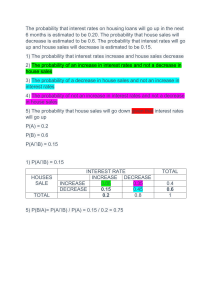
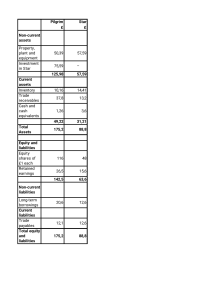
24 Balance sheets Revision answers 1 An income statement records revenue, costs and profits/losses over a period of time, often one year. A balance sheet shows the value of the assets owned and liabilities owed by a company – and shareholders’ equity – at one moment in time. 2 An asset is an item of value that is owned by a business, such as a shop or factory. A liability is owed by the company to an external person or lender, for example, a bank loan. 3 i) Premises (if the restaurant building is owned by the business). ii) Cooking equipment. 4 Both examples are of assets that the business is likely to keep for more than one year. In the case of the premises it could be many years. Current assets are those items owned by a business for less than one year. 5 i) Food stocks. ii) Debtors (customers who have been allowed time to pay, for example, business account customers). 6 Long-term loan. 7 Non-current liabilities are loans that last for more than one year. A long-term loan will be taken out for several years. 8 Examples: i) Overdraft: might have been necessary to pay for a large delivery of clay that will be used over a period of several weeks. ii) Creditors: suppliers of paint that have allowed the business time to pay. 9 a) Total current assets (x) is the sum of all current assets = 5 + 4 + 1 = 10 Total liabilities (y) are the sum of non-current and current liabilities = 8 + 11 = 19 Total shareholders’ equity (z) is the sum of share capital and retained profits (which is the same as total assets less total liabilities) = 4 + 2 = 6 b) i) They could see that current assets are greater than current liabilities – so the business should be able to pay all of its short-term debts. ii) Long-term loans are very high compared with shareholders’ equity – the business depends heavily on external long-term finance. 10 This is the value of what the shareholders own in the company – the higher shareholders’ equity is, then the greater the value that would be paid to each shareholder if the business ceased trading and assets were sold off. Increases in shareholders’ equity caused by high retained profits are likely to increase the price of the company’s shares. Answers to activities Activity 24.1 Vehicles NCA; Cash CA; 10-year loan NCL; Share capital = share capital!; Money owed by customers CA; Unsold goods CA; Factory NCA; Retained profit Reserves; Amounts owed to suppliers CL; Tax owed CL. Activity 24.2 a) Working capital (CA−CL) fell from $25m to $10m. b) This means the business is having to find less finance to pay for its working capital; perhaps this finance could be used to help expand the business instead. Cambridge IGCSE Business Studies 4th edition Teacher’s CD © Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2013 1 24 Balance sheets c) Loans increased by $55m but the other two sources of finance only increased by $20m each. d) If inventories (stocks) are reduced then more capital is freed up to be used elsewhere in the business; it would reduce chances of the goods being damaged or going out of fashion (if this is appropriate in this case). But a reduction in inventories may give the customer less choice; perhaps inventories are increasing as the business is expanding and sales are rising so more goods need to be kept in stock as well. More information might be needed before making a final decision. e) Yes: business is expanding by using a range of sources of finance; non-current assets have increased; reserves increased this year so the business is profitable. No: the company’s ability to pay short-term liabilities has fallen; long-term loans have increased rapidly: the business is taking a risk here as if interest rates increased, the costs of the business would increase. Activity 24.3 a) b) c) d) x = $71m; y = $33m; z = $15m Machines/tools/premises Wood, clay, paints KL has a slightly greater ability to pay off its short-term debts, mainly because it has low current liabilities; KL has lower inventories (relatively) than HK. HK has relatively low level of long-term loans: not as risky as KL. HK has strong cash position. Student’s overall assessment. Sample answers to Paper 1 style questions (with mark annotations for Question 2) 1 a) Assets owned by the business likely to be kept for more than one year. b) i) Stocks of bricks and other building materials. ii) Debtors, for example, customers being allowed time to pay for building work. c) i) The business made retained profits and these increased shareholder equity. ii) The business sold a new issue of shares during the year and the value of these was added to shareholders’ equity. The increase in long-term loans or debentures might have been used d) i) to expand the business by buying more land on which to buy houses in future. Once the houses are built and sold the loans can be repaid. ii) The finance raised by the long-term loans or debentures might have been used to pay for a long-term increase in working capital because of a large building project, for example, more inventories and debtors need to be financed for a long period of time. e) Quite useful: loans increased last year, so is now a good time to increase loans further to take on the other business? Current assets have increased: could these be reduced to help raise some of the capital needed for the takeover? Not very useful: much more information needed, for example, is Acme holding much cash? Is the other business profitable? Could Acme issue more shares? What is the total asset and total liability value of this other business? Overall conclusion/judgement needed. Cambridge IGCSE Business Studies 4th edition Teacher’s CD © Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2013 2 24 Balance sheets 2 a) The total value of shareholders’ investment in the company or share capital + reserves. [2K] b) i)Suppliers of car parts that have not yet been paid (creditors/accounts payable). ii) A large company (it is a plc) is likely to have an overdraft arrangement with the bank. [2App] c) i)Penang Garages might be holding a lower value of inventories of car parts. [1K; 1App] ii) Penang Garages might have sold fewer cars on credit so debtors (accounts receivable) is lower. [1K; 1App] d) i)It is a plc so the current share price and how the share price of the company has changed – potential investors will want to invest in companies whose share prices are most likely to rise in future. [1K; 1App; 1An] ii) The profitability of the company as shown on the income statement – the data given is from the balance sheet which does not show the profits of Penang Garage. Shareholders will want annual dividend payments, which are made out of profit. [1K; 1App; 1An] e) Yes: non-current assets have increased so the business has invested in more equipment/property; non-current liabilities have fallen so the company has paid back some loans during the year. No: current assets have fallen, making the business less liquid particularly when compared with the current liabilities which have increased. Student’s overall conclusion. [1K; 1App; 2An] + [2Eval] Answers to revision test 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 3) 4) 4) 4) 4) 3) 4) 3) 2) 1) Cambridge IGCSE Business Studies 4th edition Teacher’s CD © Hodder & Stoughton Ltd 2013 3