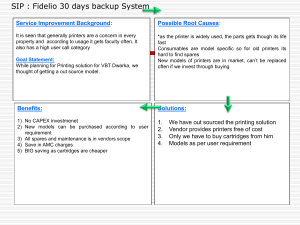
A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software Define the term hardware Computer hardware is the collection of physical parts of a computer system. This includes the computer case, monitor, keyboard, and mouse. It also includes all the parts inside the computer case, such as the hard disk drive, motherboard, video card, and many others. Computer hardware is what you can physically touch. Evaluate internal hardware devices (including: central processing unit (CPU), motherboard, random access memory (RAM), read only memory (ROM), graphics card, sound card, hard disk drive (HDD), solid state drive (SSD)) CPU Alternately referred to as a processor, central processor, or microprocessor, the CPU is the Central Processing Unit of the computer. A computer's CPU handles all instructions it receives from hardware and software running on the computer. Components of the CPU In the CPU, the primary components are the ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit) that performs mathematical, logical, and decision operations and the CU (Control Unit) that directs all of the processors operations. www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 1|Page 1|Page A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software Motherboard A motherboard is one of the most essential parts of a computer system. It holds together many of the crucial components of a computer, including the central processing unit (CPU), memory and connectors for input and output devices. The base of a motherboard consists of a very firm sheet of non-conductive material, typically some sort of rigid plastic. Thin layers of copper or aluminum foil, referred to as traces, are printed onto this sheet. These traces are very narrow and form the circuits between the various components. In addition to circuits, a motherboard contains a number of sockets and slots to connect the other components. Parts of a Motherboard If you were to open up your computer and take out the motherboard, you would probably get pretty confused about all the different parts. Depending on the make and model of your computer, it might look something like the picture below. To understand how computers work you don't need to know every single part of the motherboard. However, it is good to know some of the most important parts and how the motherboard connects the various parts of a computer system together. Some of the typical parts are described below - they are also labeled in the next photograph: A CPU socket - the actual CPU is directly soldered onto this socket. Since high speed CPUs generate a lot of heat, there are heat sinks and mounting points for fans right next to the CPU socket. A power connector to distribute power to the CPU and other components. Slots for the system's main memory, typically in the form of DRAM chips. A chip forms an interface between the CPU, the main memory and other components. On many types of motherboards this is referred to as the Northbridge. This chip also contains a large heat sink. A second chip controls the input and output (I/O) functions. It is not connected directly to the CPU but to the Northbridge. This I/O controller is referred to as the Southbridge. The Northbridge and Southbridge combined are referred to as the chipset. Several connectors, which provide the physical interface between input and output devices and the motherboard. The Southbridge handles these connections. Slots for one or more hard drives to store files. The most common types of connections are Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) and Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA). A Read-only memory (ROM) chip, which contains the firmware, or startup instructions for the computer system. This is also called the BIOS. A slot for a video or graphics card. There are a number of different types of slots, including Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) and Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe). Additional slots to connect hardware in the form of Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) slots. www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 2|Page 2|Page A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software RAM Alternatively referred to as main memory, primary memory, or system memory,Random Access Memory (RAM) is a hardware device that allows information to be stored and retrieved on a computer. RAM is usually associated with DRAM, which is a type of memory module. Because information is accessed randomly instead of sequentially like it is on a CD or hard drive, the computer can access the data much faster. However, unlike ROM or the hard drive, RAM is a volatile memory and requires power to keep the data accessible. If the computer is turned off, all data contained in RAM is lost. Random access memory (RAM) is the best known form of computer memory. RAM is considered "random access" because you can access any memory cell directly if you know the row and column that intersect at that cell. ROM Short for Read-Only Memory, ROM is a storage medium that is used with computers and other electronic devices. As the name indicates, data stored in ROM may only be read. It is either modified with extreme difficulty or not at all. ROM is mostly used for firmware updates. A simple example of ROM is the cartridge used with video game consoles, which allows one system to run multiple games. Another example of ROM is EEPROM, which is a programmable ROM used for the computer BIOS, as shown in the picture Graphics Card The graphics card in your office PC converts video data into electronic signals and sends them to your monitor. The monitor accepts the graphics card signals and turns them into colorful images. The process happens fast enough to handle videos, games and other media. All standard desktop and notebook computers have some form of graphics card. A graphics card is the component in your computer that handles generating the signals that are sent to the monitor or "graphics". It is responsible for generating all the text and pictures that are displayed on your screen. It is called a "card" because most PCs will have a physical card that is inserted in a PCI slot on the motherboard. Some motherboards have built-in graphics cards with is something of a misnomer since it is built in as part of the motherboard and no longer a separate "card". 2D, or two dimensional graphics are the kind of graphics displayed when you use a web browser, check email or work on a spreadsheet. For 2D graphics the major factors are resolution and refresh rate. Resolution determines how many little dots are used to draw the image on the screen. For example, 640x480 means that the whole screen is drawn using 307,200 little dots in 640 www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 3|Page 3|Page A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software columns and 480 rows. The more dots that are used, the finer the detail. Thus, higher resolutions provide for great detail and image quality. Another factor is color depth. You may see it expressed as a third parameter such as 640x480x256. This means 640 columns x 480 rows x 256 colors. Color depth is usually a number that is 2 raised to the power of a multiple of 8 up to 32. i.e. 2^8, 2^16, 2^24 or 2^32... or 256, 65,536, 16M or 4G colors. Obviously, the more colors the great the detail again. Sound Card Definition Most of your music collection is probably in digital format, either on CDs or as files on your computer. In order to be able to listen to your music, a sound card converts digital data to analog sound waves you can hear. The output signal is then connected to a headphone or set of speakers. You can also use a sound card to record audio with a microphone. Sound Card Features and Functions The motherboard on most computer systems has an integrated sound card, which is often sufficient for many users. However, to get higher quality sound you can upgrade to a separate sound card, which uses better and more expensive components. Audio files on a computer consist of digital data just like any other file on a computer. Sounds we can hear consist of waves that travel through the air - sounds are analog. The primary function of a sound card is to translate between digital and analog information, just like a video card. Sound cards typically have four major components: The digital-to-analog converter (DAC), which makes it possible to convert digital data to analog sound The analog-to-digital converter (ADC), which makes it possible to make digital recordings from analog sound inputs An interface to connect to the motherboard, typically using Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) Input and output connectors so you can plug in headphones, speakers or a microphone many computer systems have speakers and microphone built-in, but connectors allow you to use higher quality external devices to play or record sound www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 4|Page 4|Page A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software On some sound cards, the two types of converters are integrated into CODEC a single coder/decoder chip. Some sound cards also have a digital signal processor (DSP), a built-in processing unit. The DSP takes some of the load of the central processing unit (CPU) to convert between digital and analog. Similarly, some sound cards have their own memory. Sound cards without a DSP or memory will use the motherboard's CPU and memory. Uses of a computer sound card Games Audio CDs and listening to music Watch movies Audio conferencing Creating and playing Midi Educational software Business presentations Record dictations Voice recognition Hard drive A hard disk drive (sometimes abbreviated as hard drive, HD, or HDD) is a non-volatile memory hardware device that permanently stores and retrieves information. There are many variations, but their sizes are generally 3.5" and 2.5" for desktop and laptop computers respectively. A hard drive consists of one or more platters to which data is written using a magnetic head, all inside of an airsealed casing. Internal hard disks reside in a drive bay, connect to the motherboard using an ATA, SCSI, or SATA cable, and are powered by a connection to the PSU (power supply unit). A hard drive can be used to store just about any type of data, including pictures, music, videos, and text documents. Computers have a hard drive and use it to store files for the operating and software that run on the computer, as well as files created or downloaded to the computer by a user. The amount of data a hard drive can store depends on the storage space of the hard drive. www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 5|Page 5|Page A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software Older hard drives had a storage size of several hundred megabytes (MB) to several gigabytes (GB). Newer hard drives have a storage size of several hundred gigabytes to several terabytes. Each year, new and improved technology allows for increasing hard drive storage sizes. How is data read and stored on a hard drive? Data sent to and read from the hard drive is interpreted by the disk controller, which tells the hard drive what to do and how to move the components within the drive. When the operating system needs to read or write information, it examines the hard drive's File Allocation Table (FAT) to determine file location and available write areas. Once they have been determined, the disk controller instructs the actuator to move the read/write arm and align the read/write head. Because files are often scattered throughout the platter, the head needs to move to different locations to access all information. All information stored on a traditional hard drive, like the above example, is done magnetically. After completing the above steps, if the computer needs to read information from the hard drive, it would read the magnetic polarities on the platter. One side of the magnetic polarity is 0, and the other is 1. Reading this as binary data, the computer can understand what the data is on the platter. For the computer to write information to the platter, the read/write head aligns the magnetic polarities, writing 0's and 1's that can be read later. www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 6|Page 6|Page A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software HDD and SSD explained The traditional spinning hard drive (HDD) is the basic nonvolatile storage on a computer. That is, it doesn't "go away" like the data on the system memory when you turn the system off. Hard drives are essentially metal platters with a magnetic coating. That coating stores your data, whether that data consists of weather reports from the last century, a high-definition copy of the Star Wars trilogy, or your digital music collection. A read/write head on an arm accesses the data while the platters are spinning in a hard drive enclosure. An SSD does much the same job functionally (e.g., saving your data while the system is off, booting your system, etc.) as an HDD, but instead of a magnetic coating on top of platters, the data is stored on interconnected flash memory chips that retain the data even when there's no power present. The chips can either be permanently installed on the system's motherboard (like on some small laptops and ultrabooks), on a PCI/PCIe card (in some high-end workstations), or in a box that's sized, shaped, and wired to slot in for a laptop or desktop's hard drive (common on everything else). These flash memory chips differ from the flash memory in USB thumb drives in the type and speed of the memory. That's the subject of a totally separate technical treatise, but suf fice it to say that the flash memory in SSDs is faster and more reliable than the flash memory in USB thumb drives. SSDs are consequently more expensive than USB thumb drives for the same capacities. Advantages and Disadvantages Both SSDs and HDDs do the same job: They boot your system, store your applications, and store your personal files. But each type of storage has its own unique feature set. The question is, what's the difference, and why would a user get one over the other? We break it down: Price: To put it bluntly, SSDs are more expensive than HDDs in terms of dollar per GB. For the same capacity and form factor 1TB internal 2.5-inch drive, you'll pay about $60 to $75 for an HDD, but as of this writing, an SSD doubles that to $130 to $150. That translates into 7 cents per gigabyte for the HDD and 14 cents per gigabyte for the SSD. Since HDDs are older, more established technologies, they will remain less expensive for the near future. Those extra hundreds may push your system price over budget. www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 7|Page 7|Page A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software Maximum and Common Capacity: As seen above, SSD units top out at 4TB, but those are still very rare and expensive. You're more likely to find 500GB to 1TB units as primary drives in systems. While 500GB is considered a "base" hard drive in 2015, pricing concerns can push that down to 128GB for lower-priced SSD-based systems. Multimedia users will require even more, with 1TB to 4TB drives as common in high-end systems. Basically, the more storage capacity, the more stuff (photos, music, videos, etc.) you can hold on your PC. While the (Internet) cloud may be a good place to share these files among your phone, tablet, and PC, local storage is less expensive, and you only have to buy it once. Speed: This is where SSDs shine. An SSD-equipped PC will boot in seconds, certainly under a minute. A hard drive requires time to speed up to operating specs, and will continue to be slower than an SSD during normal use. A PC or Mac with an SSD boots faster, launches apps faster, and has faster overall performance. Witness the higher PCMark benchmark scores on laptops and desktops with SSDs, plus the much higher scores and transfer times for external SSDs versus HDDs. Whether it's for fun, school, or business, the extra speed may be the difference between finishing on time or f ailing. Fragmentation: Because of their rotary recording surfaces, HDD surfaces work best with larger files that are laid down in contiguous blocks. That way, the drive head can start and end its read in one continuous motion. When hard drives start to fil l up, large files can become scattered around the disk platter, which is otherwise known as fragmentation. While read/write algorithms have improved to the point that the effect is minimized, the fact of the matter is that HDDs can become fragmented, while SSDs don't care where the data is stored on its chips, since there's no physical read head. Thus, SSDs are inherently faster. Durability: An SSD has no moving parts, so it is more likely to keep your data safe in the event that you drop your laptop bag or your system is shaken about by an earthquake while it's operating. Most hard drives park their read/write heads when the system is off, but they are flying over the drive platter at hundreds of miles an hour www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 8|Page 8|Page A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software when they are in operation. Besides, even parking brakes have limits. If you're rough on your equipment, an SSD is recommended. Availability: Hard drives are simply more plentiful. Look at the product lists from Western Digital, Toshiba, Seagate, Samsung, and Hitachi, and you'll see many more HDD models than SSDs. For PCs and Macs, internal HDDs won't be going away completely, at least for the next couple of years. You'll also see many more HDD choices than SSDs from different manufacturers for the same capacities. SSD model lines are growing in number, but HDDs are still in the majority for storage devices in PCs. Form Factors: Because HDDs rely on spinning platters, there is a limit to how small they can be manufactured. There was an initiative to make smaller 1.8-inch spinning hard drives, but that's stalled at about 320GB, since the tablet and smartphone manufacturers have settled on flash memory for their primary storage. SSDs have no such limitation, so they can continue to shrink as time goes on. SSDs are available in 2.5-inch laptop drive-sized boxes, but that's only for convenience. As laptops become slimmer and tablets take over as primary Web-surfing platforms, you'll start to see the adoption of SSDs skyrocket. Noise: Even the quietest HDD will emit a bit of noise when it is in use from the drive spinning or the read arm moving back and forth, particularly if it's in a system that's been banged about or in an all-metal system where it's been shoddily installed. Faster hard drives will make more noise than slower ones. SSDs make virtually no noise at all, since they're non-mechanical. Overall: HDDs win on price, capacity, and availability. SSDs work best if speed, ruggedness, form factor, noise, or fragmentation (technically part of speed) are important factors to you. If it weren't for the price and capacity issues, SSDs would be the winner hands down. As far as longevity goes, while it is true that SSDs wear out over time (each cell in a flash memory bank has a limited number of times it can be written and erased), thanks to TRIM command technology built into SSDs that dynamically optimizes these read/w rite cycles, you're more likely to discard the system for obsolescence before you start www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 9|Page 9|Page A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software running into read/write errors. The possible exceptions are high -end multimedia users like video editors who read and write data constantly, but those users will need t he larger capacities of hard drives anyway. Hard drives will eventually wear out from constant use as well, since they use physical recording methods. Longevity is a wash when it's separated from travel and ruggedness concerns. Cloud Storage Cloud Storage is a service where data is remotely maintained, managed, and backed up. The service allows the users to store files online, so that they can access them from any location via the Internet. According to a recent survey conducted with more than 800 business decision makers and users worldwide, the number of organizations gaining competitive advantage through high cloud adoption has almost doubled in the last few years and by 2017, the public cloud services market is predicted to exceed $244 billion. Now, let’s look into some of the advantages and disadvantages of Cloud Storage. Advantages of Cloud Storage 1. Usability: All cloud storage services reviewed in this topic have desktop folders for Mac’s and PC’s. This allows users to drag and drop files between the cloud storage and their local storage. 2. Bandwidth: You can avoid emailing files to individuals and instead send a web link to recipients through your email. 3. Accessibility: Stored files can be accessed from anywhere via Internet connection. 4. Disaster Recovery: It is highly recommended that businesses have an emergency backup plan ready in the case of an emergency. Cloud storage can be used as a back‐up plan by businesses by providing a second copy of important files. These files are stored at a remote location and can be accessed through an internet connection. 5. Cost Savings: Businesses and organizations can often reduce annual operating costs by using cloud storage; cloud storage costs about 3 cents per gigabyte to store data internally. Users can see additional cost savings because it does not require internal power to store information remotely. www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 10 | P a g e 10 | P a g e A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software Disadvantages of Cloud Storage 1. Usability: Be careful when using drag/drop to move a document into the cloud storage folder. This will permanently move your document from its original folder to the cloud storage location. Do a copy and paste instead of drag/drop if you want to retain the document’s original location in addition to moving a copy onto the cloud storage folder. 2. Bandwidth: Several cloud storage services have a specific bandwidth allowance. If an organization surpasses the given allowance, the additional charges could be significant. However, some providers allow unlimited bandwidth. This is a factor that companies should consider when looking at a cloud storage provider. 3. Accessibility: If you have no internet connection, you have no access to your data. 4. Data Security: There are concerns with the safety and privacy of important data stored remotely. The possibility of private data commingling with other organizations makes some businesses uneasy. If you want to know more about those issues that govern data security and privacy, here is an interesting article on the recent privacy debates. 5. Software: If you want to be able to manipulate your files locally through multiple devices, you’ll need to download the service on all devices. www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 11 | P a g e 11 | P a g e A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software Hardware & Input/output Devices Keyboard Keyboard is the most common and very popular input device which helps in inputting data to the computer. The layout of the keyboard is like that of traditional typewriter, although there are some additional keys provided for performing additional functions. Keyboards are of two sizes 84 keys or 101/102 keys, but now keyboards with 104 keys or 108 keys are also available for Windows and Internet. The keys on the keyboard are as follows: Sr.No Keys Description 1 Typing Keys These keys include the letter keys (A-Z) and digit keys (0-9) which generally give same layout as that of typewriters. 2 Numeric Keypad It is used to enter numeric data or cursor movement. Generally, it consists of a set of 17 keys that are laid out in the same configuration used by most adding machines and calculators. 3 Function Keys The twelve function keys are present on the keyboard which are arranged in a row at the top of the keyboard. Each function key has unique meaning and is used for some specific purpose. 4 Control keys These keys provide cursor and screen control. It includes four directional arrow keys. Control keys also include Home, End, Insert, Delete, Page Up, Page Down, Control(Ctrl), Alternate(Alt), Escape(Esc). www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 12 | P a g e 12 | P a g e A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software 5 Special Purpose Keys Keyboard also contains some special purpose keys such as Enter, Shift, Caps Lock, Num Lock, Space bar, Tab, and Print Screen. Advantages/Disadvantages of using a Keyboard: Advantages Disadvantages People are used to using keyboards to enter data, they need very little training If you can't touch type, it can be time consuming to enter data A skilled typist can enter data very quickly Keyboards are not suitable for creating diagrams Specialist keyboards are available e.g. ergonomic, gaming keyboards Disabled people often find keyboards difficult to use. Excessive use can lead to health problems such as repetitive strain injury (R.S.I.) Mouse Mouse is most popular pointing device. It is a very famous cursor-control device having a small palm size box with a round ball at its base which senses the movement of mouse and sends corresponding signals to CPU when the mouse buttons are pressed. Generally it has two buttons called left and right button and a wheel is present between the buttons. Mouse can be used to control the position of cursor on screen, but it cannot be used to enter text into the computer. Advantages Disadvantages Faster to select icons and options when compared to a keyboard. People with wrist and hand problems (like RSI) can find mice painful to use. Very easy to move a pointer around a screen and to Ball mice can pick up dirt which will affect the navigate through documents. accuracy of pointer movement. www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 13 | P a g e 13 | P a g e A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software Mice are small and do not take up much space Mice need a flat surface in order to work properly For example - they would be difficult to use on train unless you had a flat table to rest Joystick Joystick is also a pointing device which is used to move cursor position on a monitor screen. It is a stick having a spherical ball at its both lower and upper ends. The lower spherical ball moves in a socket. The joystick can be moved in all four directions. The function of joystick is similar to that of a mouse. It is mainly used in Computer Aided Designing(CAD) and playing computer games. Advantages Disadvantages Easier to control an on-screen curser or move an ingame character than it is when using a keyboard Not as easy to control an on-screen curser when compared to using a mouse. Very simple to get used to. People with hand/wrist issues (like RSI) can find them painful to use.. Anyone can just pick one up and use it! Can be used by disabled people. Joysticks can be operated by hands or even feet. Difficult (but not impossible) to enter text. For example: some games allow you to select individual letters using the joystick in order to spell out your name when entering a high score. For example - they would be difficult to use on train unless you had a flat table to rest www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 14 | P a g e 14 | P a g e A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software Light Pen Light pen is a pointing device which is similar to a pen. It is used to select a displayed menu item or draw pictures on the monitor screen. It consists of a photocell and an optical system placed in a small tube. When the tip of a light pen is moved over the monitor screen and pen button is pressed, its photocell sensing element detects the screen location and sends the corresponding signal to the CPU. Track Ball Track ball is an input device that is mostly used in notebook or laptop computer, instead of a mouse. This is a ball which is half inserted and by moving fingers on ball, pointer can be moved. Since the whole device is not moved, a track ball requires less space than a mouse. A track ball comes in various shapes like a ball, a button and a square. Scanner Scanner is an input device which works more like a photocopy machine. It is used when some information is available on a paper and it is to be transferred to the hard disc of the computer for further manipulation. Scanner captures images from the source which are then converted into the digital form that can be stored on the disc. These images can be edited before they are printed. Advantages Disadvantages Very fast to enter hard copies into the computer (compared to retyping with a keyboard). Scanned images are usually of lesser quality than the original document. Very easy to scan and store documents and images Scanned images can take up a lot of disk space into the computer. (especially if you scan them at a high resolution). www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 15 | P a g e 15 | P a g e A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software Digital copies of the stored data can easily be duplicated and backed up. Old photo's that may be damaged can be scanned into the computer then repaired using Graphics Editing Software. Digitizer Digitizer is an input device which converts analog information into digital form. Digitizer can convert a signal from the television or camera into a series of numbers that could be stored in a computer. They can be used by the computer to create a picture of whatever the camera had been pointed at. Digitizer is also known as Tablet or Graphics Tablet because it converts graphics and pictorial data into binary inputs. A graphic tablet as digitizer is used for doing fine works of drawing and image manipulation applications. Microphone Microphone is an input device to input sound that is then stored in digital form. The microphone is used for various applications like adding sound to a multimedia presentation or for mixing music. Used to input sounds/speech for use in a range of applications. For example: Narration (spoken words) in presentations or in web sites Voice-over's in movies Speaking over the Internet using VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) An example of this would be using Skype to hold an online conversation Conducting videoconferencing (e.g. business meetings online). www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 16 | P a g e 16 | P a g e A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software Advantages Disadvantages Faster to read in text than to type it in using a Sound files can take up a lot of computer storage keyboard . space. Means that word processors can be used by people Speaking words into a word processor is not as who cannot use their hands. Words are simply spoken into the software instead of typed. accurate as typing. This means that mistakes are common with words that sound the same but have different meanings. For example: 'see' and 'sea'. Makes driving safer because people do not need to take their hands off the steering wheel in order to use their mobile phone. Background noise can interfere with voice recognition systems. Microphones are very cheap to buy. Magnetic Ink Card Reader (MICR) MICR input device is generally used in banks because of a large number of cheques to be processed every day. The bank's code number and cheque number are printed on the cheques with a special type of ink that contains particles of magnetic material that are machine readable. This reading process is called Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR). The main advantages of MICR is that it is fast and less error prone. Optical Character Reader (OCR) OCR is an input device used to read a printed text. OCR scans text optically character by character, converts them into a machine readable code and stores the text on the system memory. www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 17 | P a g e 17 | P a g e A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software Bar Code Readers Bar Code Reader is a device used for reading bar coded data (data in form of light and dark lines). Bar coded data is generally used in labelling goods, numbering the books etc. It may be a hand held scanner or may be embedded in a stationary scanner. Bar Code Reader scans a bar code image, converts it into an alphanumeric value which is then fed to the computer to which bar code reader is connected. Optical Mark Reader (OMR) OMR is a special type of optical scanner used to recognize the type of mark made by pen or pencil. It is used where one out of a few alternatives is to be selected and marked. It is specially used for checking the answer sheets of examinations having multiple choice questions. Digital Cameras Have pretty much replaced the old style film-based cameras. Digital cameras store digital photographs on a memory card and these images can easily be transferred onto a computer for viewing or editing. Most digital cameras have a built-in screen to allow for previewing the digital photograph. This is useful so that the photographer can decide which images to keep and which to delete. Digital camera image quality is measured in 'Megapixels'. These are the number of dots that make up the image. Generally speaking, the higher the Megapixels, the higher the detail quality of the image. 3 Megapixel cameras produce images made up of 3 Million pixels (dots). 24 Megapixel cameras produce images made up of 24 Million dots (8 times more detail Uses of Digital Cameras: Used to capture digital images for uses such as: Saving special moments (weddings, birthdays, family snaps etc) Gathering images for use in presentations, web pages or publications (newspapers and magazines etc) Easy to transfer images to a computer for editing. For example: using Photoshop to alter brightness or contrast www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 18 | P a g e 18 | P a g e A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software Images can be printed easily by: Uploading to a computer and then printing Connecting directly to a photo-printer and printing straight from the camera (no need to upload to a computer) Most digital cameras also allow for short, high-quality video clips to be produced. Advantages/Disadvantages of Digital Cameras: Advantages Disadvantages No film to develop. This means that producing the photo is much quicker. Camera user needs to have computer skills to be able to transfer and print digital photographs. Unwanted images can easily be deleted from the memory card. Not all digital cameras produce images as highquality as traditional cameras. Because the images are digital it is easy to make copies of them Artistry of traditional photography is being lost. No need to print at all because the images can be Camera software can automatically correct 'bad images' making photography easier to master without as much skill. viewed a computer screen. This saves paper and is better for the environment. Memory cards can store thousands of digital photographs. Traditional photographs can take up a lot of physical storage space. People using traditional 'film-cameras' had to take much more care to capture each image perfectly. Digital images can easily be transferred using blutooth, email attachments and mobile phones. Digital images can be improved and edited easily using software (sharpening the image for example) Web Cameras (web cams) Web cameras are similar to digital cameras in their function but they are directly connected to a computer and do not have memory storage. Web cameras can capture both digital images and video. Images / video are sent directly to the computer where they can be stored and used. www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 19 | P a g e 19 | P a g e A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software Uses of Web Cameras: Used to conduct face-to-face conversations with friends and family online over VoIP applications such as Skype. A similar use is to conduct face-to-face job interviews over the Internet. This removes the need for job applicants to travel very large distances to attend the interview. Used to hold video-conferencing meetings over the Internet. Can capture image and video content for presentations, web sites and even YouTube content. Web Cameras are sometimes used by parents to keep an eye on their children when they are in another room. Some people use web cams as a cheap alternative to security cameras. Sometimes used to allow drivers to view the traffic conditions on roads. Advantages/Disadvantages of Web Cameras: Advantages Disadvantages Allow for long-distance face-to-face conversations. This removes the need for people to travel. The image/video quality can sometimes be poor (low resolution). (especially useful for elderly and disabled people to keep in touch with family) Video conference business meetings and job interviews can be conducted very cheaply over long distances. They do not have their own storage and so must be permanently fixed to the computing device. (no need for expensive travel or bookings of hotel rooms to attend the meeting or interview) Parents can keep an eye on their children from a different location. Are usually in a fixed position and so cannot be easily moved around. Web cams can be left running constantly which makes them useful as security devices on properties. (as a form of security camera) www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 20 | P a g e 20 | P a g e A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software Biometrics When referring to computers and security, biometrics is the identification of a person by the measurement of their biological features. For example, a user identifying themselves to a computer or building by their finger print or voice is considered a biometrics identification. When compared to apassword, this type of system is much more difficult to fake since it is unique to the person. Below is a listing of all known biometric devices. Other common methods of a biometrics scan are a person's face, hand, iris, and retina. Types of biometric devices Face scanner - Biometric face scanners identify a person by taking measurements of a person face. For example, the distance between the persons chin, eyes, nose, and mouth. These types of scanners can be very secure assuming they are smart enough to distinguish between a picture of a person and a real person. Hand scanner - Like your finger print, the palm of your hand is also unique to you. A biometric hand scanner will identify the person by the palm of their hand. Finger scanner - Like the picture shown on this page a biometric finger scanner identifies the person by their finger print. These can be a secure method of identifying a person, however, cheap and less sophisticated finger print scanners can be duped a number of ways. For example, in the show Myth Busters they were able to fake a finger print using a Gummy Bear candy treat. Retina or iris scanner - A biometric retina or iris scanner identifies a person by scanning the iris or retina of their eyes. These scanners are more secure biometric authentication schemes when compared to the other devices because there is no known way to duplicate the retina or iris. Voice scanner - Finally, a voice analysis scanner will mathematically break down a person's voice to identify them. These scanners can help improve security but with some less sophisticated scanners can be bypassed using a tape recording. www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 21 | P a g e 21 | P a g e A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software Business card reader Similar to other computer scanners, a business card readerallows a user to scan business cards into their computer for digital storage. Computer scanners are capable of scanning and converting text documents to typed text by use of Optical Character Recognition (OCR) software. Business card readers work on a similar principle, reading the text on the business card and converting to typed text on the computer. Some business card readers offer the functionality of scanning a business card directly into a Microsoft Outlook contact record. Other readers can scan to a web format, directly to a new computer file, to a database or even to a CRM system, like SalesForce.com or Microsoft CRM. Some business card readers are capable of connecting to PDA devices, smartphones, and tablet computers. Today, many people are replacing business card readers with smartphones with apps capable of scanning and storing business card information. Light gun A light gun is a pointing input device that detects light using a photodiode in the gun barrel. When the player of the game pulls the trigger on the gun, the screen is blanked out for a fraction of a second, which allows the photodiode to determine where the gun is pointed. Light guns were most widely used with early console gaming systems such as the NES Zapper light gun, as shown in the picture. Using this gun the player could play games where they were required to point the gun at the screen and shoot targets, such as ducks in the popular Duck Hunt game. www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 22 | P a g e 22 | P a g e A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software Yoke A yoke is a hardware input device used with computer games, such as flight simulation games, that allow a player to fly up or down, or back or forth by pulling or pushing the device. The picture shows an example of a flight yoke by Saitekand is a good example what a typical yoke that connects to your computer. Paddle 1. More commonly known as a game paddle or gamepad, a paddle is an input device commonly used with games that may contain various buttons used to steer and utilize different options in a game. All console game systems utilize a paddle or gamepad for control. The picture shows an example of a game paddle used with the Atari 2600. 2. The term paddle may also be used to describe various handheld devices that are capable of controlling a function on a computer or electronic device. Computer - Output Devices Monitors Monitors, commonly called as Visual Display Unit (VDU), are the main output device of a computer. It forms images from tiny dots, called pixels that are arranged in a rectangular form. The sharpness of the image depends upon the number of pixels. There are two kinds of viewing screen used for monitors. Cathode-Ray Tube (CRT) Flat- Panel Display www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 23 | P a g e 23 | P a g e A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software Cathode-Ray Tube (CRT) Monitor The CRT display is made up of small picture elements called pixels. The smaller the pixels, the better the image clarity, or resolution. It takes more than one illuminated pixel to form whole character, such as the letter ‘e’ in the word help. A finite number of characters can be displayed on a screen at once. The screen can be divided into a series of character boxes - fixed location on the screen where a standard character can be placed. Most screens are capable of displaying 80 characters of data horizontally and 25 lines vertically. There are some disadvantages of CRT: Large in Size High power consumption Flat-Panel Display Monitor The flat-panel display refers to a class of video devices that have reduced volume, weight and power requirement in comparison to the CRT. You can hang them on walls or wear them on your wrists. Current uses of flat-panel displays include calculators, video games, monitors, laptop computer, graphics display. The flat-panel display is divided into two categories: Emissive Displays - The emissive displays are devices that convert electrical energy into light. Example are plasma panel and LED(Light-Emitting Diodes). Non-Emissive Displays - The Non-emissive displays use optical effects to convert sunlight or light from some other source into graphics patterns. Example is LCD(Liquid-Crystal Device) www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 24 | P a g e 24 | P a g e A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software Printers Printer is an output device, which is used to print information on paper. There are two types of printers: Impact Printers Non-Impact Printers Impact Printers The impact printers print the characters by striking them on the ribbon which is then pressed on the paper. Characteristics of Impact Printers are the following: Very low consumable costs Very noisy Useful for bulk printing due to low cost There is physical contact with the paper to produce an image These printers are of two types Character printers Line printers Character Printers Character printers are the printers which print one character at a time. These are further divided into two types: Dot Matrix Printer(DMP) Daisy Wheel www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 25 | P a g e 25 | P a g e A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software DOT MATRIX PRINTER In the market one of the most popular printers is Dot Matrix Printer. These printers are popular because of their ease of printing and economical price. Each character printed is in form of pattern of dots and head consists of a Matrix of Pins of size (5*7, 7*9, 9*7 or 9*9) which come out to form a character that is why it is called Dot Matrix Printer. Dot matrix printers are still used in environments where print speed and noise is not an issue (like in car garages and factories). These printers work by using a set of pins to press an inked ribbon against paper. When the pin/ribbon hits the paper a printed dot is left behind. The dots can be arranged to form basic text and images. Uses of Dot Matrix Printers: Dot matrix printers are very robust and can be used in noisy and dirty environments (like garages and warehouses). Can make ‘Carbon Copies’ of a document using special ‘Carbon Paper’ underneath normal printer paper. Advantages Disadvantages Work just fine in dusty and dirty environments Very noisy so not suitable for an office environment where laser or inkjet printers could easily be damaged. Carbon copies can be produced using carbonated paper. Very slow to print (slowest of all the types of printers) Very cheap to buy and maintain. Very poor print quality (Inked ribbons are very cheap) www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 26 | P a g e 26 | P a g e A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software Good for continuous printing. (e.g. long print jobs like wage slips) Cheaper to run than inkjets (low cost per page). Line Printers Line printers are the printers which print one line at a time. Non-impact Printers Non-impact printers print the characters without using ribbon. These printers print a complete page at a time so they are also called as Page Printers. These printers are of two types Laser Printers Inkjet Printers Characteristics of Non-impact Printers Faster than impact printers. They are not noisy. High quality. Support many fonts and different character size. Laser Printers These are non-impact page printers. They use laser lights to produce the dots needed to form the characters to be printed on a page. Uses of Laser Printers: www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 27 | P a g e 27 | P a g e A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software Very useful for printing where noise levels need to be kept low (Like in an office where people need to concentrate or use telephones etc). Good at producing high quality printouts very fast. Good for environments where high volume of printing is required (lots of printouts). This is because they have a low printing cost per page. Advantages Disadvantages Very fast at printing documents. Environmentally unfriendly (produce ozone). They also use more power than inkjets. Toner cartridges last a long time and don't need to be replaced often. Laser printers are more expensive to buy (but cheap to run). Laser printers can handle high volumes of printing. Colour laser printers are much more expensive to Very quiet when printing. buy and run than inkjets. Very high quality printouts. Reliable - don't breakdown as easily as inkjet printers. Cheaper to run than inkjets (low cost per page). They are larger in size compared to other types of printers. Inkjet Printers Inkjet printers are non-impact character printers based on a relatively new technology. They print characters by spraying small drops of ink onto paper. Inkjet printers produce high quality output with presentable features. www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 28 | P a g e 28 | P a g e A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software They make less noise because no hammering is done and these have many styles of printing modes available. Colour printing is also possible. Some models of Inkjet printers can produce multiple copies of printing also. Inkjet printers work by spraying ink onto a page of paper. The ink is held in 'ink cartridges' and there are 4 different colours - black, cyan, magenta and yellow. Uses of Inkjet Printers: Good where few printouts are needed (low volume). Ideal for single-page, very high quality printing. (Photo quality images). Often used to print photographs. Advantages Disadvantages Output is very high quality (Especially good for colour Slow printing rates, especially if several copies are photograph printing). needed. Much cheaper to buy than laser printers. Ink cartridges don’t last long and so are not suitable for large print jobs. Smaller than laser printers so take up less space. They can be expensive to run as new ink cartridges are not cheap to buy. Do not produce ozone or other harmful compounds. Very quiet whilst printing. Printouts can easily smudge if document is not left to dry properly. www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 29 | P a g e 29 | P a g e A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software Plotter Information: There are 2 different types of plotters --- drum and flatbed. Produce hard copies but are capable of printing on very large pieces of paper (e.g. 3 foot wide by 10 foot long). The print quality of plotters in very high. Plotters can also produce very large and accurate documents such as blueprints (plans) for buildings Plotters draw images on the page using colored pens which are moved around the paper by a computer. Uses of Plotters: Used to produce large, accurate drawings. Some examples are listed below: Blueprints of buildings (plans/designs) Maps Giant posters and adverts (like those we see on billboards). Pens can be replaced with cutting tools to produce large signs. www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 30 | P a g e 30 | P a g e A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software Advantages Disadvantages They can produce much larger printouts than other Their print times are very slow. printers. The print quality is extremely high. Plotters can also 'cut out' designs for use in sign making. Speakers Information: Many everyday uses of a computer require the user to listen to different types of sounds. For example: Listening to a music album Watching a movie. Browsing videos on YouTube Multimedia encyclopedias. Speakers are analogue and cannot output digital 'computerised' sounds. Digital data from the computer must first be converted into analogue sound using a sound card. The analogue sound can then be output via the speakers and we can listen to it. Uses of Speakers: Used to output sound from multimedia presentations (like famous speeches etc). Used in home entertainment (surround sound etc). Can be used by blind people to listen to words on the screen instead of reading . Note: Special software called 'screen readers' are also needed in order to convert the printed words into sound. Can be used to play downloaded music files. www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 31 | P a g e 31 | P a g e A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software Advantages Disadvantages Everyone in the room can hear the sound. Output from speakers can disturb people trying to work. They can help blind people use a computer because text can be turned into sound. High quality speakers can be expensive. Multimedia Projectors Information: These project whatever appears on a computer monitor onto a very large screen so that large numbers of people can view it. Multimedia Projectors are usually controlled using a remote control. The remote control makes it possible to direct the presentations without the need to be at the computer. Multimedia projectors are often hung from the roof on special brackets. Uses of Multimedia Projectors: Can be used for training presentations to allow the whole audience to see images from a single computer. Also used for large scale advertising of new products. For example: the famous Apple Technology Innovations presentations with Steve Jobs Home cinema systems where images from DVD’s or televisions are projected to a large screen. www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 32 | P a g e 32 | P a g e A-LEVEL IT (9626) 2.1 Hardware and software Advantages Disadvantages Many people to clearly view the same presentation. Lower image quality compared to a computer screen. Enhance the viewers experience. Very expensive to buy. For example: watching movies on a large screen is better than a small TV screen. Cooling fans in the projector are noisy. www.mrsaem.com www.mrsaem.com 33 | P a g e 33 | P a g e