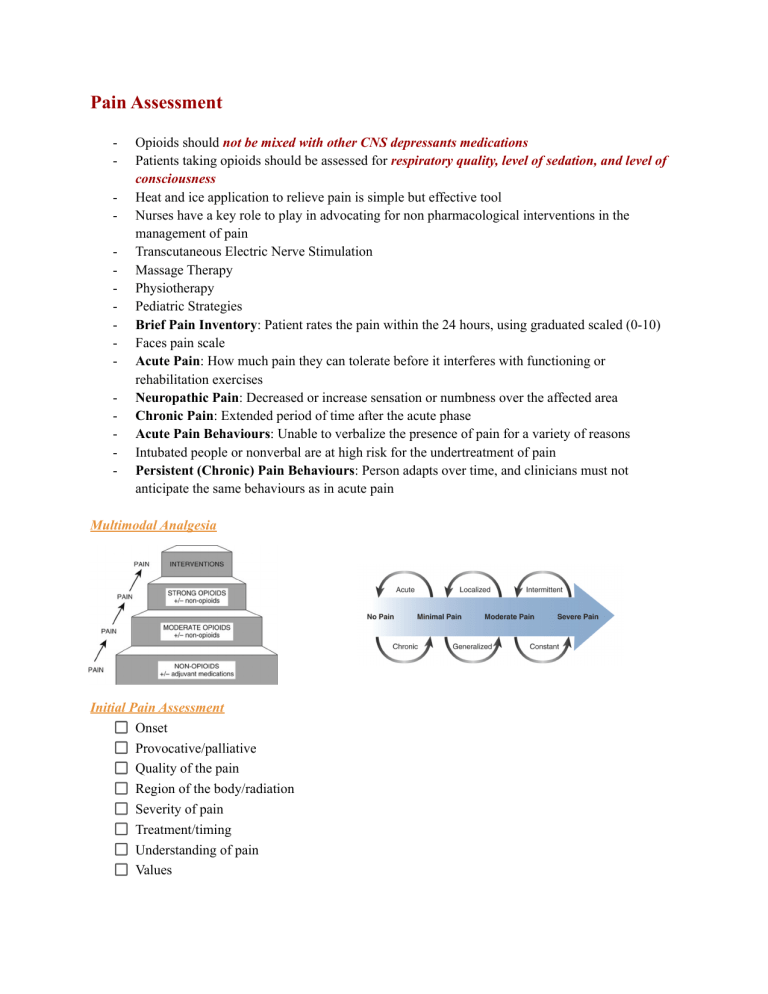
Pain Assessment - Opioids should not be mixed with other CNS depressants medications Patients taking opioids should be assessed for respiratory quality, level of sedation, and level of consciousness Heat and ice application to relieve pain is simple but effective tool Nurses have a key role to play in advocating for non pharmacological interventions in the management of pain Transcutaneous Electric Nerve Stimulation Massage Therapy Physiotherapy Pediatric Strategies Brief Pain Inventory: Patient rates the pain within the 24 hours, using graduated scaled (0-10) Faces pain scale Acute Pain: How much pain they can tolerate before it interferes with functioning or rehabilitation exercises Neuropathic Pain: Decreased or increase sensation or numbness over the affected area Chronic Pain: Extended period of time after the acute phase Acute Pain Behaviours: Unable to verbalize the presence of pain for a variety of reasons Intubated people or nonverbal are at high risk for the undertreatment of pain Persistent (Chronic) Pain Behaviours: Person adapts over time, and clinicians must not anticipate the same behaviours as in acute pain Multimodal Analgesia Initial Pain Assessment Onset Provocative/palliative Quality of the pain Region of the body/radiation Severity of pain Treatment/timing Understanding of pain Values