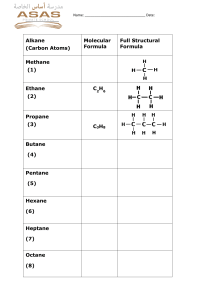
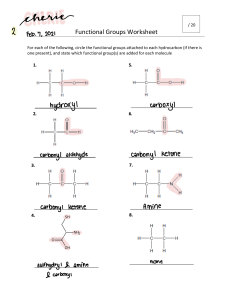
4. Organic Compounds a. Introduction b. Crude Oil c. Alkanes d. Alkenes e. Alcohols f. Carboxylic acids g. Esters h. Synthetic polymers a. Introduction Hydrocarbon: Compound that contains only hydrogen and carbon atoms Example: Diagram showing different examples on hydrocarbons 1 Chemistry Edexcel 2020, Dr.Heba Khalil, 01019226617 Representing Organic Molecules Definitions Example: Ethane (C2H6) 2 Chemistry Edexcel 2020, Dr.Heba Khalil, 01019226617 Representing Organic Molecules Homologous series: A series of organic compounds that has similar features: o Same general formula o Same functional group o Similar chemical reactions o Physical properties show graduations o Each member differs in molecular formula from the next by CH2 Example: Alkanes CH4 C2H6 C3H8 C4H10 C5H12 C6H14 Example: Alcohols CH3OH C2H5OH C3H7OH C4H9OH C5H11OH C6H13OH Functional group: A group of atoms bonded in a specific arrangement that controls the property of the homologous series: 3 Chemistry Edexcel 2020, Dr.Heba Khalil, 01019226617 4 Chemistry Edexcel 2020, Dr.Heba Khalil, 01019226617 Isomerism: Compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulae 5 Chemistry Edexcel 2020, Dr.Heba Khalil, 01019226617 Organic Compounds: Naming & Formulae Naming Compounds Note: Organic compounds are named according to IUPAC system The first part of the name comes from the number of carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon, the second part comes from the functional group present 6 Chemistry Edexcel 2020, Dr.Heba Khalil, 01019226617 Example: Further rules When there is more than one carbon a functional group can be located it is important to distinguish which carbon the functional group is on. Each carbon is numbered and these numbers are used to describe where the functional group is When 2 functional groups are present di- is used as a prefix to the second part of the name Branching also needs to be considered, the carbon atoms with the branches are described by their number When the location of functional groups and branches needs to be described the functional group takes precedence so the functional group has the lowest number 7 Chemistry Edexcel 2020, Dr.Heba Khalil, 01019226617 Examples Displayed & Structured Formulae Displayed formula: A graphic representation that shows the symbols for each atom in a compound, with straight lines joining them to represent the covalent bonds. Structural Formula: A condensed representation that shows the symbols for each atom in a compound, with straight lines joining them to represent the covalent bonds. 8 Chemistry Edexcel 2020, Dr.Heba Khalil, 01019226617 Questions: Name the following compounds according to the IUPAC system a. b. c. d. 9 Chemistry Edexcel 2020, Dr.Heba Khalil, 01019226617 Classifying Reactions of Organic Compounds 1.Substitution: A reaction where one atom is swapped with another atom o Example: Methane reacts with bromine under ultraviolet light 2.Addition: A reaction in which one molecule combines with another to form a larger molecule with no other products o Example: Bromine will react with ethene and the bromine molecule will react and add across the double bond of the ethene 10 Chemistry Edexcel 2020, Dr.Heba Khalil, 01019226617 3.Combustion: A reaction in which one molecule combines with another to form a larger molecule with no other products o Example: Alkenes burn when heated in air of oxygen o If there is an unlimited supply of air / oxygen, the products are carbon dioxide and water: CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O o This is termed complete combustion o If there is a limited supply of air / oxygen, the products are carbon monoxide and water: CH4 + ½O2 → CO + 2H2O o This is termed incomplete combustion 11 Chemistry Edexcel 2020, Dr.Heba Khalil, 01019226617 b. Crude Oil Crude oil: A mixture of hydrocarbons. Thick, sticky, black liquid that is found under porous rock (under the ground and under the sea). If any fraction from crude oil is burned, then carbon dioxide and water is produced – this shows that crude oil is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons: Fractional Distillation Fractional distillation: To separate two or more liquids that are miscible with one another Industrial process of fractional distillation: The process of fractional distillation to separate crude oil in a fractionating column 12 Chemistry Edexcel 2020, Dr.Heba Khalil, 01019226617 Explanation: Fractional distillation is carried out in a fractionating column. In the fractionating column, it is hot at the bottom and cool at the top. Crude oil will enter the fractionating column and will be heated so vapours will rise and evaporate. Vapours of hydrocarbons with very high boiling points will immediately turn into liquid and are tapped off at the bottom of the column. Vapours of hydrocarbons with low boiling points will rise up the column and condense at the top to be tapped off. The different fractions will condense at different heights according to their boiling points and will be tapped off as liquids. All the fraction are mixtures of different kinds of hydrocarbon. To conclude the smaller hydrocarbons are collected at the top of the fractionating column as gases. The bigger hydrocarbons are collected at the lower sections of the fractionating column. Trends of Crude Oil Fractions Viscosity: Viscosity refers to the ease of flow of a liquid. High viscosity liquids are thick and flow less easily. If the number of carbon atoms increases, the attraction between the hydrocarbon molecules increases, which results in the liquid becoming more viscous – this is because of the increasing length of the hydrocarbon chains. The liquid flows less easily with the increasing molecular mass. Colour: As carbon chain length increases, liquid colour gets darker, as it becomes thicker and more viscous. Melting point/boiling point: As the molecules get larger, the intermolecular attraction becomes greater, so more energy in the form of heat is needed to separate the molecules. With increasing molecular size there is an increase in boiling point. Volatility: Volatility refers to the tendency of a substance to vaporise. As their molecular size increases, hydrocarbon liquids become less volatile 13 Chemistry Edexcel 2020, Dr.Heba Khalil, 01019226617 Fuel Fuel: Substance which when burned, releases heat energy This heat can be transferred into electricity, which we use in our daily lives Complete combustion of hydrocarbons: During the complete combustion of hydrocarbons, carbon dioxide and water will be produced: Carbon will oxidise to form carbon dioxide Hydrogen will oxidise to water Hydrocarbon + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water Incomplete combustion: Occurs when there is a limited supply of air so that elements in the fuel do not fully react with Oxygen During the incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons, water will still be produced but instead of carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide (soot) will form Hydrocarbon + Oxygen → Carbon Monoxide + Water Carbon Monoxide Carbon monoxide: A poisonous gas that is colourless and odourless, produced during incomplete combustion: Hydrocarbon + Oxygen → Carbon monoxide + Water Effect of Carbon monoxide on blood: When carbon monoxide is produced by incomplete combustion, it is absorbed in the lungs and this reduces the capacity of the blood to carry oxygen. 14 Chemistry Edexcel 2020, Dr.Heba Khalil, 01019226617 Acid Rain Formation of oxides of nitrogen in car engines: When fuels are burned in car engines, high temperatures are reached which allows Nitrogen and Oxygen from the air to combine to produce Nitrogen monoxide: Nitrogen + Oxygen → Nitrogen Monoxide N2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2NO (g) When this Nitrogen monoxide is released from the engines of vehicles, it combines with Oxygen in the air to form Nitrogen dioxide: Nitrogen Monoxide + Oxygen → Nitrogen Dioxide 2NO (g) + O2 (g) → 2NO2 (g) Both Nitrogen monoxide and Nitrogen dioxide are produced in car engines as a result and is referred to as NOx Hydrocarbon fuels: Impure Hydrocarbon fuels contain Sulfur compounds Combustion of Hydrocarbon fuels: During the combustion of Hydrocarbon fuels, impurities such as Sulfur compounds will be oxidised to produce sulfur dioxide: Combustion of Hydrocarbon Fuels Sulfur + Oxygen → Sulfur Dioxide S (g) + O2 (g) → SO2 (g) Acid rain: Rain that contains dissolved acidic gases such as sulfur dioxide and oxides of nitrogen. The pH value of normal rain is slightly below 7. The pH value of acid rain is approximately 3.4. Sulfur dioxide will react with oxygen and dissolve in water droplets in clouds, forming dilute sulfuric acid which will cause acid rain: Sulfur Dioxide + Oxygen + Water → Sulfuric Acid 2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) + H2O (l) → 2H2SO4 (aq) Nitrogen oxides will dissolve in water droplets in clouds, forming dilute Nitric acid and Nitrous acid, causing acid rain: Nitrogen Dioxide + Water → Nitric Acid NO2 (g) + H2O (l) → HNO3 (aq) 15 Chemistry Edexcel 2020, Dr.Heba Khalil, 01019226617 16 Chemistry Edexcel 2020, Dr.Heba Khalil, 01019226617 Catalytic Cracking Long-chain hydrocarbons: large number of hydrocarbon molecules. More viscous and less flammable so less useful. Short-chain hydrocarbons: small numbers of hydrocarbon molecules. Cracking is simply splitting of larger molecules to simpler ones. Explanation: Cracking allows large hydrocarbon molecules to be broken down into smaller, more useful hydrocarbon molecules. Fractions containing large hydrocarbon molecules are heated at 600 – 700°c to vaporise them. Vapours will then pass over a hot catalyst of silica or alumina This process breaks covalent bonds in the molecules, causing thermal decomposition reactions. As a result, cracking produces smaller alkanes and alkenes. The molecules are broken up in a random way which produce a mixture of alkanes and alkenes. Why Cracking is Necessary Although there is use for each fraction after the fractional distillation of crude oil, the amount of longer chain hydrocarbons produced is far greater than needed. However, the amount of shorter chain hydrocarbons produced is far less than needed (e.g. gasoline fraction) and there is a higher demand for shorter chain hydrocarbons. This is why cracking is necessary to increase the supply of shorter chain hydrocarbons. Short chain hydrocarbons burn well and flow well. Cracking is used to produce petrol for cars. Cracking also produces alkenes which are raw material in the plastic industry. Cracking is used to produce hydrogen gas which is a raw material in manufacture of ammonia in Haber process. 17 Chemistry Edexcel 2020, Dr.Heba Khalil, 01019226617 Example: The Cracking of hexane (C6H14) to produce butane (C4H10) and ethene (C2H4): C6H14 (g) → C4H10 (g) + C2H4 (g) Ethene: The ethene can be used to make poly(ethene), a type of plastic. 18 Chemistry Edexcel 2020, Dr.Heba Khalil, 01019226617 Questions: 1) Many hydrocarbons are used as fuels. There are problems associated with this use. (i) Explain how the combustion of a hydrocarbon can lead to the formation of a poisonous gas. (2) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. (ii) State why this gas is poisonous to humans. (1) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. 2) Fuels used in cars often have sulfur compounds removed. Explain how the combustion of these fuels in car engines still leads to the formation of acid rain. (4) ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. ............................................................................................................................................. 19 Chemistry Edexcel 2020, Dr.Heba Khalil, 01019226617