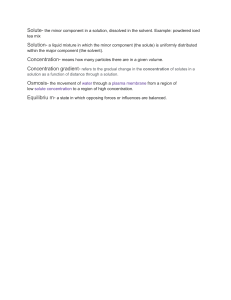
Solutions and Suspensions What are Solutions? Solutions are mixtures in which soluble particles are completely dissolved in a liquid or gas. How do we create a solution? Solute + Solvent = Solution The solid which fully dissolves The liquid which is used to dissolve the solid Example: salt + water salt solution (solute) (solvent) Properties of Solutions • Homogeneous (solvent & solute particles evenly spread throughout the solvent) • No residue (undissolved solid) is left after filtration Properties of Solutions • No separation of solute and solvent when left to stand • Light is able to completely pass through a solution Dissolving solid to form a solution When a solid dissolves to form a solution, the solute particles separate and mix evenly with the solvent particles. Uses of solutions in Homes • Soap and detergent are dissolved in water to help us wash our laundry. • Syrups are dissolved in the water to make drinks. • Salt, sugar and other condiments are dissolved in liquids when we cook. Uses of solutions in Industries • Dyes are dissolved in water to produce colourful fabrics. • Oils from plants and flowers are dissolved in alcohol to produce perfumes. Types of solutions State of solute State of solvent Examples of solution solid solid Alloys Bronze (tin dissolved in copper) Steel (iron, carbon + others) Brass (zinc dissolved in copper) gas gas Air (oxygen, carbon dioxide, noble gases dissolve in nitrogen) Types of solutions State of solute State of solvent Solid Examples of solution Amalgam ( silver, tin, gold or copper dissolves in mercury) Sugar solution Liquid Liquid (sugar dissolves in water) Alcoholic drinks (alcohol dissolves in water) Gas Aerated (Gas dissolved in water)