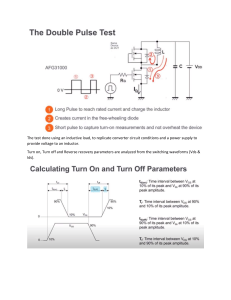
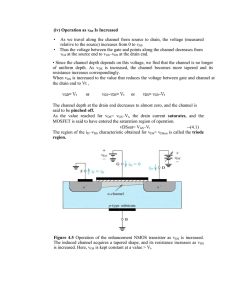
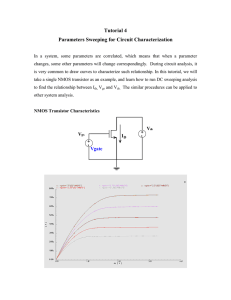
Electronics/Electronics 1 Fall 2023, ASSIGNMENT 2 Due on December 16th, 2023 by 11:30AM Istanbul time by Dr. Mustafa Aktan, Istanbul Medipol University In this assignment, we will cover MOS transistors. Question Course Learning Outcome #1 (10 points) 3 #2 (10 points) 3 #3 (10 points) 3 #4 (10 points) 3 #5 (10 points) 3 #6 (10 points) 3 #7 (10 points) 3 #8 (10 points) 3 #9 (20 points) 3 Grade Total (100 points) Electronics/Electronics 1 – hw#3 Page 1 of 4 Q1 – Consider an NMOS transistor operating in the triode region with a constant overdrive voltage VOV. Find an expression for the incremental resistance r ds ≡1/ ∂i D ∂ v DS | v DS =V DS Give the values of rds in terms of kn and VOV for VDS = 0, VDS = 0.25 VOV, VDS = 0.5 VOV, VDS = 0.75 VOV, and VDS = VOV. ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Q2 – A p-channel MOSFET with a threshold voltage Vtp = -0.5 V has its source connected to ground. (a) What should the gate voltage be for the device to operate with an overdrive voltage of |VOV| = 0.4 V. (b) With the gate voltage as in (a), what is the highest voltage allowed at the drain while the device operates in the saturation region? (c) If the drain current obtained in (b) is 0.2 mA, what should the current be for vD = -50 mV and for vD = -1 V? ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Q3 – A particular MOSFET for which Vtn = 0.5 V and kn = 2 mA/V2 is to be operated in the saturation region. If iD is to be 50 μA, find the required vGS and the minimum required vDS. Repeat for iD = 200 μA. ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Q4 – For an NMOS transistor, for which Vt = 0.5 V, operating with vGS in the range of 1 V to 2 V, what is the largest value of vDS so that the channel remains continuous? ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Q5 – Figure Q5 shows two NMOS transistors operating in saturation at equal VGS and VDS. (a) If the two devices are matched for a maximum possible mismatch in their W/L ratios of 5%, what is the maximum resulting mismatch in the drain currents. (b) If the two devices are matched for a maximum possible mismatch in their Vt values of 10 mV, what is the maximum resulting mismatch in the drain currents? Assume that the nominal value of Vt is 0.6 V. Figure Q5 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Q6 – A p-channel transistor for which |Vt| = 0.4 V and |VA| = 4 V operates in saturation with |vGS| = 1 V, |vDS| = 1.6 V, and iD = 2 mA. Find corresponding signed values for vGS, vSG, vDS, vSD, Vt, VA, λ, and kp. ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Electronics/Electronics 1 – hw#3 Page 2 of 4 Q7 – Using a PMOS transistor with Vt = -1.5 V, kp = 2 mA/V2, and λ = 0, design a circuit that resembles that in Figure Q7. Using a 10-V supply, design for a gate voltage of +6 V, a drain current of 0.5 mA, and a drain voltage of +5 V. Find the values of RS and RD. Also find the values of the resistances in the voltage divider feeding the gate, assuming a 1 μA current in the divider. Figure Q7 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Q8 – For each of the circuits shown in Figure Q8, find the labeled node voltages. The NMOS transistors have Vt = 0.4 V and kn = 4 mA/V2. Figure Q8 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Q9 – 549 – In the circuit of Figure Q9, transistors Q1 and Q2 have Vt = 0.7 V, and the process transconductance parameter kn' = 100 μA/V2. Find V1, V2, and V3 for each of the following cases Electronics/Electronics 1 – hw#3 Page 3 of 4 (a) (W/L)1 = (W/L)2 = 15 (b) (W/L)1 = 1.5(W/L)2 = 15 Figure Q9 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Electronics/Electronics 1 – hw#3 Page 4 of 4