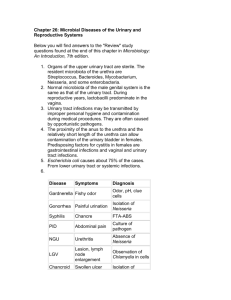
Current and future perspectives in the treatment of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative infections Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacterales (ESBL) first-line treatment Critically ill and/or After appropriate clinical experiencing response is achieved hypoalbuminemia Infections outside of the urinary tract Meropenem, OR Imipenem-cilastatin, OR Ertapenem Meropenem OR Imipenem-cilastatin uncomplicated cystitis Nitrofurantoin OR trimethoprim/ sulfamethoxazole Amoxicillin/clavulanate OR single-dose aminoglycosides OR fosfomycin (E. coli only). Pyelonephritis and cUTI TMP-SMX OR Ciprofloxacin OR Levofloxacin OR Meropenem OR Imipenem-cilastatin Fist line Transitioning to oral Trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole or Ciprofloxacin or Levofloxacin Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales (CRE) Alternative Uncomplicated Nitrofurantoin cystitis OR TMP-SMX OR Ciprofloxacin OR Levofloxacin Extended-infusion Meropenem Or Imipenem-cilastatin Single dose of Aminoglycoside OR Oral Fosfomycin (for e. Coli only) OR Colistin (only when no alternative options are available) Ceftazidime-avibactam OR Meropenem-vaborbactam OR Imipenem-cilastatinrelebactam OR Cefiderocol (2 grams IV every 8 hours, infused over 3 hours) only if ertapenem resistant, meropenem susceptible, AND carbapenemase testing results are either not available or negative. YOUSRY EL SHAFEY (CLINICAL PHARMACIST) References: IDSA Journal Of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy [AUTHOR NAME] Pyelonephritis and cutis TMP-SMX OR Ciprofloxacin OR Levofloxacin Aminoglycosides Ceftazidime-avibactam OR Meropenem-vaborbactam OR Imipenem-cilastatinrelebactam OR Cefiderocol (2 grams IV Extended-infusion Meropenem Or Imipenem-cilastatin every 8 hours, infused over 3 hours) only if ertapenem resistant, meropenem susceptible, AND carbapenemase testing results are either not available or negative. Infections Ceftazidime-avibactam outside of the OR urinary tract Meropenem-vaborbactam caused by CRE OR Imipenem-cilastatinrelebactam Infections Ceftazidime-avibactam outside of the OR urinary tract Meropenem-vaborbactam caused by CRE OR if KPC Imipenem-cilastatinproduction relebactam Infections Ceftazidime-avibactam in outside of the combination with urinary tract Aztreonam, caused by CRE if NDM OR production Cefiderocol (as monotherapy) Tigecycline OR Eravacycline For CRE infections not involving the bloodstream or urinary tract Tigecycline OR Eravacycline For CRE infections not involving the bloodstream or urinary tract Tigecycline OR Eravacycline For CRE infections not involving the bloodstream or urinary tract The tetracycline-derivative agents achieve rapid tissue distribution following administration, resulting in limited urine and serum concentrations. Therefore, the panel suggests avoiding their use for urinary and bloodstream infections. Tigecycline can be considered as alternative options for intra-abdominal infections, skin and soft tissue infections, osteomyelitis, and respiratory infections when optimal dosing is used 2 grams IV every 8 hours, infused over 3 hours Infections Ceftazidime-avibactam outside of the urinary tract caused by CRE if OXA-48like production Tigecycline OR Eravacycline are alternative options for the treatment of OXA-48-likeproducing infections not involving the bloodstream or urinary tract Colistin are not suggested for the treatment of infections caused by CRE Combination antibiotic therapy (i.e., the use of a β-lactam agent in combination with an aminoglycoside, fluoroquinolone, tetracycline, or polymyxin) is not suggested for the treatment of infections caused by CRE. YOUSRY EL SHAFEY (CLINICAL PHARMACIST) References: IDSA Journal Of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy [AUTHOR NAME] Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (CRAB) Fist line Alternative High-dose ampicillinsulbactam High-dose tigecycline in combination with at least one other agent (total daily dosages of 1827 grams (equivalent to 6-9 grams of sulbactam) as extended or continuous infusions are suggested (e.g., 9 grams IV every 8 hours infused over 4 hours) in combination with at least one other agent Colistin OR Tigecycline Meropenem or Imipenem-cilastatin are not suggested as components of CRAB therapy Combination therapy is suggested for the treatment of CRAB infections, even if a single agent demonstrates activity. In situations when prolonged durations of therapy may be needed (e.g., osteomyelitis), step-down therapy to a single active agent can be considered. Nebulized antibiotics are not suggested for the treatment of respiratory infections caused by CRAB. Fist line Not susceptible to any carbapenem agent but susceptible to traditional βlactams Infections caused by MDR P. aeruginosa Alternative High-dose extended-infusion therapy of non-carbapenem βlactam agents Piperacillin-tazobactam OR Ceftazidime OR Cefepime (1 gram IV every 8 hours, infused over 30 minutes) OR Aztreonam OR Fuoroquinolones Ciprofloxacin OR Levofloxacin YOUSRY EL SHAFEY (CLINICAL PHARMACIST) References: IDSA Journal Of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy [AUTHOR NAME] Uncomplicated Ceftazidime-avibactam cystitis OR Meropenem-vaborbactam OR Imipenem-cilastatinrelebactam OR Cefiderocol (2 grams IV every 8 hours, infused over 3 hours) Pyelonephritis and complicated urinary tract infections Ceftazidime-avibactam OR Meropenem-vaborbactam OR Imipenem-cilastatinrelebactam OR Cefiderocol (2 grams IV Single-dose of Tobramycin Or Amikacin 15 mg/kg IV as a single dose Colistin, but not polymyxin b, is an alternate consideration as it converts to its active form in the urinary tract Once-daily Tobramycin Or Amikacin There are no longer susceptibility criteria for gentamicin for p. Aeruginosa Tobramycin susceptibility criteria are available for p. Aeruginosa, regardless of source. Amikacin susceptibility criteria against p. Aeruginosa are only available for infections originating from urinary sources 15 mg/kg IV once; subsequent doses and dosing interval based on pharmacokinetic evaluation every 8 hours, infused over 3 hours) The addition of tobramycin to a β-lactam agent) to broaden the likelihood of at least one active agent for patients at risk for dtr-p. Aeruginosa infections is reasonable, data do not indicate that continued combination therapy—once the β-lactam agent has demonstrated in vitro activity—offers any additional benefit over monotherapy with the βlactam antibiotic None of the clinical trials demonstrated improved clinical outcomes or a survival benefit with the use of nebulized antibiotics compared with placebo for the treatment of ventilator-associated pneumonia Infections outside of the urinary tract Ceftazidime-avibactam OR Meropenem-vaborbactam OR Imipenem-cilastatinrelebactam Cefiderocol (2 grams IV every 8 hours, infused over 3 hours) YOUSRY EL SHAFEY (CLINICAL PHARMACIST) References: IDSA Journal Of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy [AUTHOR NAME]