![Basic terminology in genetics [Autosaved]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/027225151_1-3c7f0599da2810088977a1ca21b17306-768x994.png)
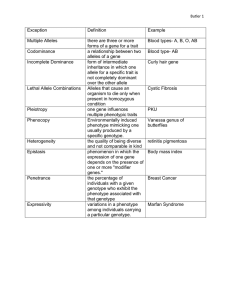
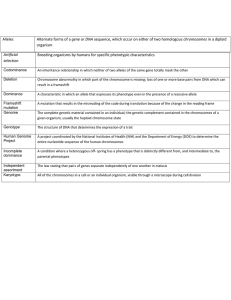
The transmission of genetic information from generation to generation How genetic is transmitted to the next generation? FERTILISATION GENETICS The study of inherited characteristics and the way they are passed on from one generation to another Gregor Mendel (1824- 1884) The Father of Modern Genetics Basic terminology in Genetics • • • • • • • • • Gene Allele Dominant allele Recessive allele Homozygous Heterozygous Pure breed Phenotype Genotype Cell Nucleus Chromosome -made up of DNA Chromosomes DNA centromere Gene Nucleotide Histone DNA -long coiled strand Gene -short section of DNA - Code information for production of protein There is about 2m of DNA in each human nucleus. The total DNA in a human body is enough to stretch to the moon and back What are chromosomes? • A thread-like structure of DNA, carrying genetic information in the form of genes • Is found inside the nucleus of a cell • Made up of DNA & protein (histone) • Each cell in each type of organism has a definite number of chromosomes • Each cell has Diploid Number of chromosomes: 1 set of Paternal Chromosomes + 1 set of Maternal Chromosomes Chromosomal number in different organisms What are DNA? • Main constituent of chromosomes, made up of nucleotides • DNA is responsible for telling the cell to make the right type of protein and this determine the type of cell • Consists of two polynucleotide strands coiled together by hydrogen bond between the pair of bases to form a double helix • Pair of bases: Adenine – Thymine Cytosine - Guanine What are DNA? DNA as gene Control production of Protein Responsible for Characteristic Cell characteristics depends on protein Cell specialisation depends on proteins: • All body cells in an organism contain the same genes but many genes in a particular cell are not expressed • The cell only makes the specific protein it needs to carry out its specialised function What are DNA? ladder Bases as the rung of the ladder What are DNA? • Adenine always pairs with thymine • Guanine pairs with cytosine What are DNA? Certain forces causes the ladder to twist around itself to form a shape similar to a spiral, called a double helix The discovery of structure of DNA Rosalind Franklin • She made many measurements on DNA, using patterns obtained by directing a beam of X-rays onto crystals of this molecule • She died before her part in the discovery of DNA structure was properly recognised Double helix structure of DNA • They used the measurement made by Franklin, and results of the chemical analysis of DNA which showed that the number of bases (A, G)was always equal to the number of bases (T, C) • Produce a working model of DNA, double helix • Watson and Crick were awarded the Nobel prize (the highest scientific award) for their work of DNA James Watson & Francis Crick What are gene? gene controlling • A length of DNA that codes for a protein skin colour • A basic unit of inheritance that determines a particular gene controlling characteristic in an tongue rolling organism/a short segment of DNA chromosome • Sequence of bases in a gene is the genetic code for putting gene controlling together amino acids in the eye colour correct order to make a gene controlling specific protein blood group • Control particular traits in an organism • “factor” The number and structures of chromosomes present in a cell nucleus Male Sex Chromosomes Male sex chromosomes of XY are different size. X chromosome is longer than Y chromosomes. Y chromosomes only carries genes which determine sex characteristics. Down Syndrome Turner Syndrome Klinefelter Syndrome Homolgous chromosomes - partner chromosomes that carry same genes & same size Each chromosome in a pair may carry alternative forms of the same gene/ allele Allele H h T T HOMOZYGOUS b RECESSIVE b HETEROZYGOUS n N DOMINANT ALLELES GENE ALLELES Dominant allele Is an allele which always shows its trait when it is present, and suppresses the effect of recessive allele; represented by a capital letter (R) • The allele that produces the phenotype of the organism/ the one that shows up in the phenotype • E.g. T is dominant allele • TT (homozygous)/ Tt (heterozygous) Recessive allele Is an allele that only expressed when there is no dominant allele present/ the one that is hidden in the phenotype represented by a lowercase letter (r) • E.g. t is recessive allele Characteristics and Traits Charateristic & Trait Characteristic Trait Phenotype Phenotype - the physical feature resulting from a genotype • The observable characteristic of an organism • Can be affected by the environmental factors • (e.g. red, white, tall) Genotype Genotype – genetic make-up of an organism in terms of the alleles present/gene combination for a trait • The genetic constituent of an organism • (e.g. RR, Rr, rr) Genotypes Homozygous genotype – When the two alleles are same • a pair of homologous chromosomes are identical (2 dominant genes or 2 recessive genes) e.g. TT or tt; also called pure breed • E.g. T T - homozygous dominant • t t - homozygous recessive Genotypes Heterozygous genotype – When the 2 alleles are different- one dominant & one recessive allele • a pair of homologous chromosomes are different (e.g. Tt); also called hybrid Genotypes Heterozygous genotype – Tt Homozygous genotype – TT – tt H h T T HOMOZYGOUS b RECESSIVE b HETEROZYGOUS n N DOMINANT ALLELES GENE ALLELES Purebreeds and Hybrids Types of Genetic Crosses Monohybrid cross - cross involving a single/one trait e.g. flower color (phenotype) Genotype- Ff / FF/ ff Dihybrid cross - cross involving two traits e.g. flower color & plant height (phenotype) Genotype- FfHh / FFHH / ffhh P1 Monohybrid Cross Parents phenotype genotype Round seeds RR R Gamete F1 generation Rr genotype phenotype ? x x Wrinkled seeds rr R r r Rr Rr Rr P1 Monohybrid Cross • Trait: Seed Shape • Alleles: R – Round r – Wrinkled • Cross: Round seeds x Wrinkled seeds RR x rr Gamete R r r Rr F1 Rr generation R Rr Rr Genotype: Rr Phenotype: Round Genotypic Ratio: All alike Phenotypic Ratio: All alike P1 Monohybrid Cross Parents phenotype Parents genotype x x (diploid) meiosis Gamete (haploid) fertilisation F1 generation genotype phenotype (diploid) Law of Segregation / Mendel’s First law • One character are determined by alleles which occur in pair.(Height-Tt) • During the formation of gametes (eggs or sperm), the two alleles responsible Tt for a trait separate from each other during meiosis. (2n n) T t • Only one of each pair of alleles in present in one gamete.(1 allele in 1 gamete) • Alleles for a trait are then "recombined" at fertilization, producing the genotype for the traits of the offspring. DRAW A SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM Homozygous black male mouse is cross with a homozygous white female mouse. Allele B is for black fur is dominant and b for white fur is recessive. Draw a schematic diagram to determine the phenotypic ratio of the off springs in the cross.