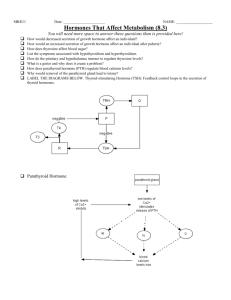
QUESTION BANK Anatomy and Physiology II Exam 1 Question Bank Endocrinology 1: Which of the following is directly related to the chemical reactions that occur in the body? A: Growth B: Metabolism C: Personally D: Sex Characteristics 2: An endocrine reaction is slow acting, but it doesn’t last very long. A: True B: False 3: The venue of message transmission for the nervous system includes hormones. A: True B: False 4: Receptors are used for these kinds of hormones. A: Steroid B: Eicosanoids C: Amino acid D: Targeted 5: Chemicals that function to communicate within animals are: A: Hormones B: Pheromones C: Calcium D: None of these 6: Pheromones are chemicals that effect physiology between animals. A: True B: False 7: Which of the following is not a function of a hormone? A: Increase mitosis B: Increase or decrease enzyme activity C: Cause cell apoptosis D: Change membrane permeability 8: Hormones can bind to any receptor A: True B: False 9: Someone who takes melatonin pills would most likely see ______ in their nervous system. A: Necrosis B: Down-regulation C: Up-regulation D: No change 10: Which of the following hormonal interactions is seen when thyroxine allows estrogen to be created. A: Permissiveness QUESTION BANK Version 1 THIS DOCUMENT IS PROTECTED BY CREATIVE COMMONS. DO NOT COPY, ALTER, OR REDISTRIBUTE WITHOUT SPECIFIC PERMISSIONS FROM AUTHOR UNDER PENELTY OF LAW 1 B: Synergism C: Antagonism D: None of these 11: Steroid hormone – hormones that are hydrophilic – can pass through the cell membrane with no additional receptor required. A: True B: False For questions X-X put the steps of the Cyclic AMP system in correct order using the column to the right. 12: Step 1 C A: Active G-protein causes adenylate cyclase to be activated B: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate actives protein kinases 13: Step 2 E C: 1st messenger (hormone) binds to receptor 14: Step 3 A D: Adenylate Cyclase makes cyclic adenosine monophosphate 15: Step 4 D E: G-Protein is activated using MTP 16: Step 5 B 17: In the IP3 system, the PIP2 is split into diacylglycerol and IP3. A: True B: False 18: What does the release of IP3 initiate? A: Release of Na++ from the cell B: Causes a ribosomal reaction C: Causes release of Ca++ from the Endoplasmic Reticulum D: Activation of Protein Kinases Use the column to the right for questions X-X. 19: Found in the dorsal body cavity, known for secretion of a sleep-wake cycle hormone. B 20: Largest endocrine gland C 21: Promotes calcium homeostasis E 22: Under direct control from the nervous system A 23: Secretes corticosteroids and neurotransmitters F 24: Contains Islets of Langerhans G 25: Involved with T-Cell maturation D 26: Secretes androgen H A: Pituitary Gland B: Pineal Gland C: Thyroid Gland D: Thymus Gland E: Parathyroid Gland F: Adrenal Gland G: Pancreas H: Gonads 27: What is the master gland according to Daempfle? A: Pituitary B: Pons C: Hypothalamus D: Thalamus 28: The hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract connects to the ______ from the ______. Version A 2 A: Hypothalamus, Thalamus B: Pituitary, Hypothalamus C: Thalamus, Hypothalamus D: Pituitary, Thalamus 29: The hypothalamus is a part of the lower brain that receives information from other parts of the body. A: True B: False Use the column to the right to answer questions X-X. 30: Stimulates the generation of corticosteroid hormones. B A: TSH 31: Released due to a positive-feedback mechanism during B: Adrenocorticotropin labor. H C: Gonadotropin 32: Stimulates development of gametes. E D: Luteinizing hormone 33: Stimulates the generation of thyroxine. A E: Follicle stimulating hormone 34: Stimulated by GnRH. C F: Prolactin 35: Involved with mammary activity. F G: Growth hormone 36: Promotes gonadal hormone production. D H: Oxytocin 37: Promotes water retention. I 38: Stimulates bones and muscles to increase in size. G I: Antidiuretic Hormone 39: What do tropic hormones have to use to relay their message? A: IP3 System B: cAMP system C: Osmotic reactions D: None, they are fat soluble and dissolve through the membrane 40: The anterior of the pituitary gland is comprised of epithelium to secrete hormones; while the pituitary section is a bundle of nervous tissue. A: True B: False 41: What lowers blood Ca++ A: Thyroxine B: Calcitonin C: Parathyroid hormone D: None of these 42: The parathyroid is only found within the thyroid. A: True B: False 43: Which of the following is not a physiologic result of parathyroid hormone? A: Increased osteoblastic activity B: Increased absorption in the intestines C: Calcium retention in nephrons of kidney Version A 3 D: These are all functions of parathyroid hormone Use the column to the right to answer questions X-X 44: Hyposecretion of adrenal cortex, results in decreased Na+, and increase K+. I 45: Decreased metabolism from a deficiency of thyroxine. D 46: Occurs when growth hormone continues to secrete after epiphyseal plates close. G 47: Thyromegaly due to a lack of iodine in diet. E 48: An autoimmune disorder where antibodies mimic TSH and overstimulate thyroid. A 49: An overactive thyroid. B 50: An underactive thyroid. C 51: Causes by a hypersecretion of growth hormone early in life. F 52: Hypersecretion of glucocorticoids from an adrenal tumor. H A: Graves’ Disease B: Hyperthyroidism C: Hypothyroidism D: Cretinism E: Goiter F: Gigantism G: Acromegaly H: Cushing disease I: Addison’s Disease 53: What hormone made by parafollicular cells is an antagonist to parathyroid hormone? A: Calcitonin B: Ca++ C: Thyroxine D: Triiodothyronine 54: Chief cells secrete parathyroid hormone. A: True B: False 55: Gonadocorticoids are made in this layer of the adrenal cortex. A: Zona glomerulus B: Zona fasciculata C: Zona reticularis D: None of these 56: Glucocorticoids are ______ that are made by the ______. A: Metabolic hormones, zona fasciculata B: Metabolic hormones, zona glomerulosa C: Steroid hormones, zona fasciculata D: Steroid hormones, zona glomerulosa 57: Mineralocorticoids are ______ and secreted by the ______. A: Water in blood, zona reticularis B: Water in blood, zona glomerulosa C: Glucagon imitators, zona reticularis D: Glucagon imitators, zona glomerulosa 58: The adrenal medulla only secretes both epinephrine and norepinephrine. A: True B: False 59: In the pancreas, alpha cells secrete ______ and beta cells secrete ______. Version A 4 A: Insulin, pancreatic juices B: Insulin, glucagon C: Glucagon, insulin D: Glucagon, pancreatic juices 60: What is the average blood sugar for humans? A: 30 mg/ml B: 60 mg/ml C: 90 mg/ml D: 140 mg/ml 61: In ______ Diabetes Meletus there is a down-regulation in insulin, and in ______ Diabetes Meletus there is an auto immune attack on the Islets of Langerhans. A: Type I, Type II B: Type II, Type I C: Type I, Type I D: Type II, Type II 62: This gland secretes more of its hormone in the winter A: Pituitary B: Pineal C: Thyroid D: Parathyroid Blood 63: ______ mostly carry oxygenated blood, and ______ mostly carry deoxygenated blood. A: Capillaries, Veins B: Capillaries, Arteries C: Arteries, Veins D: Veins, Arteries 64: Capillaries can exchange O2 and CO2 because they are made of simple cuboidal epithelium A: True B: False Use the column to the right to answer questions x-x. A: Complete Blood Count 65: Tests the rate of clotting. D 66: Tests the total of formed elements. A B: Hematocrit 67: Tests the percent of leukocytes in the blood. C C: Differential 68: Tests for different minerals in the blood E D: Prothrombin Time 69: Tests for the ratio of erythrocytes to the total volume of blood. B E: SMAC 70: Plasma – a straw colored liquid – is 90% H2O. A: True B: False 71: The normal pH of blood is ______ to ______. A: 7.25, 7.35 Version A 5 B: 7.35, 7.45 C: 7.35, 7.55 D: 7.45, 7.55 72: Arteriolar blood is usually bright red, and venous blood is usually dark red. A: True B: False 73: Which of the following is not a function of the blood? A: Body temperature B: pH homeostasis C: Fluid Volume D: None of these 74: The blood distributes hormones, wastes, and oxygen. A: True B: False 75: Antibodies are proteins for a general category of invaders, making it most effective for a frontline battle. A: True B: False 76: Na+ and plasma proteins maintain ______. A: Calcium balance B: Sodium balance C: Osmotic balance D: None of these 77: Erythrocytes are mitotic, and therefore are created efficiently. A: True B: False 78: Erythrocytes are pliable due to ______. A: Fe (iron) B: Their size (7.5 micrometers diameter) C: Seratin protein D: Enzymes 79: Why do erythrocytes not contain organelles? A: The bone marrow does not have the ability to produce the organelles B: It would take too much energy to produce the organelles C: The mitosis of the cell would take too long if there were organelles D: The erythrocyte would then use the materials it is transporting 80: Hemoglobin is comprised of ______ and ______ bound to a ring-like heme group. A: 2 alpha chains, 3 beta chains B: 2 alpha chains, 2 beta chains C: 2 alpha chains, a Fe group D: 3 alpha chains, 2 beta chains Version A 6 81: Where in the long-bone does erythropoiesis occur? A: Medullary cavity B: Diaphysis C: Epiphysis D: Endosteum 82: Hypoxemia will result in a decrease in: A: Erythropoietin production B: Leukocyte production C: Deeper breathing D: No changes 83: The lifespan of erythrocytes is approximately 110 days. A: True B: False Use the column to the right to answer questions X-X. 84: Contains the largest granules that bind to Immunoglobin E. C 85: Related to allergies. B 86: Nucleus make up most of cell volume, mature in spleen and thymus. D 87: Can become wandering macrophages E 88: Produce copious H2O2 and are polymorpho nuclear leukocytes. A 89: Most numerus leukocyte. A A: Neutrophil B: Eosinophil C: Basophil D: Lymphocyte E: Monocyte 90: The Epstein Barr virus results in clouded cytoplasm A: True B: False 91: Platelets are: A: Chunks of megakaryocytes B: Anucleic C: Kept inactive by prostaglandins D: All of the above 92: Platelets and endothelial cells release chemicals that cause: A: EPO to be released B: Release of granules C: Vasoconstriction D: Vasodilation 93: The second phase of clotting is a positive-feedback system where: A: Vasoconstriction occurs B: Vasodilation occurs to allow for clotting factors to flood the area C: Coagulation occurs at the site D: Platelets attach to collagen fibers of wounded vessel 94: Thrombin activates before the platelets are attached. A: True Version A 7 B: False Use the patient chart below to answer questions X-X. EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT PATIENT CHART PATIENT NAME: Jennie Tailiya AGE: 15 SEX: F PAST MEDICAL HISTORY: None NARRATIVE: pt was admitted to ED c/o malaise and other associated symptoms. Diff, and Hematocrit were ordered, results are attached below. Dx pending consultation from MD. LAB RESULTS: Differential: Neut: 80% Lymp: 15% Mono: 3% Eosi: 1.5% Baso: .5% Hematocrit: 67% 95: Based on the patient chart, what leukocyte has the most abnormal result? A: Neutrophil B: Lymphocyte C: Monocyte D: Eosinophil E: Basophil 96: If the patient states that they have trouble doing any activities without loosing their breath, what result would you be interested in looking at? A: Differential B: Hematocrit C: None of these 97: Does the patient have an abnormal Hematocrit? A: Yes, it is abnormally high B: Yes, it is abnormally low C: No, it is normal 98: The doctor tells that patient that they may have leukemia. What kind of leukemia does the patient have? A: Acute B: Chronic C: The patient does not have leukemia 99: Prothrombin ______, ______ Fibrin A: Fibrinogen, thrombin B: Thrombin, fibrinogen C: Fibrinogen, prothrombin activator D: Prothrombin activator, fibrinogen 100: The intrinsic pathway triggers clotting through ______; while the extrinsic pathway triggers clotting through ______. A: Platelets sticking to collagen, B: Platelets sticking to collagen, tissue factor releasing C: Tissue factor releasing, D: Tissue factor releasing, platelets sticking to collagen Version A 8