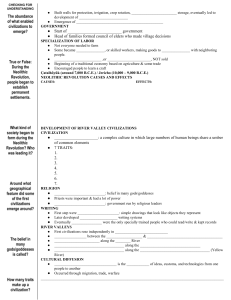
Intro to Anthropology Week 6: Agriculture and the Rise of Complex Societies Samantha Ellens September Oct. 3, 2023 Questions for Revolutions and the Origins of Civilizations: How do we define cities? What are the key features of a civilization? When, how, and why did civilizations develop? How can we recognize these in the archaeological record? Civilizations What makes a civilization? - Cities - States - Social Complexity & Political Organization - Combo of other factors (Ripple effects) The Revolutions Origins of Civilizations… Neolithic Revolution ca. 9,000 BC – 3,500 BC period of transition from huntergatherer lifestyle to settlement and agricultural production Göbekli Tepe Urban Revolution begins ca. 3,500 BC in Mesopotamia period of transformation from kin-based and smaller agricultural villages into complex, state-level urban societies The idea of Revolutions Tell El-Judeidah, Turkey V. Gordon Childe, 1930s Cultural Evolution (Childe’s inspiration) Unilinear Cultural Evolution (pre-state à state) advanced CIVILIZATION (complex societies) BARBARISM (chiefdoms, herdsmen, early agriculture) SAVAGE (hunter-gatherer) time **Problematic and ethnocentric terminology/ideology used to support unjust and racist social practices (ex. colonialism)!!** Hunter-gatherers -- Mobility -- Small village settlements -- Seasonal foodstuffs -- Subsistence cultivation -- Minimal surpluses -- Limited social stratification From at least 3 million years ago! NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION: From hunter-gatherer lifestyle to permanent settlement and agriculture Neo (new) + lithic (stone) Revolution beginning ca. 9,000 BC in southern Turkey TURKEY EGYPT *Dates on map are BP, not BC Domestication Domestication Einkorn wheat = single grain Domestication Mafdet says, “meow!” Çatalhöyük 6,500-5,500 BC The Debate: It is definitely Neolithic, but is it ALSO the oldest city in the world? Civilization and / or City? What makes a city? - Permanence - Large Population Size - High Population Density - Social Diversity Renfrew says: “A city is a substantial population center offering specialized services to a wider society” & How the settlement functioned! - How the settlement impacted region - Resources redistributed toRome, Circus Maximus and Coloseum in 302CE (4th century) Hinterland Çatalhöyük Çatalhöyük Urban Revolution + Mesopotamia Urban Revolution Complex Civilizations Emerge Urban Settlements State-level Administration & Organization Writing / Recording Systems Complex Civilizations Emerge > Agriculture is fixed and concentrated > Settlements form near agriculture > Larger crops support growing populations > Cultivation is more labor intensive and time consuming > Dwellings are permanent > New Architectural styles develop > Specialized crafts and trades emerge to support urban life > Surpluses are produced > Surpluses are stored > Surpluses are traded > Trade alliances and networks – new materials > Supervision of Production activities – hierarchies develop >Communications systems established: recordkeeping, writing > Religions institutionalized > States define selves in relation to others (nation-states, heads-of state) > Alliances are formed and broken > Conflicts, Warfare, emergence of Empires > Stresses on environment, health, resources, social welfare These are the ingredients of a COMPLEX CIVILIZATION! Ripple Effects… 4 types of archaeological evidence common to all civilizations: 1. Complex social organizations - consisting of urban settlements 2. Centralized economies based on accumulation of capital. Ex. Tribute, taxation, social status, trade, craft specialization, division of labor 3. Public buildings and monumental architecture 4. State religion – ruler also plays a role in the religion, often as sacred figure. Success based on balancing Power: Political, Social, Economic