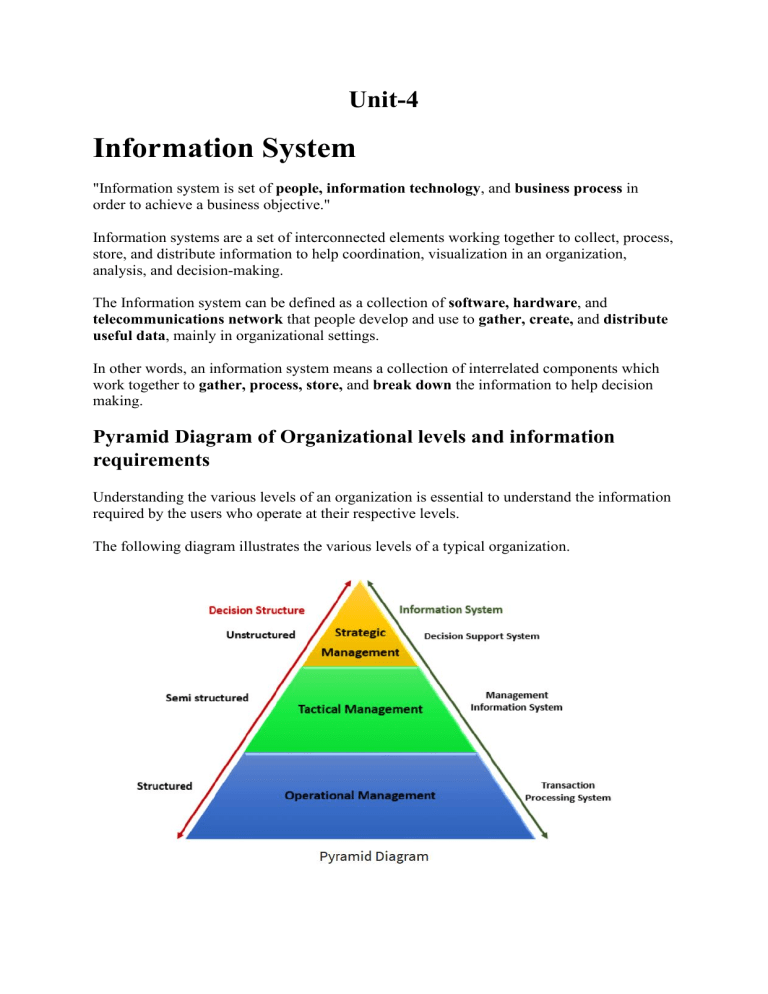
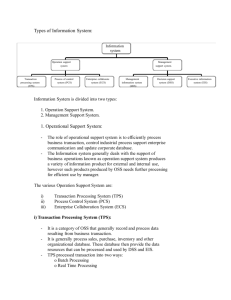
Unit-4 Information System "Information system is set of people, information technology, and business process in order to achieve a business objective." Information systems are a set of interconnected elements working together to collect, process, store, and distribute information to help coordination, visualization in an organization, analysis, and decision-making. The Information system can be defined as a collection of software, hardware, and telecommunications network that people develop and use to gather, create, and distribute useful data, mainly in organizational settings. In other words, an information system means a collection of interrelated components which work together to gather, process, store, and break down the information to help decision making. Pyramid Diagram of Organizational levels and information requirements Understanding the various levels of an organization is essential to understand the information required by the users who operate at their respective levels. The following diagram illustrates the various levels of a typical organization. Operational management level The operational level is concerned with performing day to day business transactions of the organization. Examples of users at this level of management include cashiers at a point of sale, bank tellers, nurses in a hospital, customer care staff, etc. Users at this level use make structured decisions. This means that they have defined rules that guides them while making decisions. For example, if a store sells items on credit and they have a credit policy that has some set limit on the borrowing. All the salesperson needs to decide whether to give credit to a customer or not is based on the current credit information from the system. Tactical Management Level This organization level is dominated by middle-level managers, heads of departments, supervisors, etc. The users at this level usually oversee the activities of the users at the operational management level. Tactical users make semi-structured decisions. The decisions are partly based on set guidelines and judgmental calls. As an example, a tactical manager can check the credit limit and payments history of a customer and decide to make an exception to raise the credit limit for a particular customer. The decision is partly structured in the sense that the tactical manager has to use existing information to identify a payments history that benefits the organization and an allowed increase percentage. Strategic Management Level This is the most senior level in an organization. The users at this level make unstructured decisions. Senior level managers are concerned with the long-term planning of the organization. They use information from tactical managers and external data to guide them when making unstructured decisions. Types of Information System The types of information systems are as follows: Transaction Processing System (TPS): • • • • The term "transaction processing system" refers to an information system that processes data are originating from business transactions. The primary purpose of a transaction processing system is to offer transactions to update records and produce reports required for storekeeping. Online Transaction Processing and Batching Processing are the methods which we used to complete the transaction. Examples of transaction processing systems are Stock control systems, Payroll systems, Bill systems. Transaction processing system meaning refers to an information processing system that processes all transactions taking place within the business. Such transactions include modification, collection, and retrieval of transaction data. A TPS is highly consistent, efficient, and dependable. It is the same system that online businesses utilize for e-commerce. A TPS has the following four components. One must understand them to know how the system works. 1. Inputs: Inputs are original requests for payments or products outside parties send to an organization’s TPS. Typically, inputs include bills, coupons, custom orders, and invoices. 2. Output: Outputs are the documents a TPS generates after it processes all inputs, for example, the receipts stored by companies in their records. Such documents help validate transactions and offer crucial reference details for tax and multiple official purposes. 3. Storage: A TPS’s storage component is where organizations keep their output and input data. Some businesses store the documents in a database. This component ensures the security, accessibility, and organization of all documents for late use. 4. Processing System: The processing system goes through every input and establishes a useful output, for example, a receipt. It helps outline the input data and defines what the outputs must be. One must remember that the processing time varies depending on the type of TPS an organization uses. Features The following are some crucial features of a TPS: • • • • • • Controlled Access: TPSs are powerful business tools. Hence, only authorized employees can access it. In other words, it allows only certain employees to control and process transactions. Connection With the External Environment: TPS establishes a relationship with the external environment by distributing information to suppliers and customers. Fast Response: This feature is crucial for a TPS as organizations cannot afford to keep their customers waiting long before completing a transaction. Inflexibility: A TPS processes all transactions in the same way, irrespective of the time of day, user, or customer, to maximize efficiency. Reliability: A TPS must be reliable as customers do not tolerate errors; it must have adequate security and safety measures. Distribution Of Details to Other Systems: A TPS produces and distributes information to different systems. For instance, sales processing systems provide information to general ledger systems. Types of transaction processing systems There are two types of transaction processing systems: Batch processing Through batch processing, a TPS interprets sets, or batches, of data by grouping items based on similarities. Batch processing can create a time delay because it reviews several sets of data simultaneously, requiring more computing power. Example: A customer pays for a subscription service at the end of the month, The TPS system processes the transactions as a batch because they occur at the same time. In this case, a delay in processing transactions is acceptable because the system only interprets batches once per month. Real-time processing Real-time processing is a method to process transactions as they appear. This helps prevent delays in processing and can provide a more accurate result. Example: An e-commerce website might use a TPS to process credit card transactions in realtime to ensure payment before the company starts its fulfillment process. Processing transactions in real-time also helps the company identify and address errors quickly, as well as increase its overall response times. Advantages • • • • A TPS helps organizations save funds by minimizing their need to improve their system or utilize multiple systems to fulfill demand. Companies can use a TPS to process transactions accurately and quickly. A TPS automates a significant part of a company’s revenue management and internal resources. Because of this, employees can review transactions faster. Moreover, this gives them more time to focus on critical thinking tasks. It allows businesses to carry out operations in multiple segments by working remotely. This enables organizations to explore new markets that are full of opportunities. Disadvantages • • • • A TPS does not have a standard format. Companies have to incur a high set-up cost initially for TPS. Sometimes, hardware and software have compatibility issues. A TPS may stop working or slow down due to many transactions. Decision Support System (DSS) A decision support system (DSS) is a computerized program used to support determinations, judgments, and courses of action in an organization or a business. A DSS sifts through and analyzes massive amounts of data, compiling comprehensive information that can be used to solve problems and in decision-making. Typical information used by a DSS includes target or projected revenue, sales figures or past ones from different time periods, and other inventory- or operations-related data. • • • A decision support system (DSS) is a computerized system that gathers and analyzes data, synthesizing it to produce comprehensive information reports. A decision support system differs from an ordinary operations application, whose function is just to collect data. Decision support systems allow for more informed decision-making, timely problemsolving, and improved efficiency in dealing with issues or operations, planning, and even management. Characteristics of a DSS • • • • • • • Support for decision-makers in semi-structured and unstructured problems. Support for managers at various managerial levels, ranging from top executive to line managers. Support for individuals and groups. Less structured problems often requires the involvement of several individuals from different departments and organization level. Support for interdependent or sequential decisions. Support for intelligence, design, choice, and implementation. Support for variety of decision processes and styles. DSSs are adaptive over time. Components of a Decision Support System The three main components of a DSS framework are: 1. Model Management System The model management system S=stores models that managers can use in their decisionmaking. The models are used in decision-making regarding the financial health of the organization and forecasting demand for a good or service. 2. User Interface The user interface includes tools that help the end-user of a DSS to navigate through the system. 3. Knowledge Base The knowledge base includes information from internal sources (information collected in a transaction process system) and external sources (newspapers and online databases). Types of Decision Support Systems • • • • • Communication-driven: Allows companies to support tasks that require more than one person to work on the task. It includes integrated tools such as Microsoft SharePoint Workspace and Google Docs. Model-driven: Allows access to and the management of financial, organizational, and statistical models. Data is collected, and parameters are determined using the information provided by users. The information is created into a decision-making model to analyze situations. An example of a model-driven DSS is Dicodess – an open-source model-driven DSS. Knowledge-driven: Provides factual and specialized solutions to situations using stored facts, procedures, rules, or interactive decision-making structures like flowcharts. Document-driven: Manages unstructured information in different electronic formats. Data-driven: Helps companies to store and analyze internal and external data. Advantages of a Decision Support System • • • • A decision support system increases the speed and efficiency of decision-making activities. It is possible, as a DSS can collect and analyze real-time data. It promotes training within the organization, as specific skills must be developed to implement and run a DSS within an organization. It automates monotonous managerial processes, which means more of the manager’s time can be spent on decision-making. It improves interpersonal communication within the organization. Disadvantages of a Decision Support System • • • • The cost to develop and implement a DSS is a huge capital investment, which makes it less accessible to smaller organizations. A company can develop a dependence on a DSS, as it is integrated into daily decisionmaking processes to improve efficiency and speed. However, managers tend to rely on the system too much, which takes away the subjectivity aspect of decision-making. A DSS may lead to information overload because an information system tends to consider all aspects of a problem. It creates a dilemma for end-users, as they are left with multiple choices. Implementation of a DSS can cause fear and backlash from lower-level employees. Many of them are not comfortable with new technology and are afraid of losing their jobs to technology. Experts System An expert system is the highest form of management computing office automation which allows the communication and manipulation of documents. Decision support systems aid in problem solving by allowing for manipulation of data and models. Expert systems go beyond traditional manipulation of this type as they allow experts to ‘teach’ computers about their fields so that the system may support more of the decisionmaking process for less expert decision makers. In this sense, an expert system is software that contains a knowledge base of facts and relationships and has the ability to make inferences based on that knowledge base. An expert system is a computer-based information system in which knowledge is represented in data, in which the processing of the knowledge is directed primarily by computer programs. Expert systems represent one of the most advanced facts of information technology. That is, they aid people in some of the most complex and least understood human information handling tasks, i.e., decision making, problem solving, diagnosis and learning. They do this by storing a large amount of factual information on a subject area, together with lines of reasoning employed by human experts in that area. Most of this material is supplied to the program at the time it is written, but it also has facilities for adding to this base of information as it is applied in new situations. The subject expertise is provided initially by interviews and observations of successful PR actioners of the subject. Expert system is software, which is used by the business executives to solve complex organizational problems. These are the programs, which act both as intelligently and as an expert in some area of knowledge. Modern business managers perform their duties under dynamic environment. Due to the complexity in the way, the business is conducted. There are number of variables which are involved in decision making. This has made the overall decision-making process very complex to analyze the alternatives manually. The role of operation research has been increasingly important in solving managerial problems. Expert systems are the programs, which incorporate all these decision-making techniques. Expert System Components The key components of Expert System are as followings, 1. User Interface: It contains a computerized system between the user and the machine for friendly communication. This system provides an interface to the user in a graphical way. 2. Interference Engine: It regains & determines the data process. It performs this task to deduce new facts which are subsequently used to draw further conclusions. This component is associated with an expert system as the brain of the expert system. 3. Knowledge Base: This is the most important element of an expert system because it holds the expert's knowledge of problem-solving. It is here that the expert's elicited knowledge is stored. It contains the rules, facts, and object descriptions, etc. The knowledge base is always stored in the data with the newest expert system products. The knowledgebase information is all that is needed to understand & formulate the problem, and then solve it. 4. Data Acquisition Subsystem: The specialist has to learn the information reflected in the knowledge base. Information acquisition software is used by a person who has problem experience to build, incorporate or modify the base of knowledge. Potential knowledge sources include human experts, research reports, textbooks, databases, and the experience of the user himself. Advantages of Expert System Expert System (ES) gives clear responses for routine actions, procedures, and activities. • • Expert System (ES) retains significant levels of the knowledge base. Expert System (ES) supports organizations to explain the rationale of their decisionmaking. Disadvantages Expert System • • • Expert System (ES) doesn't reply creatively as a human expert in unusual ways. Expert System (ES) requires more technical aspects due to this difficult in use. Highly costlier system. Executive Information System An Executive Information System (EIS) is a kind of decision support system (DSS) used in organizations to help executives in decision making. It does so by providing easy access to important data needed in an organization to achieve strategic goals. An EIS usually has graphical displays on a user-friendly interface. Executive information systems can be used for monitoring company performance in many different types of organizations as well as for identifying opportunities and problems. Early executive information systems were developed on mainframe computers as computerbased programs to provide the description, sales performance and/or market research data for senior executives of a company. Executives, however, were not all literate or confident about the computers. Also, EIS data endorsed only executive-level decisions that did not necessarily support the entire company or enterprise. HOW AN EIS SHOULD BE? • • • • • • EIS should be very easy to understand so that the users do not get confused while using it. A user-friendly EIS can help management to save time and collect information rather easily. EIS should be such that it helps in achieving organizational objective. EIS data should clearly reflect objectives of the organization in various core fields of the organization. EIS should be such that it encourages staff & management to work towards growth of the organization. EIS must be such that it meets the changing needs of the organization. EIS should help to reduce the workload of the top management and staff. Confidential Information should not become part of the EIS. Executive Information System (EIS) Characteristics The below mentioned figure describes about key characteristics of EIS, • • • • • Detailed data – EIS provides absolute data from its existing database. Integrate external and internal data – EIS integrates integrate external and internal data. The external data collected from various sources. Presenting information – EIS represents available data in graphical form which helps to analyze it easily. Trend analysis – EIS helps executives of the organizations to data prediction based on trend data. Easy to use – It is a very simplest system to use. COMPONENTS OF EIS • • • • USER INTERFACE: User Interface allows the users to communicate with the EIS. User interface must be easy to use and understand. Users should not be required to understand the complex query languages and other mathematical or statistical formulas. HARDWARE: Hardware refers to devices by which users give input, data processing and the output is received. Users may give input via keyboard and mouse and CPU may be used for processing and output may be received on monitor or from printer. SOFTWARE: Software is required for various calculations, providing graphical view to the management, storing data in the form of Information, etc. Software allows user to get information in the form it is actually required. TELECOMMUNICATION: In today’s world the most important thing is communication. Users may require transferring information from one point to another point. The information might be a little confidential in nature. The secrecy of the information should be well maintained. APPLICATIONS OF EIS • • • MANUFACTURING: It determines whether a process is running correctly or not. It helps in ensuring proper quality control of finished goods. It measures the actual process time and compares with the standard time required for the process. It provides management with daily production report, daily consumption report, safety stock report, economic order quantity, etc. FINANCIAL: Every organization needs to ensure financial activities are running sound. EIS may help to analyze whether payment has been realized from creditors within stipulated period of time. It can help management in managing various other sources of finance. ACCOUNTING: It helps in proper accounting and disbursement of accounting functions. ADVANTAGES • • • • EIS is easy for use and saves time of the top-level management of the organization. EIS provide access to timely information in a rapid manner. EIS provides extensive online analysis tools. EIS can easily be given a DSS support. Knowledge Management System Knowledge management (KM) is the process of identifying, organizing, storing, and disseminating information within an organization. When knowledge is not easily accessible within an organization, it can be incredibly costly to a business as valuable time is spent seeking out relevant information versus completing outcome-focused tasks. A knowledge management system (KMS) harnesses the collective knowledge of the organization, leading to better operational efficiencies. These systems are supported by the use of a knowledge base. They are usually critical to successful knowledge management, providing a centralized place to store information and access it readily. Companies with a knowledge management strategy achieve business outcomes more quickly as increased organizational learning and collaboration among team members facilitates faster decision-making across the business. It also streamlines more organizational processes, such as training and on-boarding, leading to reports of higher employee satisfaction and retention. Types of knowledge The definition of knowledge management also includes three types of knowledge—tacit, implicit, and explicit knowledge. These types of knowledge are largely distinguished by the codification of the information. • • • Tacit knowledge: This type of knowledge is typically acquired through experience, and it is intuitively understood. As a result, it is challenging to articulate and codify, making it difficult to transfer this information to other individuals. Examples of tacit knowledge can include language, facial recognition, or leadership skills. Implicit knowledge: While some literature equivocates implicit knowledge to tacit knowledge, some academics break out this type separately, expressing that the definition of tactic knowledge is more nuanced. While tacit knowledge is difficult to codify, implicit knowledge does not necessarily have this problem. Instead, implicit information has yet to be documented. It tends to exist within processes, and it can be referred to as “know-how” knowledge. Explicit knowledge: Explicit knowledge is captured within various document types such as manuals, reports, and guides, allowing organizations to easily share knowledge across teams. This type of knowledge is perhaps the most well-known and examples of it include knowledge assets such as databases, white papers, and case studies. This form of knowledge is important to retain intellectual capital within an organization as well as facilitate successful knowledge transfer to new employees. Knowledge management process Effective knowledge management system typically goes through three main steps: 1. Knowledge Creation: During this step, organizations identify and document any existing or new knowledge that they want to circulate across the company. 2. Knowledge Storage: During this stage, an information technology system is typically used to host organizational knowledge for distribution. Information may need to be formatted in a particular way to meet the requirements of that repository. 3. Knowledge Sharing: In this final stage, processes to share knowledge are communicated broadly across the organization. The rate in which information spreads will vary depending on organizational culture. Companies that encourage and reward this behavior will certainly have a competitive advantage over other ones in their industry. Knowledge management tools There are a number of tools that organizations utilize to reap the benefits of knowledge management. Examples of knowledge management systems can include: • • • • • Document management systems act as a centralized storage system for digital documents, such as PDFs, images, and word processing files. These systems enhance employee workflows by enabling easy retrieval of documents, such as lessons learned. Content management systems (CMS) are applications which manage web content where end users can edit and publish content. These are commonly confused with document management systems, but CMSs can support other media types, such as audio and video. Intranets are private networks that exist solely within an organization, which enable the sharing of enablement, tools, and processes within internal stakeholders. While they can be time-consuming and costly to maintain, they provide a number of groupware services, such as internal directories and search, which facilitate collaboration. Wikis can be a popular knowledge management tool given its ease of use. They make it easy to upload and edit information, but this ease can lead to concerns about misinformation as workers may update them with incorrect or outdated information. Data warehouses aggregate data from different sources into a single, central, consistent data store to support data analysis, data mining, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning. Data is extracted from these repositories so that companies can derive insights, empowering employees to make data-driven decisions. Benefits of knowledge management Companies experience a number of benefits when they embrace knowledge management strategies. Some key advantages include: • Identification of skill gaps: When teams create relevant documentation around implicit or tacit knowledge or consolidate explicit knowledge, it can highlight gaps in core competencies across teams. This provides valuable information to management to form new organizational structures or hire additional resources. • • • • • Make better informed decisions: Knowledge management systems arm individuals and departments with knowledge. By improving accessibility to current and historical enterprise knowledge, your teams can upskill and make more information-driven decisions that support business goals. Maintains enterprise knowledge: If your most knowledgeable employees left tomorrow, what would your business do? Practicing internal knowledge management enables businesses to create an organizational memory. Knowledge held by your long-term employees and other experts, then make it accessible to your wider team. Operational efficiencies: Knowledge management systems create a go-to place that enable knowledge workers to find relevant information more quickly. This, in turn, reduces the amount of time on research, leading to faster decision-making and costsavings through operational efficiencies. Increase productivity not only saves time, but also reduces costs. Increased collaboration and communication: Knowledge management systems and organizational cultures work together to build trust among team members. These information systems provide more transparency among workers, creating more understanding and alignment around common goals. Engaged leadership and open communication create an environment for teams to embrace innovation and feedback. Data Security: Knowledge management systems enable organizations to customize permission control, viewership control and the level of document-security to ensure that information is shared only in the correct channels or with selected individuals. Give your employees the autonomy access knowledge safely and with confidence. Recent Developments in the Field of Information Technology New trends arise within this industry every year, and it becomes essential for professionals to be familiar with these different trends and all that they entail. No matter what profession one is working in, being familiar with these can improve your professional standing and help you understand the potential upgrades for the industry you are already working in. 1. Cloud Computing One of the biggest trends that have emerged during the past year is cloud computing. More and more industries realize that it is essential for a company to have a designated place for all of its digital information and resources. Having a well-protected place that can take care of everything and keep the information safe has almost become a necessity. Cloud computing is the go-to solution for brands who want to improve their work and make it more efficient digitally. 2. Mobile Apps Mobile applications have only grown in popularity over the past few years, and this year, they are surfacing in bigger and better ways. Brands and industries worldwide are trying to improve their work by using mobile apps and implementing new resources that can make working on the go more efficient. 3. Big Data Analytics Big data analytics is a trend that has grown over the past few years. This is implemented in almost every industry using large-scale production processes, manufacturing, and supply. Big data analytics allows brands to process their information better and better understand the areas they need to develop. 4. Automation Automation is one trend that has primarily hit the manufacturing and production units and is estimated to only grow more in the coming years. Automation has also enabled processes to work faster and would allow companies to reach their goals much more efficiently. 5. Artificial Intelligence While automation grows, artificial intelligence is now seeing the light of day. The past year saw the introduction of several new mediums of artificial intelligence. This year, industries are looking at ways in which they can grow these resources and implement the work they do. Artificial intelligence is now starting to see implementation on a larger scale which is only set to grow more over the coming years. 6. Smart Technology Intelligent machines that use artificial intelligence or automation are on the rise, even in small-scale units and smaller implementations. Homes are becoming more innovative due to the intelligent technology used and opted for in homes. Simple tools such as Alexa have become essential to homes and are only estimated to increase over the next year. 7. Virtual Reality The gaming industry has always been one that has experienced growth alongside the field of information technology, and virtual reality has taken this one step further, giving customers the epitome of digital experience. Virtual reality gaming has already started to become popular due to new technology, which improves how the industry can grow. 8. Augmented Reality Augmented reality is another approach to ‘artificial experiences’ that individuals are now given access to. This has improved how the field has been able to develop. Augmented reality is seeing a lot more applicability outside the gaming industry as well and is something that is seeing more implementation as compared to virtual reality. 9. Blockchain Data Cryptocurrency might have been at an all-time high in 2017 and 2018, but the fact remains that this is yet to see significant development. Blockchain technology is only starting to grow in popularity and is being implemented by industries worldwide for all it offers. 10. CyberSecurity With the growth of digital mediums and technology, the potential threats that people can face are only rising. Because of this, cybersecurity has had to grow extensively over the past few years to stay in touch with the growth experienced. Industries all over the world also realize the importance of investing in cybersecurity, which is why the field is experiencing growth at such a rapid pace. 11. Growth of IoT Networks The Internet Of Things is a concept that all digital devices are connected by a single medium through which one can control everything within their home. More and more brands realize that this is indeed the way of the future and is within technological reach. More brands are beginning to incorporate this concept, and the statistics showcasing this are prevalent enough to attest to positive growth. 12. Predictive Analytics Implementations Predictive Analytics is analyzing large volumes of data to conclude the possible outcomes that a situation might have. Market analysts see this as a unique tool for brands to note whether they should move in a particular direction. This has proven to be a very efficient analysis method and saves the industry an incredible amount of money. 13. Cloud Migration Cloud migration has proven incredibly beneficial for businesses that want to move in a digital direction and maintain better digital data records. Cloud migration has grown over the past few years, and these statistics show positive results. More than 74% of CFOs state that cloud migration was one of the most beneficial things for the growth of their businesses. 14. Rise Of Data Officers With the growing importance of information technology and data analytics, data officers have become even more critical in institutions and industries worldwide. The number of positions open within this is plenty and is growing as more and more businesses require someone proficient in this. 15. Quantum Computing Applications Quantum Computing is a process of conducting complex equations and functions to perform several complex tasks or process large volumes of information with absolute ease. This has proven incredibly beneficial for various industries and is seeing massive growth. 16. Smart Technology Homes are now becoming more intelligent thanks to the numerous integrated devices that work to make our lives easier. Things like Alexa and other supplementary resources have proven incredibly beneficial, making homes significantly more efficient and safer. 17. Open-Source Solutions Open-Source programs give users access to some of the main files and frameworks in a particular program, enabling them to modify it easily. As more and more users become technologically proficient, allowing them to work with applications themselves is incredibly beneficial. 18. Edge Computing Edge computing is one phenomenon that has grown over the past few years and is currently seeing a wide scale of implementation. In edge computing, large volumes of data are processed near the network’s edge rather than where the data is mainly generated. This is meant to make this processing more efficient and optimized. More development mediums are choosing to go in for this form of computing over traditional types because of its efficiency. This also attests to the rising number of computing and program generation methods. 19. Rise Of Chatbots While most tech advancements help us move toward the greater good, some aren’t as beneficial as we might think. Chatbots aren’t always bad because, in some situations, they have improved the customer service that we have access to. Chatbots are a program to respond to specific queries in specific ways and are designed to help customers with some of the more basic functions they would need. These are, of course, still not in a position wherein they are a complete substitute for absolute live customer service, which has helped them stay in development. Impact of IT on Organization What is information technology? IT refers to the study and application of computing and telecommunications systems for information storage, analysis, transmission, delivery, retrieval, and manipulation. Information technology (IT) refers to the people, software, Internet, and hardware that work together to conduct an organization’s most fundamental, automated functions. Commonly referred to as “IT techs” or “IT technicians,” IT professionals research and collaborate with businesses to help them determine the types of technology they require and the benefits of IT, then assist those firms in implementing, maintaining, and servicing those solutions. Explore- marketing information technology. Why is information technology important? Information Technology entails creating, upkeep, and using computer systems, software, and networks to process and disperse information. It encompasses the individuals who work in the field of computing as well as the hardware, software, networks, and the Internet. Now, let’s learn why information technology is important. Along with this, you can explore – the importance of information in gaining insights. Impact of information systems on organizations Information systems have a greater impact on an organization. It may be affected in several ways. Let’s see1. Economic impact • • • From an economic point of view, there are three types of changes we can see. The relative cost of capital and the cost of information are changed by IT. It is viewed as a factor of production that can be substituted for traditional capital and labor • It also affects the cost and quality of the information. 2. Organization and behavioral impacts • It flattens organizations. Now, most of the decision making done by lower levels. There is no need for many managers. Only fewer managers can do this. Having technological development, large organizations are reducing their employees and number of business levels. The managers are received accurate information on time. They are going faster than previously at making their decision. Management costs are declining day by day. The percentage of revenues and hierarchy becomes more efficient. • Post-industrial organizations are based on history and sociology. In the post-industrial period, managers are chosen by competencies, skills, knowledge, and experience. Professional workers are much more decentralized, and self-managing in their decision-making. Task force network is done by workers. They meet face to face to do specific work. After completing one work, they move to the next work. Explore – the role of IT. • Understanding organizational resistance to change Sometimes, Organizations are affected by organizational politics. Because it can influence the key resources like who does what to whom, where, when, why, how, etc. one can visualize the organizational resistance. There are four factors that suggest innovating the organization. 1. 2. 3. 4. The nature of the IT innovation The structure of the organizations The culture of the organization Tasks impacted by the innovation. Moreover, organizational task management, structure, and people are influenced by technology. In this model, you need to change the technology, structure, people, procedures, tasks, and management. Organizational resistance is very hard to change. Because it is so powerful. Check-integrated marketing communication. The internet and organizations The internet increases some factors like the accessibility, storage, and distribution of information and knowledge for organizations. The internet can greatly lower costs. Businesses are growing rapidly because of access to internet technology. It is a key component of the business infrastructures. Now, organizations enjoy lower costs, fewer employees, and better production and efficiency. • Implications for the design and understanding of information systems If you want to deliver real benefits to the organization, you must build information systems. Which is important for understanding the clear information of the organization. There exist some factors which are important for planning a new system. 1. Organizational environment 2. Structure of the organization like hierarchy, specialization, the division of labor, routines, rules and regulations, and business processes. 3. Organizational culture and politics 4. The types of organizations 5. The style of the leadership 6. Who are the principal interest groups? 7. Attitudes of the workers 8. Under which situation information system is designed to assist.