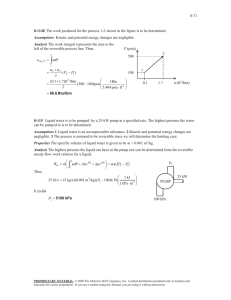
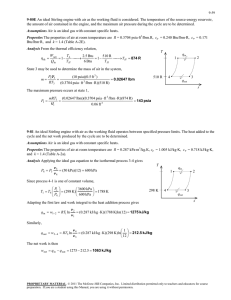
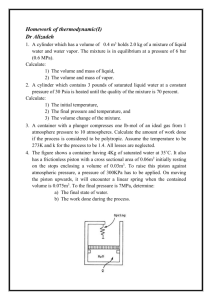
CHEMISTRY 1. It is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. a. molecular number c. mass number b. proton number d. atomic number 2. It is the number of protons plus the number of neutrons: a. atomic number c. molecular number b. mass number d. proton number 3. The _____________ is calculated by adding together all the atomic numbers: a. molecular weight c. formula weight b. compound weight d. none of these 4. An element may be defined as a substance, all the atoms of which have the same: a. number of neutrons c. atomic weight b. radioactivity d. atomic number 5. The different types of atoms in a given element are called: a. molecules c. isotopes b. neutrons d. compounds 6. All isotopes of the same element have: a. Equal no. of protons and neutrons b. Equal no. of protons c. The same atomic mass d. Equal no. of neutrons 7. What is a substance that cannot be decomposed into simpler substances during ordinary chemical reactions? a. Atom c. Molecule b. Element d. Compound 8. Salt, water, rubber, iron rust are called ____________. a. mix atom c. element b. chemical compound d. molecule 9. The particle inside the nucleus is called a. Nucleons c. Nucleic b. Nuclei d. Nuclide 10. If the volume of a confined gas is constant, the pressure is directly proportional to the absolute temperature. This is known as a. Kelvin’s law c. Boyle’s law b. Charles’ law d. Joule’s law 11. If the temperature of a confined gas is constant, the product of the pressure and volume is constant. This is known as a. Kelvin’s law c. Boyle’s law b. Charles’ law d. Joule’s law 12. Which of the following is the Ideal Gas Law? a. V/T =k c. PV = nRT b. P1/T1 = P2/T2 d. V = K x 1/P 13. The temperature to which the air must be cooled at a constant pressure to produce saturation is called: a. boiling point c. critical point b. dew point d. triple point 14. The changing of solid directly to vapor without passing through the liquid state is called: a. evaporation c. vaporization b. sublimation d. condensation 15. Sublimation refers to: a. the vaporization of solid without first becoming a liquid b. the melting of a solid c. the vaporization of a liquid d. maybe in any or all of the above into a liquid 16. At the same pressure and temperature, equal volumes of all gases contain equal number of molecules. This is known as: a. Faraday’s law c. Boyle’s law b. Lenz’ law d. Avogadro’s law 17. The number of molecules in a mole of any substance is constant, this number is called a. Thompson’s constant c. Otto cycle b. Rankine cycle d. Avogadro’s number 18. How many moles are there in one atom? a. 1.66 x 10-23 moles c. 1.66 x 1023 moles b. 1.66 x 10-24 moles d. 1.66 x 1024 moles 19. The atomic weight of hydrogen is 1 gram per gram-atom. What is the mass of a hydrogen atom? a. 1.66 x 10–24 g/atom c. 6.02 x 10–23 g/atom b. 1.0 x 10–10 g/atom d. 1 g/atom 20. The mole is a basic unit of measurement in chemistry. Which of the following is not equal to or the same as one mole of the substance indicated? a. 22.4 liters of Nitrogen (N2) gas at STP b. 6.02 x 10²³ oxygen (O2) molecules c. 16g of oxygen (O2) molecules d. 1g of hydrogen (H) atoms 21. The critical point for mixture occurs for which of the following cases? a. the vapor and the liquid have a single form b. the liquid has no absorbed gas c. the vapor phase is stable d. the liquid is completely vaporized 22. How is “molality” defined? a. the number of moles of solute in 1000 grams of solvent b. the number of moles of solute in 1 liter of solution c. the number of gram-formula weights of solute per liter d. the number of gram-equivalent weights of solute in 1 liter of solution 23. All gases at the same temperature and pressure under the action of a given value “g” have the same number of molecules per unit volume from which it follows that specific weight of a gas is proportional to its molecular weight is known as: a. Avogadro’s Law c. Torrecillis’s principle b. Boyle’s Law d. Archimedes’ principle 24. Which are the electrostatic forces that exist between ions? a. ionic bond c. chemical bond b. covalent bond d. atomic bond 25. What are Van der Waals forces? a. weak secondary bonds between atoms b. primary bonds between atoms c. forces between electrons and protons d. forces not present in liquid 26. What are valence electrons? a. the outer shell electrons b. electrons with positive charge c. the electrons with complete quantum shells d. the K – quantum shell electrons 27. Strong bonds between hydrogen atoms is known as: a. the ionic bond c. the metallic bond b. ionic and metallic bond d. the covalent bond 28. Which of the following is the strongest type of bond: a. Van Der Waals c. covalent b. metallic d. ionic 29. In molecules of the same composition, variations of atomic arrangements is known as: a. polymers c. isomers b. monomers d. crystal systems 30. In a crystal structure, what is an interstitial atom? a. an extra atom sitting at a non-lattice point b. an atom missing at a lattice point c. a different element at a lattice point d. a line defect 31. As the amount of slip increases, additional deformation becomes more difficult and it decreases until the plastic flow finally stops. Slip may begin again only if a larger stress is applied. What is this phenomenon called? a. cooling c. crowding b. strain hardening d. twinning 32. What causes the vinyl interiors of automobiles to crack when subjected to prolonged direct sunlight? a. the volatilization of plasticizers b. repetitive expansion and contraction of the plastic c. oxidation of the plastic by sunlight and oxygen d. all of the above 33. Low density polyethylene undergoes extensive elongation (over 100%) prior to rupture, while polystyrene undergoes only 1 to 2 percent elongation. What is the main reason for this difference? a. the polyethylene is less dense b. the large styrene groups in the polystyrene prevent slippage c. more cross linking occurs in the polystyrene d. polyethylene is less crystalline 34. How is the quality, x, of a liquid-vapor mixture defined? a. the fraction of the total volume that is saturated vapor b. the fraction of the total volume that is saturated liquid c. the fraction of the total mass that is saturated vapor d. the fraction of the total mass that is saturated liquid 35. It is defined as a measure of the amount of negative ions in the water. a. b. alkalinity acidity c. turbidity d. solubility 36. The measure of acids in solutions is called: a. alkalinity c. turbidity b. acidity d. solubility 37. Which of the following is the standard temperature and pressure (STP)? a. 0°K and one atmospheric pressure b. 0°F and zero pressure c. 32°F and zero pressure d. 0°C and one atmospheric pressure 38. Which of the following elements and compounds is unstable in its pure form? a. sodium (Na) c. helium (He) b. carbon dioxide (CO2) d. hydrochloric acid (HCl) 39. A substance is oxidized when which of the following occurs? a. it turns red c. it becomes more negative b. it losses electrons d. it gives off heat 40. Boiling point of water occurs when: a. its vapor pressure equals the atmospheric pressure b. its vapor pressure is ½ the atmospheric pressure c. its vapor pressure is twice the atmospheric pressure d. none of these 41. Two major types of chemical bonds are absorbed in chemical bonding: ionic and covalent. Which of the following has a bond that is the least ionic in character? a. NaCl c. CH4 b. H2 d. H2O 42. In order to assign oxidation states in polyatomic molecules, which of the following rules is followed? a. the oxidation of all elements in any allotropic form is zero b. the oxidation state of oxygen is always –2 c. the oxidation state of hydrogen is always +1 d. all of the above rules are used 43. Reactions generally proceed faster at higher temperature because of which of the following? a. the molecules collide more frequently b. the activation energy is less c. the molecules are less energetic d. both a and b 44. It is a process of application of chlorine that results in minimum chloramines residuals? a. breakpoint chlorination b. distillation c. coliform d. electrodialysis 45. Which of the following affects most of the electrical and thermal properties of materials? a. the atomic weight expressed in grams per gram-atom b. the electrons, particularly the outermost ones c. the magnitude of electrical charge of the protons d. the weight of the atoms 46. Which of the following describes diffusion in a crystal structure? a. it is not possible b. it occurs only in alloys, never in pure crystals c. it often uses an exchange or vacancy mechanism d. it occurs primarily as a result of mechanical work 47. Compare the metallic iron atom Fe and the ferric ions Fe 2+ and Fe3+. Which has the smallest atomic radius? (Assume that all are at the same temperature.) a. Fe c. Fe2+ b. Fe3+ d. they have the same radii 48. When Fe++ changes to Fe+++ in a reaction: a. it losses a proton c. it gains a proton b. it gains an electron d. it losses an electron 49. Which of the following is a line defect in a lattice crystal structure? a. tilt boundary c. screw dislocation b. vacancy d. Schottky imperfection 50. Cesium (Cs) and sodium (Na) both have the same valence (+1), yet with chlorine (Cl), cesium has a coordination of 8 in CsCl, while sodium has a coordination number of only 6 in NaCl. What is the main reason for this difference? a. the atomic weight of Cs is larger than the weight of Na b. Cs forms covalent bonds in CsCl c. Cs contains more electrons than Na d. Cs is too large to be coordinated by only 6 chloride ions 51. Which of the following materials is not a visco-elastic material? a. plastic c. metal b. rubber d. glass 52. Polymers that favor crystallization are least likely to have which of the following: a. an atactic configuration of side groups b. small side groups c. only one repeating unit d. small chain length 53. Which crystal structure possesses the highest number of close-packed planes and closepacked directions? a. simple cubic c. close-packed hexagonal b. body-centered cubic d. face-centered cubic 54. What is transformed in a eutectoid reaction? a. one solid is transformed into two solids of different composition b. a solid becomes a liquid at the eutectic temperature c. a liquid becomes a solid at the solidus temperature d. a solid becomes a liquid at the liquidus temperature 55. On an alloy phase diagram, what is the solidus temperature? a. the point at which all solids completely reach the liquid stage b. the temperature of the liquid phase at which the first solid forms for a given overall composition c. the temperature of the solid phase at which the first liquid forms for a given overall composition d. the temperature at which the solid is at equilibrium 56. What are the most common slip planes for face-centered cubic and body-centered cubic structures, respectively? a. face-centered: (111), body-centered: (110) b. face-centered: (100), body-centered: (110) c. face-centered: (110), body-centered: (111) d. face-centered: (111), body-centered: (100) 57. Which of the following statements is false? a. ceramics are inorganic, nonmetallic solids that are processed or used at high temperatures. b. metals are chemical elements that form substances that are opaque, lustrous and good conductors of heat and electricity. c. most metals are strong, ductile and malleable. In general, they are heavier than most other substances. d. polymers are formed from many atoms with low molecular weight, bonded together by primary valence bonds. 58. Comparing the face-centered cubic lattice with the hexagonal close-packed lattice, which of the following features describes the hexagonal close-packed structure only? a. it has the closest packed lattice structure b. its coordination number is 12 c. its deformation properties are more directional d. its stacking order is ABCABC 59. Which of the following accurately describes differences between crystalline polymers and crystals? I. Crystalline polymers are made of folded chains of atoms unlike simple crystals. II. Crystal size can be increased by raising the crystallization temperature only in polymers. III. White simple crystal may be totally crystallized, a polymer can reach only partial crystallization. a. I only c. III only b. II only d. I and III 60. What is the atomic packaging factor for simple cubic crystal? a. 0.48 c. 0.52 b. 1.00 d. 1.92 61. How many atoms are in the unit cell of a body-centered cubic structure? a. 1 c. 3 b. 2 d. 4 62. How many atoms are there per units cell for a face-centered cubic structure? a. 1 c. 3 b. 2 d. 4 63. What is the first coordination number of a body-cubic structure? a. 4 c. 6 b. 8 d. 10 64. What is the first coordination number if a face-centered cubic structure? a. 2 c. 4 b. 8 d. 12 65. Which of the following statement is false? a. b. c. d. both copper and aluminum have a face-centered cubic crystal structure. both magnesium and zinc have a hexagonal close-packed crystal structure. all of the alkali metals have a body-centered cubic crystal structure. both lead and cadmium have a hexagonal close-packed crystal structure. 66. How are the close-packed planes in a face-centered cubic metal designated? a. (100) c. (200) b. (110) d. (111) 67. Which is Fick’s first law for one-dimensional, steady diffusion? C, is the volume concentration of atoms; x, is the distance along diffusion occurs; D, is the diffusion coefficient; and J is the flux or current density. a. J = -D ∂C/∂x c. J = C ∂D/∂x b. J = -∂C/D∂x d. J = 2D ∂C/D∂x 68. Which of the following are true about Fick’s first law of diffusion? I. It is only applicable to liquids, not solids. II. The law states that the flux moves from high to low concentration. III. J, the flux may be in units of cm³/cm²s. a. I only c. III only b. II only d. II and III 69. A substance that losses electron during redox act is: a. oxidizing agent c. reducing agent b. catalyst d. solvent 70. A substance which changes the speed of a chemical action without itself being changed is called: a. catalyst c. reactant b. additive d. product 71. It is also called the “laughing gas”. a. Methane c. Cyanic acid b. Nitrous oxide d. Ethane 72. Which of the following is not an important criterion for forming a complete binary solid solution? a. the difference in radii should be less than 15%. b. the constituent elements must have the same crystal structure. c. the atoms should be close to one another in the periodic table. d. the difference in atomic number should be small. 73. How can an ordered solid solution be distinguished from a compound? a. In an ordered solid solution, the solute atoms occupy interstitial position within the lattice. b. The solute atoms in an ordered solid solution substitute for atoms in the parent lattice. c. The atoms in an ordered solid solution form layers in the lattice structure. d. When heated, an ordered solid solution becomes disordered before melting. 74. It is a mixture of two or more non-volatile liquids in which separation takes place very slowly. a. suspension c. solutions b. colloids d. emulsion 75. This type of solution contains enough solute a solvent can hold at a given temperature and pressure. a. unsaturated solution b. supersaturated solution c. saturated solution d. dilute solution 76. It is the property of a solution that depends on the number on solute particles present not on the nature of the particles. a. boiling point c. vapor pressure b. colligative d. osmotic pressure 77. It is the transfer of solvent molecules through a semi-permeable membrane to equalize the solute concentration on both sides of the membrane. a. osmotic pressure c. evacuation b. osmosis d. transformation 78. Carrier mobility depends on: a. resistivity b. conductivity c. recombination rate d. temperature and the regularity of the crystal structure 79. The movement of charges from an area of high carrier concentration to an area of low carrier concentration is called: a. gradient c. recombination b. diffusion d. lifetime 80. The process of one substance mixing with another because of molecular motion. a. saturation c. adhesion b. absorption d. diffusion 81. The freezing point of water is 0°C. Its melting point is: a. slightly less than 0°C c. 0°C b. slightly more than 0°C d. 32°C 82. The materials with the highest heat conductivities are the: a. gases c. liquids b. woods d. metals 83. The quantum number n of the lowest energy state of a hydrogen atom is: a. 0 b. depends on the orbit size c. 1 d. depends on the electron speed 84. The number of quantum number needed to determine the size and shape of the probability cloud of an atomic electron is: a. 1 c. 3 b. 2 d. 4 85. Each probability cloud in an atom can be occupied by: a. one electron b. two electrons with spins in the same direction c. two electrons with spins in opposite direction d. any number of electrons 86. The chemical process which occurs when the water is added to cement is: a. hydration c. oxidation b. Brownian movement d. plastic flow 87. Superheated vapor behaves a. just as gas b. just as ordinary vapor c. just as steam d. approximately as a gas 88. The molecular volume of any perfect gas at 600 x 10³ N/m² and 27°C will be a. 41.7 m³/kg mol c. 85.3 m³/kg mol b. 4.17 m³/kg mol d. 2.085 m³/kg mol 89. Antifreeze chemicals are a. same as refrigerants b. those that are added to refrigerants for better performance c. those that lower down the freezing point of liquids d. those that do not freeze at all 90. Clog point of an oil refers to a. the point of maximum contamination of oil b. the level of impurities beyond which oil ceases to flow c. the temperature at which oil solidifies d. the temperature at which paraffin and waxes in oil start precipitating 91. Which of the following gas can be used to measure the lowest temperature? a. nitrogen c. oxygen b. helium d. hydrogen 92. In actual gases, molecular collisions are a. plastic b. elastic c. inelastic d. inplastic The opposite of alkali: a. acid b. fluid c. none of these d. substance 93. 94. A kilo mole of methane is 16 kg. compute the density of methane at 20oC and 6 – atm pressure: a. 2.66 kg/m3 c. 6.02 kg/m3 b. 3.33 kg/m3 d. 4.80 kg/m3 95. A tank having a capacity of 2 cu. ft. is filled with oxygen which has a gauge pressure of 60 psi when the temp. is 47oC. At a later time it is found that because of the leak the pressure has dropped to 50 psi and the pressure has decreased to 27 oC. What is the amount of oxygen that has leak out: a. None of these c. 0.0915 b. 0.0583 d. 0.153 96. In two molecules of Ba(OH)2 there are _______________ oxygen atoms: a. one c. four b. two d. seven 97. In a compound MnCl2 there are _______________ different types of atoms: a. five c. three b. two d. four 98. In a compound Ba3(PO4)2 there are a total of _____________ atoms: a. Five c. Thirteen b. Twelve d. Ten 99. Removal of electrons from the neutral atoms increases the positive charge resulting in a positively ion called _____________: a. proton c. anion b. cation d. none of these 100. To determine the molecular formula we must know ______________: a. weight percent composition only b. molecular weight only c. both molecular weight and weight percent composition d. weight percent composition and atomic weight 101. One isotope if the element Uranium has 143 neutrons. Uranium has an atomic number of 92. The mass number of this isotope is _________: a. 143 c. 235 b. 82 d. 51 102. Covalent compounds composed of two elements are called __________: a. diatomic c. binary b. polyatomic d. bielementary 103. In ionic compounds, anions and cations are mixed so that the number of electrons lost in cation formation is ________ to the number of electrons gained in anion formation: a. one half c. one third b. equal d. greater 104. Which is the most toxic? a. O2 b. N2 c. CO2 d. CO 105. A 2-liter sample of argon gas at STP is expanded into a 5-liter flask, with the temperature held constant. What will be the new pressure of the gas? a. 0.4 atm c. 1.0 atm b. 2.4 atm d. 0.2 atm 106. Nitrogen oxides from automobiles are chiefly associated with a pollution problem called _____________: a. acid rain c. smog b. green house effect d. annoying 107. Why is water a liquid, even though it has a low molecular weight? a. it is a hydride b. due to dipole forces c. oxygen is a group of elements d. due to hydrogen bonding 108. Which of the following would you expect to have a highest melting point? a. mercury c. potassium b. sodium chloride d. toe 109. An increase in vapor pressure is accompanied by a decrease in _________: a. volatility c. temperature b. boiling point d. partial pressure 110. Neoprene belongs to which class? a. plastic b. elastic c. elastic-plastic d. rubber-like plastic 111. What is the number of semi-conductors in periodic table? a. 3 c. 5 b. 7 d. 13 112. The process of zinc coating used extensively for protecting steel from atmospheric deterioration is called: a. anodizoing c. galvanizing b. parkerising d. colourizing 113. The properties or effects produced, not essentially in the same order are: a. grain refinement c. temper brittleness b. hardenablity d. rust resistance When the following pairs correctly represents the alloying elements and properties or effect produced by it? a. a – (ii) c. c – (iii) b. b– (iv) d. c– (iv) 114. Which of the following material has density closer to that of gold? a. lead c. chromium b. tungsten d. nichrome 115. Thermosetting polymers are generally: a. injection molded c. cast molded b. extruded d. none of the above 116. Which of the ff. method can NOT be used for thermoplastic materials? a. extrusion c. injection molding b. blow molding d. all of the above 117. Ligancy is: a. the number of atoms (or ions) surrounding and touching a central atom b. a covalent bond between two atoms c. the angle between the two closest directional bonds of an atom d. none of the above 118. The melting point of carbon is about: a. 800 oC c. 2150 oC b. 3500 oC d. 6600 oC 119. Gel is: a. b. c. d. a polymer having side groups distributed randomly along s vinyl polymer chain a polymer having secondary chains branching from the molecular chains particles linked together and containing a fluid is its interstices a solid framework of colloidal a polymer in which the repeating unit of each molecule has vinyl group 120. What is the formula of the compound Carbon Diselinide consisting of Carbon (C) and Selenium (Se)? a. CSe2 c. (CSe)2 b. CSe d. C2Se 121. In preparing a metallographic iron specimen the grain boundaries are made most visible by which of the following steps? a. grinding the sample with silicon carbide abrasive b. polishing the sample with powdered diamond dust in oil c. etching the sample in 2% solution of nitric acid in alcohol d. mounting the sample in an epoxy mold 122. The ratio of oxygen available to the oxygen required for stabilization of sewerage is called: a. relative stability b. oxygen-ion concentration c. concentration factor d. biochemical oxygen 123. The crystalline structure of metals can be modified by several processes. Plastic deformation of the crystalline structure resulting in a misalignment of atoms, dislocations and large stresses, and strains in small regions are characteristics of which process? a. cold forming c. tempering b. twinning d. isostatic pressing 124. It has the highest melting point of all metals a. tungsten c. silver b. copper d. aluminum 125. The formula for Dinitrogen Pentoxide is a. N2O5 b. (NO)5 c. NO5 d. none of these 126. Polymers that favor crystallization are least likely to have which of the ff? a. an atactic configuration b. small sides group c. only in repeating unit d. small chains lengths 127. Coke may be prepared commercially by the destructive distillation of: a. anthracite coal c. peat b. bituminous d. lignite 128. Reactions generally proceed faster at high temperatures because of which of the ff: a. the molecules are less energetic b. the molecules collide more frequently c. the activation energy is less d. the molecules collide more frequently and the activation energy is less 129. Which of the following statements regarding organic substances is false? a. organic substances generally dissolve in high concentration acids b. all organic matter contain carbon c. organic matter is generally stable at very high temperature d. organic matters generally do not dissolve in water 130. A deuteron is: a. a neutron plus two protons b. a nucleus containing a neutron and a proton c. an electron with positive charge d. a helium nucleus 131. Determine the molecular weight of the potassium hexachloroiridate (lV) K2 lrCl6 atomic mass: K = 39.1, lr = 192.22, Cl = 35.453 a. 500 g/mole c. 458.21 g/mole b. 483.12 g/mole d. 485.32 g/mole 132. How much 58.0 % sulfuric acid solution is needed to provide 150 g H2SO4? a. 295 g c. 250 g b. 259 g d. 249 g 133. How many kg of Ca3(PO4) must be treated with carbon and sand in an electric furnace to make kg of phosphorous? a. 4.95 kg c. 5.49 kg b. 5.01 kg d. 4.5 kg 134. How many grams of 5% NaCl solution by weight are necessary to yield 3.2 g NaCl? a. 46 kg c. 45 kg b. 64 kg d. 50 kg 135. How many grams solute are required to prepare 1 liter of 1 MPb(NO 3)2? Molecular weight of Pb(NO3)2 = 331.2: a. 330 g c. 332.1 g b. 331.2 g d. 345 g 136. The density of 2.03 M solution acetic acid in water is 1.017 g/ml. Calculate the molality of the solution: a. 22.7 m c. 0.27 m b. 2.27 m d. 0.0227 m 137. An aqueous solution boils at 100.5 °C. What is the freezing point of the solution? a. –0.182 °C c. 1.82 °C b. –1.82 °C d. 0.018 °C 138. A sample gas occupies 2 liters at 760 mmHg. What is its volume at 1.25 atm at the same temperature? a. 1.06 liters c. 0.160 liter b. 1.60 liters d. 10.6 liters 139. The most satisfactory way to separate and identify sugars is to use: a. Buret reagent c. Fractional crystallization b. Chromatography d. Benedict’s solution 140. In a crystal structure, what is an interstitial atom? a. a different element at a lattice point b. an extra atom setting at a non-lattice point c. an atom is missing at a lattice point d. a line defect 141. Which one of the following is most likely to prove that a substance is inorganic? a. the substance is heated together with copper oxide and the resulting gases are found to have no effect on limestone b. the substance evaporates in room temperature and pressure c. analysis shows that the substance contains hydrogen d. the substance floats in water 142. By weight, atmospheric pressure is approximately 23.15% oxygen and 76.85% nitrogen. What is the partial pressure of oxygen in the air at standard temperature and pressure? a. 3.8 psia c. 3.4 psia b. 4.4 psia d. 3.1 psia 143. Twenty grams of oxygen gas (02) are compressed at a constant temperature of 30 degree C to 5% of their original volume. Find the work done on the system. a. 944 cal c. 924 cal b. 1124 cal d. 1114 cal 144. Water boils when a. its saturated vapor pressure equals the atmospheric pressure b. its vapor pressure equals 76 cm of mercury c. d. its temperature reaches 212 centigrade its vapor pressure is 1 gram per sq. cm. 145. Which of the following statements is FALSE? a. Both lead and cadmium have a hexagonal close-packed crystal structure. b. Both magnesium and zinc have hexagonal close-packed crystal structure. c. Both copper and aluminum have face-centered cubic crystal structure d. All of the alkali metals have a body-centered cubic crystal structure. 146. How many dependents properties are required to completely fix the equilibrium state of a pure gaseous compound? a. 4 c. 2 b. 3 d. 1 147. 100 grams of water are mixed with 150 g alcohol (ρ = 790 kg/m3). What is the specific volume of the resulting mixture, assuming that the two fluids mix completely? a. 0.63 cm3/g c. 0.82cm3/g b. 1.20 cm3/g d. 0.88 cm3/g 148. In an ideal gas mixture of constituents i and j, what is the mole fraction x1, equal to? a. b. P i P P i j PV i i RT c. T i T T i j d. Z i Z Z i j 149. Which of the following statements is false? a. Ceramics are inorganic, non-metallic solids that are processed or used at high temperatures b. Most metals are strong, ductile and malleable. |In general, they are heavier than most other substances. c. Oxides. Carbides and nitrides are considered to be with in the class of materials known as glasses. d. Metals are chemical elements that from substances that are opaque, lustrous and good conductors of heat and the electricity. 150. Whish are the oxidizing and reducing agent in the following reaction? 2CCl4 + K2CrO4 + 2KCl a. Oxidizing agent: oxygen; reducing agent: chloride b. Oxidizing agent: chromium; reducing agent: chloride c. Oxidizing agent: oxygen; reducing agent: chloride d. There are no oxidizing or reducing agents in the reaction 2Cl2CO + CrO2Cl2 151. When 0.5 g of a liquid is completely evaporated and collected in a 1 liter manometer, the pressure is 0.25 atm and the temperature is 27 deg C. Assume ideal gas behavior, find the molecular weight, the gas constant is R = 0.0821 l-atm/mole K a. 49.2 g/mole c. 2.2 g/mole b. 12.3 g/mole d. 64.0 g/mole 152. Which of the following reactions relate to the softening procedure in water purification? a. 2H2O + O2 2H2O2 b. Ca(HCO3)2 + Ca(OH)2 2CaCO3 + H2O c. d. 528. CO2 + Ca (OH)2 CaCO3 + H2O NaOH + HCl NaCl + H2O 153. One method of removing moisture from air is to cool the air so that the moisture condenses or freeze out. To what temperature must air at 100 atm be cooled at constant pressure in order to obtain in a humidity ratio of 0.0001? a. 58 degree F c. 35 degree F b. 47 degree F d. 22 degree F 154. A blue color obtained as a result of the borax bead test indicates the presence of: a. cobalt c. aluminum b. magnesium d. nickel 155. In a crystal structure, what is an interstitial atom? a. A different element at a lattice joint b. An extra atom setting at a non-lattice joint c. An atom missing at a lattice joint d. A line defect 156. The most satisfactory way to separate and identify sugar is to use a. Biuret reagent c. Chromatography b. Frantional crystallization d. Benedict’s solution 157. Which one of the following is most likely to prove that a substance is inorganic? a. The substance evaporates in room temperature and pressure b. The substance is heated together with copper oxide and the resulting gases are found to have no effect on limestone c. Analysis shows that the substance contains hydrogen d. The substance floats in water 158. Which of the following statements is TRUE for an ideal gas, but not for a real gas? a. PV = nRT b. An increase in temperature causes increases in the kinetic energy of the gas c. The total volume of molecules in a gas is nearly the same as the volume of the gas as a whole d. No attractive forces exist between the molecules of a gas 159. Which of the following statements is true for real gas, but not for an ideal gas? a. pV – nRT b. an increase in temperature causes an increase in the kinetic energy of the gas c. the total volume of molecules in a gas is nearly the same as the volume of the gas as a whole d. no attractive forces exist between the molecules of a gas 160. Which of the following statements is FALSE? a. In general, as reaction products are formed, they react with each other and reform reactants. b. At equilibrium, the net reaction rate is zero c. The differential rate low is the mathematical expression that shows how the rate of a reaction depends on volume d. The net at which a reaction proceeds from the left to right is equal to the forward rate minus the reverse rate 161. What is the first coordination number of BODY-CENTERED cubic structure? a. 10 c. 6 b. 4 d. 8 162. For an ideal gas, what is the specific molar entropy change during an isothermal process in which the pressure change from 200 kPa to 150 kPa called? a. b. 2.39 J/mole-K 2.78 J/mole-K c. 2.00 J/mole-K d. 3.12 J/mole-K 163. The ores from which the zinc is obtained is: a. Sphalerite c. Pyrite b. Magnetite d. Dolomite 164. Tin is produced from a. Cassiterite b. Bauxite c. Sphalerite d. Magnetite 165. Determine the volume occupied by 4 grams of oxygen at STP. Molecular weight of oxygen is 32. Standard molar volume of any gas 22.4 liters/mol. a. 4.8 liters c. 2.8 liters b. 3.6 liters d. 1.4 liters 166. Determine the formula weight of potassium hexachloroiridate (IV), K2IrCl6. Atomic weights: K = 39.098; Ir = 1922.22; Cl = 35.453 a. 86.089 c. 387.344 b. 285.799 d. 483.14 167. A seated tank contains oxygen at 27 deg C at a pressure of 2 atm. If the temperature increases to 100 deg C. What will be the pressure inside the tank? a. 4.92 atm c. 2.49 atm b. 4.29 atm d. 9.24 atm 168. An ideal gas at 0.60 atmosphere and at 87 deg C occupies 0.450 liter. How many moles are in the sample? (R = 0.0821 1-atm/mole-K) a. 0.0198 mole c. 0.0091 mole b. 0.0002 mole d. 0.0378 mole 169. When 50 L of air at STP is isothermally compressed to 10 L, how much heat must flow from the gas? (Patm = 100 lPa). a. 8.35 kJ c. 8.05 kJ b. 8.23 kJ d. 8.48 kJ 170. How much 58% sulfuric acid solution is needed to provide 150 gram of H2SO4? a. 240 grams c. 180 grams b. 215 grams d. 259 grams 171. At STP a gas occupies 0.213 liters. How many moles are there in this sample of gas? a. 0.9050 mole c. 0.0890 mole b. 0.0089 mole d. 0.0095 mole 172. A liter of sample of air at 1 atm. Pressure is allowed to expand isothermally into a 20 liters vessel. What will its new pressure be? a. 0.25 atm. c. 2.0 atm. b. 1.5 atm. d. 0.5 atm. 173. In the periodic table of elements, which of the following is NOT a transition metals? a. copper c. silver b. sodium d. nickel 174. In the periodic table of elements, which one of the following elements DOES NOT belong to group IIA? a. calcium c. radium b. sodium d. magnesium 175. A cylinder contains oxygen (O2) at a pressure of 10 atm and a temperature of 300°K. The volume of the cylinder is 10 liters. What is the mass of oxygen? MW of O° is 32 g/mole. a. 120.08 g c. 130.08 g b. 125.08 g d. 135.08 g 176. When 10.0 g of silicon dust, Si, is exploded with 100.0 g of oxygen, O 2 , forming silicon dioxide, SiO2, how many grams of O2 remain uncombined? The reaction of the equation is: Si + 02 SiO2. The MW of Si = 28, MW of O2 = 32 a. 85.8 g c. 87.8 g b. 86.5 g d. 88.5 g 177. Which of the following is NOT related to crystallization? a. hot working c. elastic modulus b. cold working d. melting temperature 178. What is the molarity of a solution of 600 g of H2SO4 (which has a specific gravity of 1.83) dissolved in 3 l of water? a. 1.84 M c. 3.09 M b. 2.04 M d. 4.00 M 179. 0.064 kg of octane vapor (MW = 114) is mixed with 0.91 kg of air (MW = 29.0) in the manifold of an engine. The total pressure in the manifold is 86.1 kPa, and the temperature is 290°K. Assume octane behaves ideally. What is the total volume of this mixture? a. 0.652 m3 c. 0.895 m3 b. 0.722 m3 d. 0.563 m3 180. 0.064 kg of octane vapor (MW = 114) is mixed with 0.19 kg of air (MW = 29.0) in the manifold of an engine. The local pressure in the manifold is 86.1 kPa, and the temperature is 290°K. Assume octane behaves ideally. What is the partial pressure of the air in the mixture? a. 64.8 kPa c. 48.6 kPa b. 84.6 kPa d. 46.8 kPa 181. The RMS velocity of hydrogen gas at N.T.P. is approximately a. 3838 m/s c. 4839 m/s b. 1839 m/s d. 839 m/s 182. What is the RMS velocity of 275°K argon (MW = 39.9) molecules? a. 313.7 m/sec c. 616.7 m/sec b. 515.7 m/sec d. 414.7 m/sec 183. What is the RMS velocity of oxygen at 700F? a. 448 m/sec c. 479 m/sec b. 568 m/sec d. 864 m/sec 184. What is the molarity of ethanol in 90% proof whisky? Density of alcohol = 98g/ml. a. 8.73 M c. 8.37 M b. 3.78 M d. 7.83 M 185. Two liquids mixed together with densities of 500 kg/m 3 and 1500 kg/m3 until the 100liter container was full and their joint density becomes 500 kg/m 3. What are the masses of two liquids? a. 49 kg, 50 kg c. 32 kg, 46kg b. 35 kg, 45 kg d. 30kg, 50 kg 186. Acid turns litmus paper into ________. a. red c. blue b. yellow d. green 187. A mixture of 35% ethyl alcohol, 15% sulfuric acid, and 50% water, the molecular weight of the ethyl alcohol is 46. What is the MOL concentration of ethyl alcohol if the total mixture concentration is 3.724? a. 0.314 c. 0.625 b. 0.288 d. 0.204 188. The molecular diameter of CO is 3.19 x 10–8 mm at 300 K and the given pressure of the 100 mm Hg. What is the mean free path of the gas in the cm? a. 2.86 x 10-3 c. 6.86 x 10-6 -3 b. 6.86 x 10 d. 6.86 x 10-9 189. The molecular diameter of CO is 3.19 x 10-8 at 300 K and pressure of 100 mmHg. What is the number of biomolecular collisions? a. 1.02x1024 c. 2.12x1020 26 b. 2.12x10 d. 1.12x1027 190. At STP, the density of chlorine is 3.22 kg/m3. What weight of gas is contained in a flask of 100 cm3 at 24°C and 100 kPa? a. 0.321 gram c. 0.563 gram b. 0.420 gram d. 0.292 gram 191. Hydrogen peroxide solution for hair bleaching is usually prepared by mixing 5.0 g of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) molecular weight = 43 g/mole) per 100 ml of solution. What is the molarity of this solution? a. 1.0 M c. 2.0 M b. 1.5 M d. 2.5 M 192. The miller indices of a crystal is (2,1,0) what does (2,1,0) mean? a. (2,1,0) 1/5 : 1/7 : 1/40 b. (2,1,0) 1 ½ : 1/1 : 1/ c. (2,1,0) 1/9 : 1/6 : 1/10 d. (2,1,0) 1/2 : 1/6 : 1/ 193. What radioactive delay is described by the capture of electron from the inner shells? a. Beta decay c. electron capture b. Gamma decay d. electromagnetic radiation 194. One-half of a molecular weight of a perfect gas exists at a pressure of 100 psia. A heat transfer of 200 BTU at constant volume causes the temperature to change by 100°F. Find the specific heat for constant pressure processes on a molar basis. a. 8 BTU/pmole-°R c. 4 BTU/p/mole-°R b. 6 BTU/pmole-°R d. 12 BTU/pmole-°R 195. Are hydrocarbons containing one or more carbon – carbon triple bonds? a. acid c. alkenes b. alkali d. alkynes 196. Determine the specific gravity of carbon dioxide (150°F, 20 psi) using STP air as a reference: a. 1.7 c. 1.85 b. 1.8 d. 1.87 197. What is the subject which covers the retirement of pure metals from their ores? a. Oreic Metallurgy b. Refinement Metallurgy c. d. Extractive Metallurgy Pure Metallurgy 198. The energy change that a occurs when electron is added to gaseous atom or ion is called… a. Electromotive force c. Electron density b. Electron capture d. Electron affinity 199. A large Molecule with two alternating Mers is know as… a. Monomers b. Elastomer c. Mers d. Copolymer or interpolymer 200. The ore from which aluminum is obtained is a. Bauxite c. Galena b. Cassiterite d. Sphalerite 201. Two thirds of the atom in molecule of water (H2O) are hydrogen. What percentage of the weight of water molecule is the weight of the two hydrogen atoms? The atomic weight of hydrogen is 1.008g/mole and of oxygen is 16.00 g/mole. a. 12.19% c. 19.00% b. 11.19% d. 19.12% 202. The atomic weight of iron is 55,847 amu. If one has 6.02 g of iron. How many atoms are present? a. 6.49 x 1022 c. 6.49 x 1024 b. 6.49 x 1023 d. 6.49 x 1025 203. Is accomplished by heating raw rubber with small amounts of sulfur? a. Polymerization c. Sulfurization b. Vulcanization d. Monomerization 204. If 20 ml of 0.5N salt solution is diluted to 1 liter, what is the new concentration? a. 0.02 N c. 0.03 N b. 0.04 N d. 0.01 N 205. Which one of the following elements is NOT radioactive? a. Californium c. Plutonium b. Cobalt d. Uranium 206. The number of bonds in the mer that can be broken open for attachment to the other mer is known as the: a. property of the mer b. proportionality of the mer c. functionality of the mer d. crystallinity of the mer THERMODYNAMICS 207. When the expansion or compression of gas takes place without transfer of heat to or from the gas, the process is called a. isothermal c. isentropic b. adiabatic d. reversible 208. The chief differences between liquids and gases are: The chief differences between liquids and gases are: A. Liquids are practically incompressible whereas gases are compressible B. Liquids occupy definite volumes and have free surfaces, whereas a given C. Mass of gas expands until it occupies of any containing vessel D. Liquids obey the principle of fluid mechanics; gases do not a. all three, A, B, and C b. B and C c. the first two, A and B d. none of these 209. The ratio of the density of a substance to that density of some standard substance is called a. relative density c. specific gravity b. specific density d. relative gravity 210. The total energy in a compressible or incompressible fluid flowing across any section of a pipeline is a function of: a. pressure and velocity b. pressure, density and velocity c. [ressure, velocity, density and viscosity d. flow energy, kinetic energy, height above datum and internal energy 211. The fundamental reference dimension are mass, length and time. The fundamental SI units for them are kilograms (kg), meter (m) and seconds (s). The unit of force derived from these units is Newton (N). Consequently, the unit of pressure in N/m is called a. Pascal c. Mega Pascal b. Gage d. stress 212. This law states that pressure applied at a point in a confined liquid is transmitted equally to all other points. a. Boyle’s law c. Charles’ law b. Lenz’ law d. Pascal’s law 213. If the strain rate of the fluid is linearly proportional to the applied shear stress and is zero when the later is zero, the fluid is: a. Brownian c. Archimedean b. Newtonian d. Bernoullian 214. A fluid for which the constant proportionality (the viscosity) does not change with rate of deformation is said to be: a. Newtonian fluid c. compressible fluid b. incompressible fluid d. ideal fluid 215. If the shear stress in a fluid varies linearly with the velocity gradient, which of the following describes the fluid? a. it has a constant viscosity b. it is a Newtonian gas c. it is a perfect gas d. it is at constant temperature 216. The ratio of the change in pressure to the relative change in density, and measures the compressibility of a material is known in fluid mechanics as: a. bulk modulus of elasticity b. compression index c. compression ratio d. modulus of volume 217. Refers to the formula giving the terminal velocity of spherical articles in liquid. a. Buckingham-Pi c. Newton’s law b. Archimedes’ law d. Stroke’s law 218. This is the mechanical energy balance based on the first law of thermodynamics. It includes potential energy (PE), kinetic energy (KE), flow energy, losses and shaft work inputs, but omits thermal energy. Similar to the Euler equation, though written in differential form. a. Manning equation c. Bernoulli’s equation b. Kutter equation d. Hazen-Williams equation 219. This formula relates the head loss with friction factor (f), the length to diameter ratio (L/D), and the kinetic energy v²/2g. a. Chezy c. Manning b. Kutter d. Dracy-Weisback 220. This law is used for diffusional flow, and closely parallels conductive heat transfer. The form of the formula is Q = kIA where Q is the volume flow rate, k is the coefficient of permeability, I is the gradient, and A is the cross-sectional area of the flow. a. Darcy’s law c. Newton’s law b. Chezy’s law d. Bernoulli’s law 221. Refers to the gradient at which flow in a pipe of a particular diameter will carry away any solids in it. a. critical c. sub-critical b. self-cleansing d. super critical 222. A law that states that in a perfect fluid, the pressure exerted on it anywhere gets transmitted in all directions. a. Archimedes’ law c. Stoke’s b. Darcy’s d. Pascal’s law 223. If the relative density of oil is 0.75, its density is a. 750 MPa c. 750 N/m² b. 750 Pa d. 750 kg/m³ 224. The first law of thermodynamics is based in which of the following principles? a. conservation of mass b. action-reaction c. the enthalpy-entropy relationship d. conservation of energy 225. At constant pressure, it is the increase in enthalpy per unit of mass when the temperature is increased one degree with its volume held constant is called: a. specific weight c. isotropic process b. adiabatic process d. isentropic process 226. The equation of state of the gas for isothermal conditions: a. PV = constant c. PVK = constant n b. PV = constant d. none of these 227. The equation of state of the gas for isentropic conditions: a. PV = constant c. PVK = constant b. PVn = constant d. none of these 228. The equation of state of the gas for adiabatic conditions: a. PV = constant c. PVK = constant b. PVn = constant d. none of these 229. In analyzing the steady flow of compressible fluids, the process involved which there is no change in temperature is involved is called: a. isothermal process c. adiabatic process b. isentropic process d. stagnation process 230. The process involved in the analysis heat is added or taken away from the a. isothermal process c. b. isentropic process d. 231. The process involved in the analysis of a steady flow of compressible fluids is also a frictionless adiabatic process is called: a. isothermal process c. adiabatic process b. isentropic process d. stagnation process 232. During an adiabatic, internally reversible process, which is true about the change in entropy? a. it is always zero b. it is always greater than zero c. it is always less than zero d. it is temperature dependent 233. The compressibility (change in volume due to change in pressure) of a liquid is inversely proportional to its volume of elasticity is known as: a. bulk modulus c. modulus of elasticity b. shear modulus d. strain modulus 234. Cavitation occurs when the pressure in the liquid falls below the _________ of that liquid. a. vapor pressure c. atmospheric pressure b. turbine speed d. peripheral speed 235. Which statement is true for a fluid? a. it cannot sustain a shear force b. it cannot sustain a shear force at rest c. it is a liquid only d. it has a very regular molecular structure 236. A fluid either liquid or gas, tangential or shearing force always come into being whenever motion takes place, thus giving rise to fluid friction because these forces oppose to movement of one particle past another. a. real fluid c. ideal fluid b. compressible fluid d. incompressible fluid 237. One atmospheric pressure is equal to: a. 1013 mbars b. 10.3 m of H2O 238. of a steady flow of compressible fluids in which no flow system is called: adiabatic process stagnation process c. 760 mm of Hg d. all of these The pressure exerted by the atmosphere in every surface with which it comes in contact is known as: a. atmospheric pressure c. absolute pressure b. vapor pressure d. gage pressure 239. Under normal condition at sea level, the atmospheric pressure is most nearly: a. 101.3 kPa c. 103.1 kPa b. 110.3 kPa d. 130.1 kPa 240. Which of the following is most accurate about a streamline? a. it is a path of fluid particle b. it is a line normal to the velocity vector everywhere c. it is fixed in space in steady flow d. it is defined for non-uniform flow only 241. Absolute pressure is computed by the equation: a. Pabs = Patm + Pgage c. Pabs = Pgage – Patm b. Pabs = Patm – Pgage d. none of these 242. All of the following is true about absolute pressure except: a. absolute pressure can be negative b. absolute pressure is the sum of atmospheric and gage pressure c. absolute pressure is measured above the absolute zero d. absolute pressure can never be negative 243. Under which conditions is mass conserved in fluid flow? a. the fluid is baratropic b. the flow is adiabatic c. the flow is isentropic d. it is always conserved 244. Under which of the following conditions is Bernoulli’s equation valid? a. all points evaluated must be on the same streamline b. the fluid must be incompressible c. the fluid must be inviscid d. all of the above 245. Select the correct statement: a. local atmospheric pressure depends upon the deviation of locality only b. local atmospheric pressure is always c. standard atmospheric pressure is the mean d. standard atmospheric pressure is 720 mm Hg abs 246. Which of the following is true for water at a reference temperature where enthalpy is zero? a. internal energy is negative b. entropy is non-zero c. specific volume is zero d. vapor pressure is zero 247. What is the value of the work done for a closed, reversible, isometric system? a. positive c. negative b. zero d. positive or negative 248. How does an adiabatic process compare to an isentropic process? a. adiabatic: heat transfer=0; isentropic: heat transfer ≠ 0 b. adiabatic: heat transfer≠0; isentropic: heat transfer = 0 c. adiabatic: reversible; isentropic: not reversible d. both heat transfer = 0; isentropic: reversible 249. Which of the following thermodynamic cycles is the most efficient? a. Brayton c. Rankine b. Carnot d. Rankine with reheat 250. The ideal, reversible Carnot cycle involves four basic processes. What type of processes are they? a. two isothermal and two isentropic b. all isothermal c. two adiabatic and two isentropic d. all adiabatic 251. Which of the following is not an advantage of a superheated, closed Rankine cycle over an open Rankine cycle? a. lower equipment cost c. increased boiler life b. increased turbine life d. increased efficiency 252. The bulk modulus of elasticity, K, for a gas constant temperature T is given by: a. P (p) c. R (T) b. P/p d. none of these 253. The continuity equation: a. relates mass rate flow along a stream b. relates the relationship between work and energy c. requires that the flow must be laminar d. relates the momentum concept 254. What is the Arrhenius equation for the rate of a thermally activated process? (A = reaction constant; T = absolute temperature; R = gas constant; Q = activation energy) a. rate = A℮-Q/RT c. rate = A℮Q/RT b. rate = A℮-QRT d. rate = A℮QRT 255. An adiabatic process in a system is one in which: a. no heat enters or leaves the system b. the system does not work nor is work done on it c. the temperature of the system remains constant d. the pressure of the system remains constant 256. A Carnot engine that operates between the absolute temperature T1 and T2: a. is 100% efficient b. has the maximum efficiency possible under these circumstances c. has an efficiency of T1/T2 d. has an efficiency equal to the actual engine that operates between T1 and T2 257. Which of the following engines is normally the least efficient? a. gasoline engine c. diesel engine b. gas turbine d. Carnot engine 258. A refrigerator a. produces coldness b. causes heat to vanish c. removes heat from a region and transport it elsewhere d. changes heat to coldness 259. Heat is absorbed by the refrigerant in a refrigerator when it: a. melts c. vaporizes b. condenses d. is compressed 260. How much heat is required to change 100 lbs of ice at 10°F to steam at 212°F? Assume the following: specific heat of ice = 0.5 BTU/lb∙°F heat of fusion of ice = 144 BTU/lb specific heat of water = 1 BTU/lb∙°F heat of vaporization of water = 970 BTU/lb a. 125,000 BTU c. 130,500 BTU b. 150,000 BTU d. 110,500 BTU 261. What will be the pressure in KPa, at height of 2000 m in an isothermal atmosphere? Assuming T=20°C and Patm = 100 KPa a. 87 c. 79 b. 82 d. 71 262. What pressure differential, in Pascals, exists at the bottom of a 3 m vertical wall when the temperature inside is 20°C and outside is 20°C. Assume equal pressure at the top. a. 15 c. 9 b. 12 d. 6 263. The mass of water vapor per unit volume of air. a. absolute humidity c. relative humidity b. specific humidity d. critical humidity 264. When gas is heated at constant pressure, the process called a. Isometric c. polytropic b. Isobaric d. isothermal 265. When gas is heated at constant volume, the process is called a. isotropic c. isometric b. isobaric d. adiabatic 266. An engine cycle containing two adiabatic and two isothermal processes. a. Carnot cycle c. Diesel cycle b. Rankine cycle d. Otto cycle 267. It is the condition, pressure and temperature at which a liquid and its vapor are indistinguishable. a. dew point c. relative humidity b. absolute humidity d. critical point 268. States that a heat engine cannot transfer heat from a body to another at higher temperature unless external energy is supplied to the engine. a. first law of thermodynamics b. Planck’s law c. second law of thermodynamics d. third law of thermodynamics 269. Entropy is the measure of a. the change in enthalpy of a system b. randomless or disorder c. the internal energy of a gas d. the heat capacity of a substance 270. The amount of heat passing through a body of 1m² cross-section and 1m thick in 1 hour at a temperature difference of 1°C. a. quantity of heat c. latent heat of solid b. specific heat d. thermal conductivity 271. This heated air, being lighter, rises and circulates through the house or is forced through by a fan called a. vacuum c. steam b. vapor d. forced convection 272. Is one whose pressure is higher that the saturation pressure corresponding to its temperature. a. compressed gas c. combustion b. compressed liquid d. expansion ratio 273. Is one whose temperature is below the saturation temperature corresponding to its pressure. a. sub-cooled liquid c. compression b. condensation d. constant volume process 274. It is a chart on which enthalpy is the ordinate and entropy is the abscissa. a. Ericson cycle c. Charles’ law b. Mollier chart d. Bernoulli’s chart 275. Is one with rigid boundaries exchanging neither energy nor mass with its surroundings. a. entropy c. isolated system b. ideal gas d. heat 276. Which of the following give the optimum intermediate pressure in case of two stage compression? a. p4 = (p1 +p2)/2 c. p2 = √p1p2 b. p3 = p1 +(p1+p2)/2 d. p = p1 + √(p1² +p3²) 277. In the polytropic process we have the PVⁿ= constant, if the value of n is infinitely large, the process is called? a. constant pressure process b. constant temperature process c. adiabatic process d. constant volume process 278. The thermodynamic cycle used in a thermal power plant is a. Ericsson c. Carnot b. Brayton d. Rankine 279. For the same heat input and the same compression ratio a. b. c. d. 280. none of the above ΔH = CU ΔT c. ΔH = (C/CV) ΔT ΔH = CP ΔT d. ΔH = CP ΔT dS = du + pd (1/p) c. S = u +pVs dS = TdqH d. dS = dqH/t In a polytropic process, if the work done in heat unit is w, then the amount of heat transferred is given by a. b. 283. efficiency depends mainly on working substance Entropy, for reversible flow, is given by the relation a. b. 282. Otto cycle is less efficient compared to Diesel cycle The change in enthalpy for small temperature change, ΔT, for an ideal gas is given by the relation a. b. 281. both Otto cycle and Diesel cycle are equally efficient W ΤW c. (τ - 1)W/(n – τ) d. (τ –n)W/(τ –1) A heat exchange process wherein the product of pressure and volume remains constant is called a. heat exchange process c. throttling process b. 284. isentropic process The S.I. unit for pressure is a. mm of water column b. Pascal d. hyperbolic process c. dynes/cm² d. all of the above 285. Sterling cycle has a. two isothermal and two adiabatic process b. two adiabatic and two isentropic process c. two adiabatic and two constant pressure processes d. two isothermal and two constant volume processes 286. Brayton cycle has a. two isentropic and two constant volume processes b. two isentropic and two constant pressure processes c. one constant pressure, one constant volume, two adiabatic processes d. two isothermal, a constant volume and a constant pressure processes 287. Diesel cycle consists of a. isentropic, isothermal, constant volume, constant pressure processes b. two constant volume, one constant pressure, one isothermal process c. two isotropic, one constant volume, one constant pressure process d. two constant pressure, one constant volume, one isentropic process 288. Ericsson cycle has a. two isothermal and two constant volume processes b. two isothermal and two isentropic process c. two adiabatic, constant volume and constant pressure process d. two isothermal and two constant pressure processes 289. Brayton cycle cannot be used in reciprocating engines even for same adiabatic compression ratio and work output because a. Otto cycle is highly efficient b. Brayton cycle is less efficient c. Brayton cycle is for slow speed engines only d. large volume of low pressure air cannot be efficiently handled in reciprocating engines 290. Which cycle is generally used for gas turbines? a. Otto cycle c. Dual cycle b. Rankine cycle d. Brayton cycle 291. The constant pressure gas turbine works on the principle of a. Carnot cycle c. Rankine cycle b. Bell – Coleman cycle d. Brayton cycle 292. Which of the following provides the basis for measuring thermodynamic property of temperature? a. first law of thermodynamics b. second law of thermodynamics c. third law of thermodynamics d. zeroth law of thermodynamics 293. Under ideal conditions, isothermal, isobaric, isochoric and adiabatic processes are a. dynamic process c. quasi-static process b. stable process d. static process 294. Isentropic flow is a. b. c. d. perfect gas flow irreversible adiabatic flow ideal fluid flow reversible adiabatic flow 295. Exhaust gases from an engine possess a. solar energy c. chemical energy b. kinetic energy d. stored energy 296. The extension and compression of helical spring is an example of a. isothermal cycle c. irreversible process b. adiabatic process d. reversible process 297. Which of the following relations is not applicable in a free expansion process? a. heat supplied = zero b. heat rejected = zero c. work done = zero d. change in temperature = zero 298. An ideal engine absorbs heat a temperature of 127 °C and exhaust heat at a temperature of 77 °C. Its efficiency will be a. 50% c. (127-77)/127 % b. 33% d. 13% 299. The triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which a. the solid and liquid phases are in equilibrium b. the liquid and gaseous phases are in equilibrium c. the solid, liquid and the gaseous phases are in equilibrium d. the solid does not melt, liquid does not boil and the gas does not condensate 300. According to Clausius Inequality statement for any cycle of process, reversible or irreversible a. cyclic δQ/T > 0 c. cyclic δQ/T = 0 b. cyclic δQ/T < 0 d. cyclic δQ/T ≤ 0 301. A heat engine has the following specifications: Power developed = 50 kW, Fuel burned per hour = 3 kg, Heating value of fuel = 75,000 kJ per kg, Temperature limits = 627°C and 27°C This engine is a. real c. costly b. impossible d. cheaper 302. A heat engine is supplying heat at the rate of 30,000 J/s and gives an output of 9 kW. The thermal efficiency of the engine is a. 43% c. 55% b. 50% d. 30% 303. According to Clausius statement, a. heat flows from hot substance to cold substance b. heat flows from hot substance to cold substance, unaided c. heat can flow from cold substance to hot substance with the aid of external work d. both (b) and (c) 304. Select the cycle that consists of two isothermal and constant volume process. a. Joule cycle c. Otto cycle b. Diesel cycle d. Ericsson cycle 305. “It is impossible to construct a heat engine that operates in a cycle and receives a given quantity of heat from a high temperature body and equal amount of work” The above statement is known as a. Gay Lussac law c. Kelvin – Planck law b. Kinetic theory d. Joule – Thomson law 306. Which of the engine is used for fighter bombers? a. turbo prop c. ramjet b. turbojet d. pulsejet 307. In a diesel engine, fuel is injected a. at the beginning of compression stroke b. before the end of compression stroke c. at the end of compression stroke d. after the end of compression stroke 308. Which is not correct for calculating air standard efficiency? a. all processes are reversible b. specific heat remains unchanged at all temperature c. no account of the mechanism of heat transfer is considered d. gases dissociate at higher temperature 309. A Bell – Coleman cycle is a reversed a. Stirling cycle b. Brayton cycle c. Joule cycle d. Carnot cycle 310. According to Prettlier Thomson effect a. it is possible to construct a heat engine that operates in a cycle and receives a given quantity of heat from a high temperature body and does equal amount of work b. it is possible to construct a device that operates in a cycle and produces no effect other than the transfer of heat from a cooler body to hotter body c. heat can be converted into work d. work can’t be converted into heat 311. A control volume refers to a. a specified mass b. a reversible process c. an isolated system d. a fixed region in space 312. The Beattie – Bridgeman equation of state is quite accurate in cases of a. all pressures above atmospheric pressures b. densities less than about 0.8 times the critical density c. near critical temperature d. near critical pressure 313. Which of the following statement about Van der Waal’s equation is correct? a. it is valid for all pressure and temperature b. it represents a straight line on pv versus v plot c. it has three roots of identical value at the critical point d. the equation is valid for diatomic gases only 314. A hydrometer scale for measuring the relative density (specific gravity) of liquids: a. Beckman scale c. Baume scale b. Beaufort scale d. Buckley scale 315. Energy can neither be destroyed nor created, law of: a. none of these b. conservation of energy c. conservation of momentum d. conservation of mass 316. A sealed tank contains 27oC at a pressure of 2 atm. If the temperature increases to 100 oC the pressure inside the tank will be: a. 4.15 atm. c. 1.60 atm. b. 0.54 atm. d. 2.49 atm. 317. The negative sign is for a gage reading called: a. transmission of pressure c. vapor pressure b. vacuum pressure d. pressure head 318. Total energy in a compressible or incompressible fluid flowing across any suction in a pipeline is a function of: a. pressure and velocity b. flow energy, kinetic energy, height above datum and internal energy c. pressure, density and velocity d. pressure, velocity and volume 319. Is one whose pressure is higher than the saturation pressure corresponding to the temperature: a. combustion c. expansion ratio b. compression liquid d. compressed gas 320. An instrument which is used to determine the specific gravity of a substance a. substance c. hydrometer b. throttling calorimeter d. odometer 321. Assuming that the barometer reads 760 mm Hg, what is the absolute pressure for 90 cm Hg gage? a. 74.213 kPa c. 221.24 kPa b. 48 kPa d. 358 kPa 322. During an adiabatic, internally reversible process, what is TRUE about the change in entropy? a. it is temperature dependent b. it is always less than zero c. it is always zero d. it is always greater than zero 323. An instrument which used to measure small pressure a. venture c. orifice b. aneroid d. manometer 324. The stress in a 90 cm. diameter pipe having a wall thickness of 9.5 cm. and a static head of 70 m of water is: a. 3.25 MPa c. 32.5 MPa b. 32.5 Kpa d. 325 Kpa 325. An open chamber rests on the ocean floor in 49 cm. of sea water (sp. gr. = 1.03) What air pressure in Kpa must be maintained inside to exclude water: a. 495.1 Kpa c. 500.5 KPa b. 490.5 Kpa d. 496.7 Kpa 326. For a heat engine operating between two temperatures (T2 > T1), what is the maximum efficiency attainable? a. 1 – T1 /T2 c. 1 – T2 / T1 b. T1 / T2 d. 1 – (T1)2 / T2 327. When property changes cease, the bodies are said to be in: a. change in volume c. slug b. triple point d. thermal equilibrium 328. A device produces 37.5 joules per cycle. There is one power stroke per cycle. Calculate the power output if the device is run at 45 rpm. a. 4.69 W c. 27.56W b. 28.125 W d. 14.063 W 329. What height of mercury column is equivalent to a pressure of 100 psig? Density of mercury is 848 lb/ft3. a. 14 ft c. 12 ft b. 17 ft d. 11 ft 330. A piston and cylinder arrangement contains saturated water vapor at 110 deg C. The vapor is compressed in a reversible, adiabatic process until the pressure is 1.6 MPa. What is the work done by the system per kilogram of water? a. –330 KJ/kg c. –509 KJ/kg b. –637 KJ/kg d. –432 KJ/kg 331. What is the efficiency of an Otto cycle with a compression ratio of 6:1? The gas used is air: a. 0.512 c. 0.800 b. 0.488 d. 0.167 332. During an adiabatic, internally reversible process, what is TRUE about the change in entropy: a. it is temperature dependent b. it is always less than zero c. it is always zero d. it is always greater than zero 333. One leg of mercury U-tube manometer is connected to a pipe containing water under a gage pressure of 14.2 lb/in2. The mercury in this leg stands 20 in. below the water. What is the height of mercury in the other leg which is open to the air? Specify gravity of mercury is 13.6? a. 3.6 ft c. 3.2 ft b. 1.5 ft d. 2.6 ft 334. Five moles of water vapor at 100 degree C and 1 atmosphere are compressed isobarically to from liquid at 100 degree C. The process is reversible and the ideal gas laws apply. Compute the work, in joules, done on the system. a. 10.5 MJ c. 6 MJ b. 15 MJ d. 6 kJ 335. Gas is enclosed in a cylinder with a weighted piston as the top boundary. The gas is heated and expands from s volume of 0.40 m3 at a constant pressure of 200 KPa. Find the work done on the system. a. 16 KJ c. 14 KJ b. 10 KJ d. 12 KJ 336. For a heat engine operating between two temperature (T2>T1), what is the maximum efficiency attainable? 529. a. T 1 1 T 2 c. T 1 2 T 1 b. T 1 T 2 d. 1 (T )² 1 T 2 337. A 20 liter sample of gas exerts a pressure of 1 atm. At 25 deg C. If its is expanded into a 40-liter vessel that is held at 100 deg C, what will be its final pressure? a. 0.50 atm. c. 0.315 atm. b. 1.0 atm. d. 0.63 atm. 338. A 36 inch petcock is anchored by a thrust block at a point where the flow makes a 20 degree change in direction. The water flow rate is 185 ft/sec. The water pressure is 2,880 lb/ft2 everywhere in the penstock. What is the resultant force on the thrust block? a. 8,900 lb c. 2,800 lb b. 29,800 lb d. 120,300 lb 339. As cylinder and piston arrangement contains saturated water vapor at 110 degree C. The vapor is compresses in a reversible adiabatic process until the pressure is 1.6 MPa. Find the work done by the system per kilogram of water: a. –432 kJ/kg c. –300 kJ/kg b. –637 kJ/kg d. –509 kJ/kg 340. A reversible thermodynamic system is made of follow the Carnot cycle between the temperature limits of 650 degree F, and 150 degree F. 300 BTU of heat are supplied per cycle to the system. What is the change in entropy during the heat addition? a. 0.27 BTU/degree R c. 1.30 BTU/degree R b. 0.46 BTU/degree R d. 0.75 BTU/degree R 341. A mercury barometer at the base of Mt. Makiling reads 654 mm and at the same time another barometer at the top of the mountain reads 480 mm. Assuming sp. weight of air to be constant at 12N/m3. What is the approximate height of Mt. Makiling? a. 1,934.5 m c. 4,168.2 m b. 3,508.4 m d. 2,647.7 m 342. In a diesel engine, the cylinder compresses air from approximately standard pressure and temperature to about one-sixteenth the original volume and a pressure of about 50 atm. What is the temperature of the compressed air? a. 853 K c. 893 K b. 863 K d. 878 K 343. If atmospheric air is 14.7 psia and 60°F at sea level, what is the pressure at 12,000 feet altitude if the air is compressed isothermally? a. 11.64 psia c. 19.54 psia b. 9.53 psia d. 19.63 psia 344. An ideal gas in a cylinder is compressed adiabatically to one third its original volume. During the process 45 J of work is done on the gas by the compressing agent. By how much did the internal energy of the gas change in the process? a. 55 J c. 40 J b. 50 J d. 45 J 345. Which of the following relationships is true for an ideal gas going through a reversible adiabatic process? a. cvdT + pdV = 0 c. cpdT + pdV = 0 b. cvdT – Vdp = 0 d. du + dh = ds 346. Air at 400°F and 50 psia is compressed isothermally to one-tenth of its original volume, What is the final pressure? a. 100 psia c. 375 psia b. 1000 psia d. 500 psia 347. A gas is compressed in a reversible process from 15 psia and 68°F to 75 psia. If the compression process follows a polytropic relationship with n = 1.4, what work is done by the gas during the compression? a. 1.7 x 106 ft-lb/pmole c. –1.2 x 106 ft-lb/pmole b. –1.7 x 106 ft-lb/pmole d. 1.2 x 106 ft-lb/pmole 348. For which type of process does the equation dQ = TdS hold? a. iothermal c. reversible b. isometric d. irreversible 349. Which process does not belong to Carnot cycle process? a. Isentropic compression b. Irreversible adiabatic compression c. Reversible adiabatic expansion d. Constant temperature adding heat 350. What is the sea level (g = 32.2 ft/sec2) specific weight (lb/ft3) of liquid with density of 58.3 lbm/ft3? a. 58.3 lbm/ft3 c. 64.3 lbm/ft3 b. 48.3 lbm/ft3 d. 25.3 lbm/ft3 351. An instrument use to measure pressure by using height-pressure relationship. a. hdrometer c. manometer b. hygrometer d. siphon 352. A tank has gauge pressure of 500mmHg vacuum. Find the pressure in kPa gauge? Use a conversion factor from mmHg to kPa (pascal = N/m2) is 133.4. a. 66.7 kPa c. –66.7 kPa b. 70 kPa d. 80 kPa 353. A Carnot cycle operates at maximum thermal efficiency. This is one statement in the second law of thermodynamics. a. True c. Partly False b. False d. Do not follow 354. A gas has a density of 0.094 lbm/ft³ at 100 and 2 atm. What pressure is needed to change the density to 0.270 lbm/ft³ at 250F? a. 5.28 atm c. 7.28 atm b. 6.28 atm d. 8.28 atm 355. Find the charge in internal energy of 10 lbm of oxygen gas when the temperature changes from 1000F to 1200F, Cv = 0.157 BTU/lbm-OR. a. 23.55 BTU c. 14.63 BTU b. 15.70 BTU d. 10.23 BTU 356. 4 lbm/sec of steam enter a turbine with velocity of 65ft/sec and enthalpy of 1350 BTU/lbm. The steam enter the condenser after being expanded to 1075 BTU/lbm and 125 ft/sec. The total heat loss from the turbine casing is 50 BTU/sec. What power is generated by the turbine? a. 1400 hp c. 1500 hp b. 1600 hp d. 1700 hp 357. The amount of heat required to raised the temperature of 2 kg of iron (sp.heat = 0.115 kcal/kg-0C) from 270C to 1000C is: a. 16.8 kcal c. 15.8 kcal b. 18.6 kcal d. 14.8 kcal of the useful 358. What is the maximum height that a vacuum pump can lift 60 0 water if the atmospheric pressure is 14.6 psia and local gravity is 28 ft/sec2? a. 11.64 psia c. 19.54 psia b. 9.53 psia d. 19.63 psia 359. Oil (density of 55 lbm/ft3) flows a 1 ft/sec through a 1-inch diameter pipe. A 0.2-inch diameter orifice (Cf= 0.6) is installed. What is the indicated pressure drop? a. 1682.7 lbf/ft2 c. 2082.7 lbf/ft2 b. 1482.7 lbf/ft2 d. 1882.7 lbf/ft2 360. No heat can be produced without any losses of heat. This is one of the useful statement of the second law of thermodynamics. a. true c partly false b. partly true d. false 361. The draft of a ship with 4700 ft 2 of water line cross-section is 12 feet. What cargo load is required to increase the draft 3 inches? Assume that sea water has a density of 64.0 lbm/ft3. a. 85,400 lbm c. 3,609,600 lbm b. 3,684,800 lbm d. 75,200 lbm 362. With what terminal velocity will an air bubble 1 mm in diameter rise in a liquid of viscosity 150 cp and density 0.90 gram/cc? Pair = 0.00129 gram/cc a. 0.42 cm/sec c. 0.32 cm/sec b. 0.54 cm/sec d. 0.24 cm/sec 363. A turbine uses and essentially of the steam is a. 1240.8 b. 1540.5 364. How many BTU’s are needed to isothermally compress 4 lbm of 240° air twice the original pressure? a. –150 BTU c. +160 BTU b. +140 BTU d. –132 BTU 365. What is the heat flow when 3 lbm of nitrogen undergo a closed system isothermal process at 300°F from an initial volume of 40 cubic feet to final volume of 22.5 cubic feet? a. 70 BTU c. 80 BTU b. –72 BTU d. –93 BTU 366. What is the specific enthalpy of 4 lbs of water, which is initially 80°F and to which 240 BTU are added? a. 115 BTU/lb c. 108 BTU/lb b. 120 BTU/lb d. 150 BTU/lb 367. If atmospheric air is 14.7 psia and 60F at sea-level, what is the pressure at 12,000 feet altitude if the air is compressed adiabatically? a. 29.62 psia c. 9.36 psia b. 9.26 psia d. 39.36 psia 368. If the atmospheric air is 14.7 psia and 60°F at sea level, what is the pressure at 12,000 feet altitude if the air is compressed isothermally? a. 11.64 psia c. 15.54 psia b. 9.53 psia d. 18.63 psia 100,000 lbm/hr of steam which enter with an enthalpy of 1400 BTU/lbm zero entrance velocity. 10,000 horsepower are developed. The exit velocity 500 fps. Expansion is adiabatic. What is the exit enthalpy? BTU/lbm c. 1140.5 BTU/lbm BTU/lbm d. 1680.4 BTU/lbm 369. The entrance enthalpy, velocity, and height of a 5 lbm/sec system are 1000 BTU/lbm, 100 ft/sec, and 100 feet respectively. 50 BTU/sec are lost to the surroundings. The exit enthalpy, velocity and height are 1020 BTU/lbm, 10 ft/sec and 0 feet respectively. What is the input horsepower? a. 20 c. 210.8 b. 250 d. 300 370. Gas is enclosed in a cylinder with a weighted piston as the top boundary. The gas is heated and expands from a volume of 0.04 m3 to 0.1 m3 at a constant pressure of 150 kPa. Calculate the work done by the system. a. 14 kJ c. 9 kJ b. 12 kJ d. 15 kJ 371. The barometer reads 29.0 inches or mercury. What s the absolute pressure if a vacuum gage reads 9.5 psi? a. 4.74 lbf/in2 (psi) c. 474 lbf/in2 (psi) 2 b. 47.4 lbf/in (psi) d. 474.4 lbf/in2 (psi) 372. Assuming atmospheric conditions at sea level are 14.7 psia and 59°F. What is the expected pressure at 35,000 feet altitude? Assume the temperature decreases 3.5°F per 1,000 feet altitude. a. 6.789 psia c. 3.456 psia b. 4.567 psia d. 5.678 psia 373. Two liquids enter a mixing chamber and are discharged at 80 0F at the rate of 50 gal/min. Liquid A enter at 1400F with a specific heat of 10 BTU/gal-0F. Liquid B enters at 650F with specific heat of 8.33 BTU/gal-0F. What is the volume flow for liquid B? a. 63.38 gal/min c. 41.38 gal/min b. 32.38 gal/min d. 74.38 gal/min 374. Two liquids enter a mixing chamber and are discharged at 80°F at the rate of 50 gal/min. Liquid A enters at 140°F with a specific heat of 10 BTU/gal-°F. What is the specific heat of the mixture? a. 4.12 Btu/gal-°F c. 8.62 BTU/gal-°F b. 5.32 BTU/gal-°F d. 6.02 BTU/gal-°F 375. A Carnot machine operates between the hot reservoir at 200°C and a cold reservoir at 20°C. When operated as an engine it receives 1000 kJ/kg. Find the coefficient of performance (COP) when used as refrigerator. a. 1.77 c. 1.99 b. 1.63 d. 2.63 376. To what height will a barometer column rise if the atmospheric conditions are 13.9 psia and 68°F and the barometer fluid is water? a. 676.7 inches c. 476.7 inches b. 576.7 inches d. 376.7 inches 377. One kg of air 1.2 kg/sq.cm at 30°C is compressed according to the law of PV where C = 1.36 until its volume is 0.5 cu.m. If it is compressed isothermally, what will be the % of saving work? a. 7.1% c. 6.9% b. 6.6% d. 7.0% 378. An artificial satellite, constructed of aluminum, encircles the earth at a speed of 9,000 m/sec. Find the ratio of kinetic energy to the energy required to raise its temperature by 600C. The melting point of aluminum is 660. Assume constant specific heat capacity of 0.2 cal/g-C. a. 147.5 c. 337.5 b. 257.5 d. 538.7 379. Helium ( R=0.468 BTU/lbm-R) is compressed isothermally from 14.7 psia and 68F. the compression ratio is 4. Calculate the work done by the gas in BTU/lbm. a. –564 c. –567 b. –375 d. –364 380. A tank contains 3 cubic feet of 120 psig air at 80F. How many tires of volume 1.2 ft³ can be inflated to 28 psig at 80F. a. 8 c. 5 b. 4 d. 3 381. A quantity of air 180F originally occupies 20 ft³ at 30 psig. The gas is compressed reversibly and adiabatically to 180 psig. What is the heat flow? a. 200 BTU c. 100 BTU b. 120 cal d. 0 382. What horsepower is required isothermally compress 800ft 3 of air per minute from 14.7 psia to 120 psia? a. 100 hp c. 115 hp b. 108 hp d. 150 hp 383. What is the pressure 8000 feet below the surface of the ocean? Neglect compressibility. a. 312,000 lbf/ft2 (psfg) c. 912,000 lbf/ft2 (psfg) 2 b. 512,000 lbf/ft (psfg) d. 712,000 lbf/ft2 (psfg) 384. What is the sea level (g = 32.2 ft/sec2) specific weight (lbf/ft3) of liquid with density of 58.3 lbm/ft3? a. 58.3 lbm/ft3 c. 64.3 lbm/ft3 b. 43.3 lbm/ft3 d. 25.3 lbm/ft3 385. A 50 horsepower motor (75% efficient) drives a 900-rpm pump (90% efficient) that moves 5 ft3/sec of gasoline (SG = 0.728). What is the specific speed? a. 1381 c. 1679 b. 1466 d. 1569 386. What is the pressure 8,000 feet below the surface of the ocean? Neglect compressibility. a. 512,000 lbf/ft2 (psfg) c. 312,000 lbf/ft2 (psfg) 2 b. 712,000 lbf/ft (psfg) d. 912,000 lbf/ft2 (psfg) 387. A Carnot machine operates between the hot reservoir at 2000C and a cold reservoir at 200C. When operated as an engine it receives 1000KJ/kg. Find the coefficient of performance (COP) when used as heat pump. a. 4.1 c. 2.63 b. 2.95 d. 2.88 388. To what height will a barometer column rise if the atmospheric conditions are 13.9 psia and 680F and the barometer fluid is ethyl alcohol? a. 157.9 inches c. 257.9 inches b. 359.9 inches d. 457.9 inches 389. Assuming atmospheric conditions at sea level 14.7 psia and 59 0F. what is the expected 35,000 feet altitude? Assume the temperature decreases 3.5 0F per 1000 feet altitude. a. 3.456 psia c. 5.678 psia b. 4.567 psia d. 6.789 psia 390. If atmosphere air is 14.7 psia and 600F at sea level. What is the pressure at 12,000 feet altitude if the air is compressed isothermally? a. b. 11.64 psia 9.53 psia c. 15.54 psia d. 18.63 psia 391. The efficiency of an Otto cycle is 50% and k = 1.50. what is the compression ratio? a. 2 c. ½ b. 4 d. ¼ 392. A quality of air at 1800F originally occupies 20ft 3 at 30 psig. The gas is compressed reversibly and adiabatically to 180 psig. What is the heat flow? a. 200BTU c. BTU b. cal d. 0 393. The difference between stagnation and static What is the relative velocity in air at 700F and a. 348.7 ft/sec c. b. 333.7 ft/sec d. 394. What is the specific enthalpy of 4 lbs of water, which is initially at 800F and to which 240 BTU are added? a. 115 BTU/lb c. 108 BTU/lb b. 120 BTU/lb d. 150 BTU/lb 395. Determine the specific reference. a. 1.7 b. 1.8 pressures in pilot/static tube is 2.0 inch Hg. 14.7 psia? 444.7 ft/sec 258.7 ft/sec gravity of carbon dioxide (150 0F , 20 psia) Using STP air as a c. 1.85 d. 1.87 396. What horsepower is required to isothermally compress 800ft 3 of air per minute from 14.7 psia to 120 psia? a. 100 hp c. 115 hp b. 108 hp d. 150hp 397. Helium (R = 0.4968 BTU/lbm-0R) is compress isothermally from 14.7 psia and 68 0F. The compression ratio is 4. Calculate the work done by the gas. a. –364 BTU c. –584 BTU/lbm b. –357 BTU/lbm d. –537 BTU/lbm 398. A quantity of gas occupies 1.2 cubic feet at STP. The gas is allowed to expand to 1.5 cubic feet and 15psia. What is the new temperature? a. 4500R c. 6280R 0 b. 590 R d. 7840R 399. A motorist equips his automobile tires with a relief-type valve so that the pressure inside the tire never will exceed 240 kPa (gage). He starts a trip with a pressure of 200 kPa (gage). He starts a trip with a pressure of 200 kPA (gage) and a temperature of 230C in the tires. During the long drive, the temperature of the air in the tires reaches 83 0C. each tire contains 0.11 kg of air. Determine the mass of air escaping each tire. a. 6.39 x 10-3 kg c. 2.59 x10–10 kg –3 b. 6.39 x 10 kg d. 2.59 x 10-5 kg 400. Oil (density of 55 lbm/ft3) flows at 1 ft/sec through a 1 inch-diameter pipe. A 0.2 inch diameter orifice (C=0.6) is installed. What is the indicated pressure drop? a. 1,428.7 lbf/ft2 c. 1,882.7 lbf/ft2 b. 1652.7 lbf/ft2 d. 2,082.7 lbf/ft2 401. A scuba diver at depth of 200 feet notices the bubbles he exhales have diameter of ½ inch. Assume the tension and water temperature remain relatively constant. What is the pressure on the bubble at a depth of 400 feet? a. b. 155.0 lbf/in2 (psia) 188.0 lbf/in2 (psia) c. 177.0 lbf/in2 (psia) d. 166.0 lbf/in2 (psia) 402. A Scuba diver at a depth of 200 feet notices the bubbles he exhales have diameter of ½ inch. Assume the tension and water temperature remains relatively constant what is the pressure on the bubble? a. 404.40 9 (psia) c. 303.40 psia b. 101.40 psia d. 202.40 psia 403. To what height will a barometer column rise if the atmospheric conditions are 13.9 psia and 680F and the barometer fluid is ethyl alcohol? a. 157.9 inches c. 457.9 inches b. 357.9 inches d. 257.9 inches