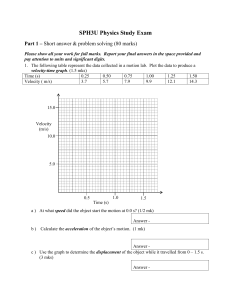
SPH3U Physics Practice Exam Part 1 – Problem solving and short answer 80 mks 100 minutes Part 2 – Multiple choice 20 mks 20 minutes 1. A separate Scantron sheet is provided for the multiple-choice section. You may write on the multiple-choice questions but be sure to record your answers on the Scantron sheet. 2. Answer the remainder of the questions in the space provided. Be sure to report your final response in the space/box provided for your answer. You may write your short answers in point form. 3. A list of equations and constants is found at the end of the exam package. It can be removed for your convenience. 4. At the end of the exam package, the Rough Work Sheet can be removed and used. It will not be marked! 5. A calculator is permitted, however, no borrowing or sharing of calculators is allowed. 6. A ruler and protractor may also be used, but not shared. 7. Should you have any questions or concerns, please notify a proctor. 8. Please ensure that the exam package is complete and that you have entered your name on it. Good luck! Page 2 of 11 MTHS SPH3U Part 1 – Short answer & problem solving Please show all your work for full marks. Report your final answers in the space provided and pay attention to units and significant digits. 1. The following table represent the data collected in a motion lab. Plot the data to produce a velocity-time graph. (1.5 mks) Time (s) 0.25 0.50 0.75 1.00 1.25 1.50 Velocity ( m/s) 3.7 5.7 7.9 9.9 12.1 14.3 15.0 Velocity (m/s) 10.0 5.0 1.0 0.5 1.5 Time (s) a ) At what speed did the object start the motion at 0.0 s? (1/2 mk) Answer b ) Calculate the acceleration of the object’s motion. (1 mk) Answer c ) Use the graph to determine the displacement of the object while it travelled from 0 – 1.5 s. (3 mks) Answer - Page 3 of 11 MTHS SPH3U 2. A stone is dropped from a bridge that is 75.0 m above the water. The person waits 2.00 s after releasing the stone and throws a second stone so that the two stones hit the water at the same time. Calculate the initial velocity the second stone must be released with? (4 mks) Answer 3. A large 45.5 kg box is pushed along the floor at a constant velocity of 0.75 m/s [forward]. Calculate the coefficient of friction if the applied force is 375 N [forward]. (4 mks) Answer - Page 4 of 11 MTHS SPH3U 4. As 7700 kg airplane glides to a landing. It has a 12500 N [down] force of gravity pulling it toward the Earth’s surface and a 58800 N [horizontally forward] force of lift acting on it. a ) At what angle, relative to the horizontal, does the airplane approach the ground? (1 mk) Answer - 5. Describe a situation where an object is in motion but no physical work is being accomplished. Explain why there is no work being done in this case. (2 mks) 6. A 75.0 g arrow is fired vertically into the air. At a point in its flight, it is determined that the arrow has 33.4 J of gravitational potential energy. How high above the surface of the Earth is it with this energy? (3 mks) Answer - Page 5 of 11 MTHS SPH3U 7. A candle has 7525 J of energy stored in its chemical bonds. That energy is used to heat 150 g of o water, which has a starting temperature of 21.0 C. Calculate the final temperature of the water o if all the energy is transferred to the water. The specific heat capacity for water is 4186 J/kg C. (3 mks) Answer 8. Use graphing techniques to determine how much work is required to stretch an elastic bungee cord to a final length of 6.0 m. (4 mks) Force (N) 2000 1500 1000 500 2 Length (m) 4 6 Answer 9. An elevator has a motor that can produce 25000 W. If this power were used to raise an 850 kg elevator to a height of 35.5 m, how much time would be required for the motion? (3 mks) Answer - Page 6 of 11 MTHS SPH3U o 10. A tow truck pulls a car by a cable that makes an angle of 30 to the 3 horizontal. The force applied to the tow cable is 7.2 x 10 N. How much work is done in pulling the car horizontally 5.5 km? (3 mks) 30 o Answer 11. A wave with an amplitude of 50.0 cm travels down a 7.75 m spring in 3.00 s. The student who creates the wave moves their hand through 4 cycles in 1.00 s. Calculate the wavelength of the wave? (3 mks) Answer 12. When two tuning forks are vibrating at the same time one observes that the sound grows louder then softer at regular intervals. The change in volume occurs at a rate of exactly 48 times in 16.0 s. If one tuning fork is known to have a frequency of 256.0 Hz, what are the two possible frequencies of the second tuning fork? (3 mks) Answer - Page 7 of 11 MTHS SPH3U 13. A vibrating tuning fork with a frequency of 324 Hz is held over a tube of air whose length can be adjusted by raising and lowering a column of water in the tube. The starting length of the column of air is very short and letting the water out slowly gradually lengthens it. If the speed of sound in air is 336 m/s, how long is the column of air when the first constructive interference is heard. (4 mks) Answer 14. A cannon is fired from a distant hilltop and you see the smoke followed by hearing the explosion. Calculate how far away the cannon is if the temperature on the day this is observed o is 18 C and time between the smoke and the sound is 4.7 s. (2 mks) Answer 15. A nuclear physicist carries out a nuclear reaction where the reactants had a total mass of 3.251 438 g and the products had a mass of 3.251 429 g. Determine the maximum amount of energy involved in this reaction and whether it was produced or consumed. (3 mks) Answer - Page 8 of 11 MTHS SPH3U 16. A bullet is fired horizontally from a rifle and hits a target that is 150 m away. If the bullet landed 15 cm below the point at which the marksmen aimed, how fast was the bullet travelling? (5 mks) Answer 17. Determine the missing values in the following circuit. (5 mks) #1 V (V) I (A) R () 1 2 3 0 120 1 45 2 5 3 4 5 5 4 15 6 Page 9 of 11 MTHS SPH3U 18. Label the current and the north pole of the magnetic field in each coil. (2 mks) G This magnet is being pulled away. N Part 2 – Multiple Choice Select the best answer for each question. You may write on these questions but be sure to record your final selections on the provided Scantron sheet. 1. Which of the following values is a scalar value? a ) velocity b ) time c ) displacement d ) force e ) acceleration 2. Which of the following velocity-time graphs represents the motion of an arrow, which is fired vertically upward, upon leaving the bow? v v t a) t b) v v c) t v t d) 3. Which of the following fundamental forces is the weakest? a) Gravitational b) Weak c) Strong d) Electromagnetic nuclear nuclear 4. Which of the following vectors represents the resultant force acting on object “X”? e) t e) Frictional X e) a) b) c) d) 5. As a truck moves down the road the driver slams on the brakes to avoid hitting a cat. The fuzzy dice hanging on his mirror swing toward the window. The motion of the dice show a) Newton’s b) Newton’s c) Newton’s d) the universal e) cats are “big first law of second law third law law of time” trouble. motion. of motion. of motion. gravitation. 6. Which of the following are equivalent to a watt (W)? a) (kg m)/s3 b) (N m)/s c) (kg J)m d) (C V)/ e) (kg m3)/s2 Page 10 of 11 MTHS SPH3U 7. Which of the following forms of energy is a form of potential energy? a) sound b) thermal c) nuclear d) radiant e) mechanical energy 8. As you sit on the stool in the science lab, you place your hand on the metal leg of the stool and o the wooden counter top. The science lab has been maintained at 18 C for the past week. Apply the concept of thermal equilibrium to identify the correct statement. a) The leg of the b) The wooden c) The leg and d) Thermal e) It is impossible stool’s counter top’s the counter equilibrium to determine temperature temperature is top are both at predicts that which object is less than greater than a temperature cold will flow will be cooler o o o to the object without 18 C. 18 C. of 18 C with the lowest knowing their specific heat specific heat capacity. capacities. 9. A student throws their physics text vertically upward. As the textbook rises, which of the following quantities increases? a) mechanical energy b) speed c) acceleration d) kinetic energy e) gravitational potential energy 10. The frequency range for human hearing is approximately a) 2 Hz to 2000 Hz. b) 20 Hz to 20 000 Hz. c) 200 Hz to 200 000 Hz. d) 2 Hz to 2 kHz. e) 2 kHz to 2 MHz. 11. An ambulance races toward you with the siren sounding. The property of sound that accounts for the siren sounding different as it approaches as compared to when it departs is a) resonance. b) a standing c) frequency d) nodal lines. e) the Doppler effect. wave. beats. 14. The process of combining two smaller nuclei into one larger nucleus is called . . . a) nuclear b) nuclear c) chemical d) chemical e) one heck of an fusion. fission. fusion. fission. explosion! 15. Consider the following nuclear reaction and identify the missing entity in the balanced reaction. 232 228 90Th 88Ra + ?? a) 4 2He b) 0 +1e 0 −1e c) d) 16. Which of the following units is a unit for power? kg m kg m kg s f) g) h) 3 s s m3 i) 1 0n e) Nm j) s 1 1p Jm s3 17. Which of the following situations represents the correct relationship between the current, magnetic field and force acting on the conductor? a) Force N S b) Force S N c) Force N S Page 11 of 11 MTHS SPH3U d) e) Force N S Force N S 18. Which of the following compass needles is accurately representing the direction of the magnetic field associated with this coil? E C A B D a) A b) B c) C d) D e) E