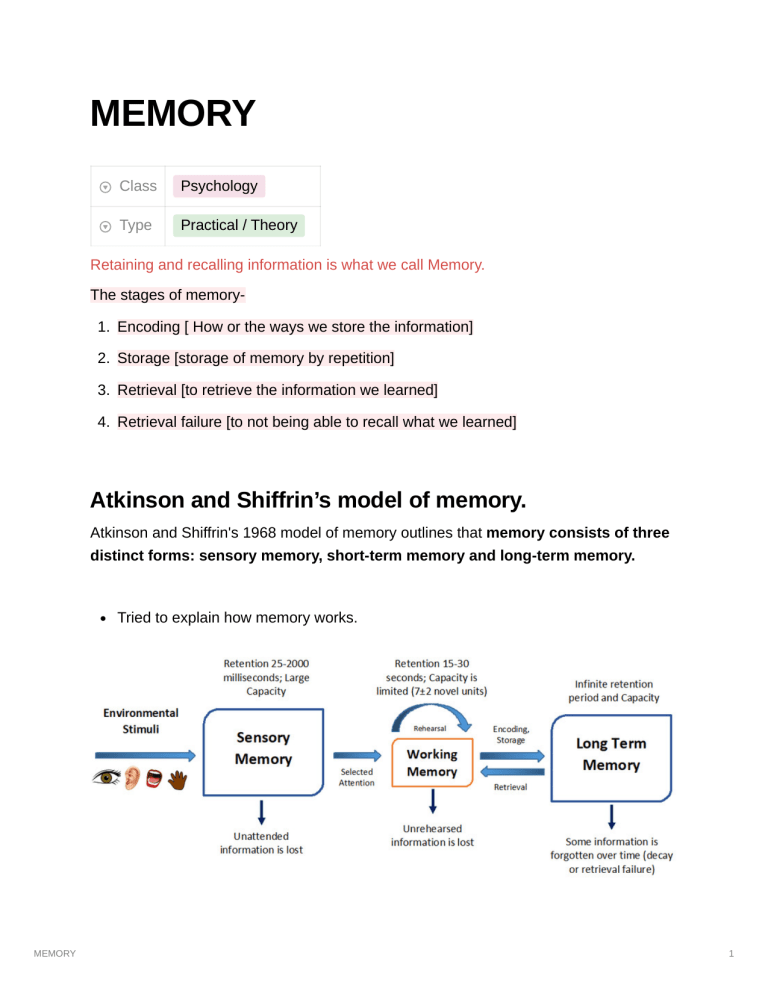
MEMORY Class Psychology Type Practical / Theory Retaining and recalling information is what we call Memory. The stages of memory1. Encoding [ How or the ways we store the information] 2. Storage [storage of memory by repetition] 3. Retrieval [to retrieve the information we learned] 4. Retrieval failure [to not being able to recall what we learned] Atkinson and Shiffrin’s model of memory. Atkinson and Shiffrin's 1968 model of memory outlines that memory consists of three distinct forms: sensory memory, short-term memory and long-term memory. Tried to explain how memory works. MEMORY 1 for exYou are in a public place ,let it be a park or a mall. You are aware of your surroundings, hearing and looking [sensory memory]. Now you are watching two little kids playing[selective attention] , you smile at yourself and think “how cute”[short-term memory] and then get on with whatever you were doing. But now you just can’t stop yourself from looking at them,so you keep taking a peek at them from time to time [encoding].After a few days, you visited the park and you smiled at yourself as your mind reminded you of the two little kids [long-term memory]. OR After a few days, you visited the park and you smiled at yourself but you can't seem to find the reason as to why you smiled as soon as you entered the park [ retrieval failure]. The Serial Position effect The psychological tendency to remember the first and last items in a list better than those in the middle. Primacy effect- the tendency to remember the information shown or written at the beginning of the list. Recency effect- the tendency to remember the information shown or written at the end of the list. Distinctiveness effect- the ability to remember the piece of information that stands out the most. False memory- the perception of recalling that the past event occurred when in reality it didn’t. Show your subject 21 flashcards/slides with different words written on each, repeat a word on 2-3 slides and also write a word that is different from all the words you have MEMORY 2 written. When you are done with the slides ask them to write what they recall, and then categorize those words into primacy effect, recency effect, distinctiveness effect and false memory Do the same experiment on at least 5-6 people, and then calculate the mean of the first seven words, mid-seven words and the last seven words. And lastly, make a graphical representation of it. You’ll find a U-shape figure on the graph as we join the mean of the first seven words with the mean of the mid-seven words to the mean of the last seven words. You can write up to as many words as you’d like, make sure you list the words beforehand into first, mid and last. You can also write numbers or alphabets if you want. Also, ask for your subject’s consent before experimenting. MEMORY 3