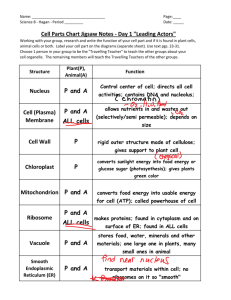
Cell (Plasma) Membrane: ○ A thin, two-layered film that surrounds the entire cell. ○ Made up of proteins and lipids ○ It is described as semi-permeable (selectively permeable): permits the passage or transport of certain materials into and out of the cell and prevents the transport of other materials. ○ It keeps the internal conditions of the cell constant to help maintain homeostasis. Cytoplasm: ○ Fluid-like material inside the plasma membrane and outside the nucleus of the cell ○ Many of the substances in cell metabolism are dissolved here. Nucleus: ○ A large, dense membrane-enclosed body that controls the cell's metabolism and reproduction. Nuclear Membrane (Envelope): ○ Selectively permeable double structure that surrounds the nucleus. ○ The pores control the passage of substances into and out of the nucleus. ○ The nucleoplasm remains chemically different from the rest of the cell. Nucleolus: ○ Structure within the nucleus that is involved in the synthesis of the RNA found in the ribosomes. ○ Site of the production of ribosomes. ○ It disappears at the beginning of cell division and reappears at the end. Endoplasmic Reticulum: ○ A network of channels in the cytoplasm that function in synthesizing, transporting, and storing substances made in the cell. ○ Provide a large surface area on which many biochemical reactions may occur. Ribosomes: ○ Small structures that are the sites of protein synthesis. ○ Found in the cytoplasm and lining the membranes of the ER. Mitochondria: ○ Round, slipper-shaped organelle that release the energy in food molecules for use by the cell. ○ Site of Aerobic Cellular Respiration. ○ Powerhouse of the cell; ATP (energy) is made here. Golgi Complex(Body/Apparatus): ○ Membrane-bound channels in which materials are synthesized or packaged. Lysosome: ○ Small sac-like structures that contain digestive enzymes and which take part in the digestion of food materials. ○ They break down worn-out cell organelles, kill bacteria, part of the body's defense against disease. Vacuoles: ○ Spaces in the cytoplasm enclosed by a membrane storing water, food, wastes and other materials. ○ Turgor Pressure Centrioles: ○ Cylindrical structures found outside the nuclear membrane in most animal cells ○ Involved in cell division Cell Wall: ○ Non-living structure made up of cellulose found only in plant cells. Gives the cell its shape and provides protection for the cell. ○ Chloroplasts (Plastid): ○ Found in plant cells and some protists that contain the pigment chlorophyll and are the sites of photosynthesis. Microtubules: ○ Long, hollow, cylindrical structures found in the cytoplasm that serves as a sort of skeleton for the cell giving it shape. ○ Involved in movement of the chromosomes during cell division. Microfilaments: ○ Long, solid, thread-like strands found in some cells that are associated with cell movement Cilia: ○ Tiny beating hairs for locomotion ○ Ex. Paramecium, Cilia Flagella: ○ Long, whip-like tail involved in locomotion ○ Ex. A sperm cell Parts of Cilia and Flagella: Cells Cells have 3 main jobs ● make energy ○ need energy for all activities ○ need to clean up waste produced while making energy ● make proteins ○ proteins do all the work in a cell, so we need lots of them ● make more cells for growth ○ to replace damaged or diseased cells Organelles (Eukaryotic cells) Cell Membrane Function - separates cell from outside - controls what enters or leaves cell - O2, CO2, food, H2O, nutrients, waste - recognizes signals from other cells - allows communication between cells Structure - double layer of fat - phospholipid bilayer - receptor molecules - proteins Vacuoles and Vesicles Function - moving material around the cell (vesicles) - storage for Oxygen, H2o, etc. (vacuoles) - larger in plant cells because plant cells do not move Structure - membrane sac Lysosomes Function - digest food - used to make energy - clean up & recycle - digest broken organelles Structure - membrane sac of digestive enzymes Mitochondria Function - make ATP energy from cellular respiration - sugar + O2 → ATP - fuels the work of life Structure - double membrane - has its own DNA Chloroplasts - make energy + sugar from sunlight - photosynthesis - sunlight + CO2 → ATP & sugar - ATP = active energy - sugar = stored energy - - build leaves & roots & fruit out of the sugars found only in plant cells Nucleus Function - control center of cell - protects DNA - instructions for building proteins Structure - nuclear membrane - nucleolus - ribosome factory - chromosomes - DNA Ribosomes Function - protein factories - read instructions to build proteins from DNA Structure - some free in cytoplasm - some attached to rough ER ER (endoplasmic reticulum) Function - works on proteins - helps complete the proteins after ribosome builds them - makes membranes Structure - rough ER - ribosomes attached - works on proteins - smooth ER - makes membranes Golgi Apparatus Function - finishes, sorts, labels & ships proteins - like UPS headquarters - shipping & receiving department - ships proteins in vesicles - “UPS trucks” Structure - membrane sacs - only in animal cells - cell plates in plant cells Structure - one pair in each cell Centrioles Function - help coordinate cell division Animal Cell Organelles Cell membrane: Border of the cell, allows things in Centrioles: Cell division and out by size Lysosomes: For food digestion, garbage disposal and Nucleus: protects DNA, holds chromosomes and recycling. nucleolus Golgi Apparatus: Finishes, packages and ships Nucleolus: Ribosome factory proteins Chromosomes: Shrinked versions of DNA Mitochondria: Produces ATP Rough ER: Connected to nucleus, holds ribosomes Vacuoles: Storage for Oxygen, H2o, etc which make proteins Vesicles: Transports proteins both inside and outside Ribosomes: Make proteins the cell Smooth ER: Stores and creates lipids and steroids Cytoplasm: Holds organelles in place Plant Cell Organelles Cell membrane: Border of the cell, allows things in Lysosomes: For food digestion, garbage disposal and and out by size recycling. Nucleus: protects DNA, holds chromosomes and Golgi Apparatus: Finishes, packages and ships Nucleolus proteins Nucleolus: Makes ribosomes Mitochondria: Produces ATP Chromosomes: Shrinked versions of DNA Vacuoles: Storage for Oxygen, H2o, etc Rough ER: Connected to Nucleus, holds ribosomes Vesicles: Transports proteins both inside and outside which makes proteins the cell Ribosomes: Makes proteins Cell Wall: Provides structure and protection for the Smooth ER: cell Cell Plate: Cell division Cytoplasm: Holds organelles in place Enzymes - A protein catalyst - Enzymes are important proteins found in living things. An enzyme is a protein that changes the rate of a chemical reaction. - They speed metabolic reactions. Chemical Reactions of Life ● ● Processes of life building molecules ○ synthesis ● breaking down molecules ○ digestion All chemical reactions in living organisms require enzymes to work - building molecules - synthesis enzymes breaking down molecules Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction - each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job - enzymes are named for the reaction they help - sucrase breaks down sucrose - proteases breakdown proteins - lipases breakdown lipids - DNA polymerase builds DNA - end in -ase Enzymes aren’t used up - Enzymes are not changed by the reaction - used only temporarily - re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules - very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions Lock & Key model - shape of protein allows enzyme & substrate to fit - specific enzyme for each specific reaction Enzyme vocabulary - Enzyme- helper protein molecule - Substrate- molecule that enzymes work on - Products- what the enzyme helps produce from the reaction - - digestive enzymes enzymes speed up reactions - “catalysts - Active site- part of enzyme that substrate molecule fits into What affects enzyme action? - Correct protein structure - - correct order of amino acids Temperature - Effect on rates of enzyme activity - Optimum temperature - greatest number of collisions between enzyme & substrate - human enzymes - - Raise temperature (boiling) - - - 35°- 40°C (body temp = 37°C) denature protein = unfold = lose shape Lower temperature T° - molecules move slower - fewer collisions between enzyme & substrate pH (acids & bases) - Effect on rates of enzyme activity - changes in pH changes protein shape~ Denatures - most human enzymes = pH 6-8 - depends on where in body - pepsin (stomach) = pH 3 - trypsin (small intestines) = pH 8 Why? enzyme has to be right shape - order of amino acids - wrong order = wrong shape = can’t do its job - amino acids are the blocks to make proteins