End of WW1 & Treaty of Versailles: GCSE History
advertisement

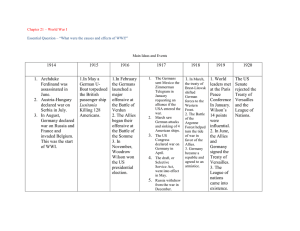
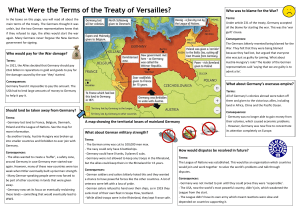
The End of World War One GCSE MODERN WORLD HISTORY The End of WW1 and the Treaty of Versailles • Why do countries go to war? – List as many reasons as possible Devastation • Much of north-eastern France and Belgium had been devastated • Britain and France were in severe debt and their economies ruined YPRES 1918 Ypres recently Casualties • Over 9 million had been killed • One quarter of all French men aged 18-27 had been killed • Four million Frenchmen had been wounded La Targette British Cemetery Thiepval, the Somme German cemetery at Langemarck Treaty of Versailles WW1 has just finished and Britain has finished on the winning side. What is your immediate reaction? Consider the advantages and disadvantages and explain your choice. a. Go ahead and invade Germany b. Demand lots of money as compensation c. Forgive and hope for better relations in the future The Key Points: 1. Territory Alsace Lorraine Should Alsace-Lorraine be returned to France? (Alsace-Lorraine has both French and German people living there and has lots of natural resources like iron). Rhineland Should Germany be allowed to keep the Rhineland? If so should they be allowed to place troops on it? If not, who should be given the Rhineland? Alsace - Lorraine Rhineland The Key Points: 2. Army Armed Forces The Allies debated whether Germany should be prevented from fighting again by taking away their army. Should Germany be allowed to keep her army, navy and air force? Should just the navy and air force be taken away? Should the Germany army be reduced to the point where it can only be defensive not offensive? The Key Points: 3. Prevention of Future Wars Prevention of Future War Should there be an international council set up to preserve peace through negotiation? How will this council have any power? Will it have an army? Should Germany just be left to fend for itself now? The Key Points: 4. Guilt War Guilt: Which country should be blamed for starting the war? Would it be fairer to share the blame or to entirely blame Germany? The Key Points: 5. Reparations War Guilt: Should Germany have to pay money to the Allies for the damage it caused or should it be equally shared? How much should they pay? • Explain why some people wanted to punish Germany after WW1. • Explain what could happen if Germany was punished too harshly. The Big Three • Lloyd-George • Woodrow Wilson • Georges Clemenceau British Prime Minister Lloyd George The British attitude • Lloyd George, the British Prime Minister, wanted a compromise peace • Public opinion demanded he punish the Germans • But a stronger Germany could stand up to the French and resist Communism • He wanted German colonies and an end to the naval threat French Prime Minister Georges Clemenceau The French attitude • He wanted revenge on the Germans • Germany should pay for the war through reparations • Germany had to be permanently weakened both financially and militarily • Germany should be occupied American President Woodrow Wilson The American attitude • He hoped the Fourteen Points would serve as the blue-print for a new world peace • The War had helped the economy and much of the Allied side was in debt to the USA The Fourteen Points 1. No secret treaties: all diplomacy should be open 2. Freedom of the seas in peace and war 3. Free trade between all countries: no customs barriers 4. Disarmament by all nations 5. The wishes of people in colonies should be listened to when deciding their future 6. German forces to leave Russia 7. Belgium should be independent 8. Alsace-Lorraine, taken by Germany in 1871, to be returned to France 9. Italy’s frontier with Austria to be changed 10. Self-determination for the peoples of eastern Europe. 11. Serbia to have access to the sea 12. Self-determination for peoples of the Turkish Empire 13. Poland should become independent, with access to the sea 14. An international organisation to be set up to settle disputes between countries, called the League of Nations Other factors • The impact of the Russian Revolution and the possible spread of Communism • The collapse of eastern Europe into anarchy • The Allies had made secret deals with Italy and Japan • The Allies had no real plans for the future of the world • Over a million died from the flu in 1919 The Versailles Conference January-June 1919